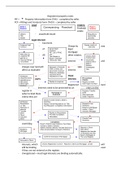
Redundancy
Outcomes
1. Analyse the merits of employees’ redundancy payment claims and calculate the statutory
redundancy payments.
2. Apply redundancy selection criteria appropriately and explain how redundancies may be
handled fairly.
3. Assess the other claims which may arise from a redundancy dismissal.
Overview
• Redundancy is a potentially fair reason for dismissal in an unfair dismissal scenario
• Redundancy can also give rise to WD or UD claims but it is also a stand-alone claim where
the redundancy was the cause of dismissal.
• An eligible employee, dismissed by reason of redundancy, will be entitled, at a minimum, to a
statutory redundancy payment from their employer ERA 1996 s.163 UNLESS
o The employer offered an alternative job and
o The employee accepted this OR
o The employee unreasonably refused the offer
, Step 1: Eligibility- burden of proof on employee
Within time limits? Must be brought within 6 months of dismissal, the ET are strict on this and will rarely
extend- s.164
• May extend the time limit to 12 months if they think just and equitable.
Relevant date- s.145- same as EDT for UD
• Termination with notice = date the notice expires
• Termination without notice = date of the dismissal- even if PILON
• Failure to renew fixed term contract = date the fixed term expired
Constructive dismissal
• Date the employee departs or date the employee’s notice expires if the
employee gives notice
Th ET will not investigate the commercial or economic reasons for redundancies,
they only investigate to satisfy that the reason for dismissal was genuinely for
redundancy (James W Cook & Co v Tipper)
Employee? s.230(1) ERA 1996
• Someone who works under a contract of employment
• Can be evidenced under the statement of written terms s.1
2 years continuous s.155
employment? • Need at least 2 years’ continuous employment to bring a claim
• The relevant date employment ends defined under s.145(2)
o the date the notice period expires if terminated by notice
o date terminate takes effect if no notice
o fixed term contract that is not renewed the date the termination
takes effect
Excluded class? • Police
• Armed forces
• Government or crown
Step 2: has the employee been dismissed?
Actual dismissal Expiry and non-renewal of fixed-term contract
• Always be treated as dismissal s.136(1)(b)
Actual dismissal
• Terminated by the employer with or without notice s.136(1)
Constructive dismissal
• Employee is entitled to terminate without notice by reason of th
employer’s conduct resulting in repudiatory breach
• Contractual or implied term
• Applies to the last straw doctrine- smaller but consistent events having
regard to the cumulative effect.
• Employee recognises the breach within a reasonable time so as to
not waive the breach
Summary dismissal • Where the employee has breached a term of the employment contract-
thus will be gross misconduct and not entitling to a claim
Outcomes
1. Analyse the merits of employees’ redundancy payment claims and calculate the statutory
redundancy payments.
2. Apply redundancy selection criteria appropriately and explain how redundancies may be
handled fairly.
3. Assess the other claims which may arise from a redundancy dismissal.
Overview
• Redundancy is a potentially fair reason for dismissal in an unfair dismissal scenario
• Redundancy can also give rise to WD or UD claims but it is also a stand-alone claim where
the redundancy was the cause of dismissal.
• An eligible employee, dismissed by reason of redundancy, will be entitled, at a minimum, to a
statutory redundancy payment from their employer ERA 1996 s.163 UNLESS
o The employer offered an alternative job and
o The employee accepted this OR
o The employee unreasonably refused the offer
, Step 1: Eligibility- burden of proof on employee
Within time limits? Must be brought within 6 months of dismissal, the ET are strict on this and will rarely
extend- s.164
• May extend the time limit to 12 months if they think just and equitable.
Relevant date- s.145- same as EDT for UD
• Termination with notice = date the notice expires
• Termination without notice = date of the dismissal- even if PILON
• Failure to renew fixed term contract = date the fixed term expired
Constructive dismissal
• Date the employee departs or date the employee’s notice expires if the
employee gives notice
Th ET will not investigate the commercial or economic reasons for redundancies,
they only investigate to satisfy that the reason for dismissal was genuinely for
redundancy (James W Cook & Co v Tipper)
Employee? s.230(1) ERA 1996
• Someone who works under a contract of employment
• Can be evidenced under the statement of written terms s.1
2 years continuous s.155
employment? • Need at least 2 years’ continuous employment to bring a claim
• The relevant date employment ends defined under s.145(2)
o the date the notice period expires if terminated by notice
o date terminate takes effect if no notice
o fixed term contract that is not renewed the date the termination
takes effect
Excluded class? • Police
• Armed forces
• Government or crown
Step 2: has the employee been dismissed?
Actual dismissal Expiry and non-renewal of fixed-term contract
• Always be treated as dismissal s.136(1)(b)
Actual dismissal
• Terminated by the employer with or without notice s.136(1)
Constructive dismissal
• Employee is entitled to terminate without notice by reason of th
employer’s conduct resulting in repudiatory breach
• Contractual or implied term
• Applies to the last straw doctrine- smaller but consistent events having
regard to the cumulative effect.
• Employee recognises the breach within a reasonable time so as to
not waive the breach
Summary dismissal • Where the employee has breached a term of the employment contract-
thus will be gross misconduct and not entitling to a claim