Physiology notes
Hepatitis: dark urine.
Diabetes insipidus: kidneys cannot hold enough
fluid a lot of urine and constantly thirsty.
Not enough vasopressin/ADH. ADH = helps control
blood pressure by acting on the kidneys and blood
vessels. Conserves fluid volume of your body by
reducing the amount of water passed out in the
urine.
- Brattleboro rats have little vasopressin.
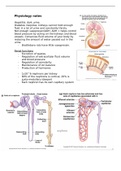
Renal functions
- Excretion of wastes
- Regulation of extracellular fluid volume
and blood pressure
- Regulation of osmolarity
- Maintenance of ion balance
- Production of hormones
- 1x10^6 nephrons per kidney
- 80% of the nephrons is cortical, 20% is
juxta-medullary (deeper)
- Each nephron has its own capillary system
Hepatitis: dark urine.
Diabetes insipidus: kidneys cannot hold enough
fluid a lot of urine and constantly thirsty.
Not enough vasopressin/ADH. ADH = helps control
blood pressure by acting on the kidneys and blood
vessels. Conserves fluid volume of your body by
reducing the amount of water passed out in the
urine.
- Brattleboro rats have little vasopressin.
Renal functions
- Excretion of wastes
- Regulation of extracellular fluid volume
and blood pressure
- Regulation of osmolarity
- Maintenance of ion balance
- Production of hormones
- 1x10^6 nephrons per kidney
- 80% of the nephrons is cortical, 20% is
juxta-medullary (deeper)
- Each nephron has its own capillary system