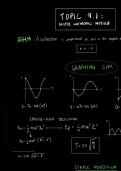
Pneumonia
- Infection of the lungs caused by microbial pathogens – bacteria, fungi and viruses
- Infection causes inflammation of the alveoli
- Viral and bacterial pneumonia is spread to others by inhalation of airbourne droplets, also
spread by coming into contact with contaminated surfaces
- Fungal pneumonia is contracted from the environment, via fungal spores, but cannot be
transmitted between people
Pathophysiology
- Symptoms include cough with sputum, fever, sweats/chills, shortness of breath and pleuritic
chest pain
- Bacterial pneumonia often initially presents as a non-productive cough,
- Streptococcus pneumoniae is the most common causative agent of bacterial pneumonia,
with the type III strain being one of the most virulent
- Streptococcus pneumoniae type III strain is present in cases of all ages, but particularly
prominent in patients over 70
- Other causative agents of pneumonia include:
o Bacterial
Mycoplasma pneumoniae – common in children and young people
Haemophilus influenzae (Pittman capsular type B) – rare, mainly in infants
Legionella pneumophila – common in patients 45 and over
o Viral
Influenza
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV)
Rhinoviruses
o Fungal
Pneumocystis jirovecii
Cryptococcus sp.
Histoplasmosis sp.
Aspergillus sp.
- Infection of the lungs caused by microbial pathogens – bacteria, fungi and viruses
- Infection causes inflammation of the alveoli
- Viral and bacterial pneumonia is spread to others by inhalation of airbourne droplets, also
spread by coming into contact with contaminated surfaces
- Fungal pneumonia is contracted from the environment, via fungal spores, but cannot be
transmitted between people
Pathophysiology
- Symptoms include cough with sputum, fever, sweats/chills, shortness of breath and pleuritic
chest pain
- Bacterial pneumonia often initially presents as a non-productive cough,
- Streptococcus pneumoniae is the most common causative agent of bacterial pneumonia,
with the type III strain being one of the most virulent
- Streptococcus pneumoniae type III strain is present in cases of all ages, but particularly
prominent in patients over 70
- Other causative agents of pneumonia include:
o Bacterial
Mycoplasma pneumoniae – common in children and young people
Haemophilus influenzae (Pittman capsular type B) – rare, mainly in infants
Legionella pneumophila – common in patients 45 and over
o Viral
Influenza
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV)
Rhinoviruses
o Fungal
Pneumocystis jirovecii
Cryptococcus sp.
Histoplasmosis sp.
Aspergillus sp.