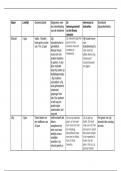
Animal Studies
1. Lorenz;
Aim – to examine imprinting
Method –
Randomly divided goose eggs
Control group = hatched by mother, experimental group = hatched by Lorenz
Control group saw biological mother first, experimental group saw Lorenz first
Both groups were put together in a box and were later released to see whether they would go
to their biological mother or Lorenz
Findings –
Control group went to their mother, experimental group went back to Lorenz
This imprinting was long term and irreversible
Conclusion – imprinting occurs on the first moving object which is encountered
2. Harlow;
Aim – examine importance of contact comfort
Method –
Infant monkeys were placed in a cage with two surrogate mothers
One mother was made out of wire and could dispense milk
Other mother was made out of a soft cloth and could not dispense milk
Findings –
Monkeys preferred the soft surrogate mother
Only went to wired mother to be fed
Conclusion – attachment is not just based on food. There is an innate drive to seek comfort.
Evaluation;
Animal studies may be difficult to generalise to humans
Harlow’s study has real world applications
1. Lorenz;
Aim – to examine imprinting
Method –
Randomly divided goose eggs
Control group = hatched by mother, experimental group = hatched by Lorenz
Control group saw biological mother first, experimental group saw Lorenz first
Both groups were put together in a box and were later released to see whether they would go
to their biological mother or Lorenz
Findings –
Control group went to their mother, experimental group went back to Lorenz
This imprinting was long term and irreversible
Conclusion – imprinting occurs on the first moving object which is encountered
2. Harlow;
Aim – examine importance of contact comfort
Method –
Infant monkeys were placed in a cage with two surrogate mothers
One mother was made out of wire and could dispense milk
Other mother was made out of a soft cloth and could not dispense milk
Findings –
Monkeys preferred the soft surrogate mother
Only went to wired mother to be fed
Conclusion – attachment is not just based on food. There is an innate drive to seek comfort.
Evaluation;
Animal studies may be difficult to generalise to humans
Harlow’s study has real world applications