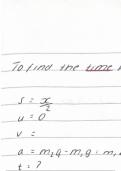The purpose of a business activity is to provide consumers with goods and services that meet our needs and wants.
Need – a good or service which is essential to living
Want – a good or service which people would like but is not essential for living.
Economic problem – Unlimited wants cannot be met because there are limited factors of production
Scarcity and opportunity cost
Production of goods and services requires 4 factors of production:
1. Land: natural resources
2. Labour: number of people available to work
3. Capital: machinery, equipment and finance
4. Enterprise: people prepared to take the risk of setting up businesses – entrepreneurs.
Purpose – Combine factors of production to make products (goods & services) which will satisfy people’s wants and
needs
As there aren’t enough of these factors of production in the world there is a problem of –
Scarcity – there are not enough goods and services to meet the wants of the population leading to
Opportunity cost – the benefit that could have been gained from an alternative use of the same resource
Choice and Opportunity Cost
Limited resources creates a need to choose – Should I go to the cinema with my friends or spend my money on a
new app?
If I go to the cinema -> the app is the Opportunity Cost
– the next best alternative given up by choosing another item
– The limiting factor is the money – I don't have enough for both!
eg. I have 20€ 19€ jeans – I buy this
20€ concert – so this is the opportunity cost
, 12 09 19 specialisation
Types of goods and services –
Consumer Goods are products which are sold to the final consumer (public).
Can be durable (can be used repeatedly) or non-durable (can only be used once).
Consumer Services are non-tangible products, performed for the public such as insurance or banking
Capital Goods are products sold to other businesses to help them in their production process such as machinery,
delivery vehicles…
Specialization – people and businesses concentrate on what they are best at
Specialisation of factors of production – Instead of workers producing one product from start to finish, they focus
on just one skill.
More efficient businesses – lower cost of production and goods and services at lower prices
Division of labor – production is divided into separate tasks and each person does one of them.
eg. Car manufacturer: paint, engines, interiors
Benefits of division of labor to the business – Workers are more efficient
-Production becomes cheaper per good
-(DL) less time spent moving from one workbench to another
Drawbacks of division of labor for the business – Greater cost of workers
-Quality may suffer if workers become bored
-If a worker is absent and no one else can do the job production may be stopped.
13 09 19 Business activity
Added value formula – Selling price - cost of materials and components bought = added value
Value added is not profit – the business still needs to pay wages, advertisement, rent, etc…
The lower the cost and the higher the selling price, the higher the added value, resulting in a bigger profit
How could a business increase added value?
1. Reduce the cost of materials but keep selling price the same. Will this reduce the quality of the product?
2. Increase selling price but keep cost of materials the same. Higher quality image? Lower sales?
3. improving Branding, convenience, features and service quality