1
NapierC ENVS 3100 Fall2021
Sustainability topic lecture
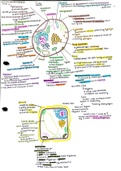
Human Population
History of the human population
10’000ya: 2-3million people
o Plant and animal domestication
o Development of villages around fertile areas of land
Historical population crashes
14th century
o Great famine: poor weather and low crop output (killed 10-25% European
population)
o Bubonic plague: rats as infection vector (killed 1/3 European population)
th
17 century
o Suffered epidemics, conflicts, and famine
o Easter Island: deforestation, reduction in birds/wood, rampant disease
th
19 century
o Densely populated industrial cities
o Dust bowl
o Poor sanitation, waste accumulation
Recent population growth
Total fertility rate (TFR): avg. number of offspring a women has throughout her
reproductive years within a population
Replacement fertility: TFR of 2.1 (no change in population)
Crude death rate: total number of deaths per year per 1000 people
Green revolution: high yield of wheat/corn/rice varieties, introduction of pesticides,
better management techniques
Introduction of antibiotics and vaccines
Carrying capacity: the maximum number of individuals of a species that a habitat can
sustainably support
Population control
Contraception
o Abortions: 20% of pregnancies end in abortions)
o Abstinence: promoted by some religious groups
o Celibacy: adopted by some religious leaders OR by adoption-only
communities
o Prolonged breast-feeding: release of prolactin suppresses ovulation
o Condoms/Pills/IUD: greatly reduces chance of pregnancy
NapierC ENVS 3100 Fall2021
Sustainability topic lecture
Human Population
History of the human population
10’000ya: 2-3million people
o Plant and animal domestication
o Development of villages around fertile areas of land
Historical population crashes
14th century
o Great famine: poor weather and low crop output (killed 10-25% European
population)
o Bubonic plague: rats as infection vector (killed 1/3 European population)
th
17 century
o Suffered epidemics, conflicts, and famine
o Easter Island: deforestation, reduction in birds/wood, rampant disease
th
19 century
o Densely populated industrial cities
o Dust bowl
o Poor sanitation, waste accumulation
Recent population growth
Total fertility rate (TFR): avg. number of offspring a women has throughout her
reproductive years within a population
Replacement fertility: TFR of 2.1 (no change in population)
Crude death rate: total number of deaths per year per 1000 people
Green revolution: high yield of wheat/corn/rice varieties, introduction of pesticides,
better management techniques
Introduction of antibiotics and vaccines
Carrying capacity: the maximum number of individuals of a species that a habitat can
sustainably support
Population control
Contraception
o Abortions: 20% of pregnancies end in abortions)
o Abstinence: promoted by some religious groups
o Celibacy: adopted by some religious leaders OR by adoption-only
communities
o Prolonged breast-feeding: release of prolactin suppresses ovulation
o Condoms/Pills/IUD: greatly reduces chance of pregnancy