Polina Lobacheva
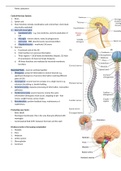
Central Nervous System:
1. Brain
2. Spinal cord
3. Main functions include coordination and control (fast, short-lived,
electrically mediated)
4. Glial cells (neuroglia):
a. Ependymal cells – e.g. Line ventricles, assist in production of
CSF
b. Microglia –remove debris, waste by phagocytosis
c. Astrocytes –BBB, absorb/recycle neurotransmitters
d. Oligodendrocytes – myelinate CNS axons
5. Neurons:
a. Functional units of the NS
b. Main function is to process information
c. Three regions = (1)Cell body and dendrites (Inputs), (2) Axon
(Transmission), (3) Axon terminals (Outputs)
d. All these functions are mediated by neuronal membrane
functions
Neuronal Pools – neurons working together
1. Divergence: spread of information to several neurons e.g.
significant divergence of sensory information reaching different
parts of CNS
2. Convergence: several neurons synapse on a single neuron e.g.
voluntary breathing vs. breath-holding
3. Serial processing: stepwise processing of information, nociceptive
pathways
4. Parallel processing: several neurons receive the same
information (divergence must occur), stepping on pin –foot
moves, weight moves, sense of pain
5. Reverberation: positive feedback loop, maintenance of
wakefulness
Protecting your brain:
- Bone (skull)
- Meninges (membrane), this is the area that gets affected with
meningitis
- Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF): between the brain and the skull
Divisions (order of increasing complexity):
1. Medulla
2. Pons
3. Midbrain
4. Limbic system
5. Diencephalon
6. Cerebrum
, Polina Lobacheva
7. Cerebellum
Brainstem (medulla, pons, midbrain):
- These 3 regions are evolutionarily the oldest, because they carry out ‘basic’ functions within their own centers -
respiratory rhythm, blood pressure regulation, vomiting
- Origin of cranial nerves
- Midbrain constitutes part of the reticular formation - maintenance of wakefulness, aspects of visual and auditory
processing
Cranial nerves:
- Twelve cranial nerves
- All innervate head and neck except Vagus nerve
Diencephalon (thalamus and hypothalamus):
1. Thalamus: final relay point for sensory information that will be transmitted to the cortex - acts as a filter
2. Hypothalamus:
a. Controls and integrates activity of the ANS
Central Nervous System:
1. Brain
2. Spinal cord
3. Main functions include coordination and control (fast, short-lived,
electrically mediated)
4. Glial cells (neuroglia):
a. Ependymal cells – e.g. Line ventricles, assist in production of
CSF
b. Microglia –remove debris, waste by phagocytosis
c. Astrocytes –BBB, absorb/recycle neurotransmitters
d. Oligodendrocytes – myelinate CNS axons
5. Neurons:
a. Functional units of the NS
b. Main function is to process information
c. Three regions = (1)Cell body and dendrites (Inputs), (2) Axon
(Transmission), (3) Axon terminals (Outputs)
d. All these functions are mediated by neuronal membrane
functions
Neuronal Pools – neurons working together
1. Divergence: spread of information to several neurons e.g.
significant divergence of sensory information reaching different
parts of CNS
2. Convergence: several neurons synapse on a single neuron e.g.
voluntary breathing vs. breath-holding
3. Serial processing: stepwise processing of information, nociceptive
pathways
4. Parallel processing: several neurons receive the same
information (divergence must occur), stepping on pin –foot
moves, weight moves, sense of pain
5. Reverberation: positive feedback loop, maintenance of
wakefulness
Protecting your brain:
- Bone (skull)
- Meninges (membrane), this is the area that gets affected with
meningitis
- Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF): between the brain and the skull
Divisions (order of increasing complexity):
1. Medulla
2. Pons
3. Midbrain
4. Limbic system
5. Diencephalon
6. Cerebrum
, Polina Lobacheva
7. Cerebellum
Brainstem (medulla, pons, midbrain):
- These 3 regions are evolutionarily the oldest, because they carry out ‘basic’ functions within their own centers -
respiratory rhythm, blood pressure regulation, vomiting
- Origin of cranial nerves
- Midbrain constitutes part of the reticular formation - maintenance of wakefulness, aspects of visual and auditory
processing
Cranial nerves:
- Twelve cranial nerves
- All innervate head and neck except Vagus nerve
Diencephalon (thalamus and hypothalamus):
1. Thalamus: final relay point for sensory information that will be transmitted to the cortex - acts as a filter
2. Hypothalamus:
a. Controls and integrates activity of the ANS