7.1 Specialised Exchange Surfaces
7.1 Specialised exchange surfaces
- Large multicellular organisms have a higher metabolic
rate than small unicellular organisms because they 7.2 the mammalian gaseous exchange system
have more cells. 7.3 Measuring the process
- The demand for O2 and glucose to be supplied and
CO2 to be removed much higher 7.4 ventilation and gas exchange in other organisms
- In large multicellular organisms the surface area to
volume ratio is too small and the diffusion differences are too large and therefore the rate of diffusion
is too slow to meet these demands alone.
- Therefore, they have exchange surfaces like the lungs linked up to the organs by transport systems
e.g., blood.
Specialised Exchange surfaces:
- Compact
- Very large surface area
- Maintains gradients – ventilation (breathing) movements and movements of blood.
- Reduced barriers (only 2 layers of cells so few cell membranes)
- Good blood supply
- Short diffusion distance – alveoli and capillary wall 1 cell thick, and cells are thin (squamous epithelium).
- Surface must be permeable – cell membranes are
- Way to pick up O2 easily – respiratory pigment
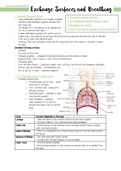
Nasal Cavity
Palate
7.2 The Mammalian Gaseous Exchange System Buccal Cavity
Pharynx
- Exchange surfaces have:
Epiglottis
o Increased/large surface area – giving Larynx
Oesophagus
more area for diffusion Trachea
o Thin 1 cell thick wall – giving short Ribs
diffusion pathway Bronchus
Pleural
o Good blood supply – maintains a steep Membranes
concentration gradient Pleural Cavity
o Good ventilation – maintains Intercostal Muscles (filled with
pleural fluid)
steep gradients for O2 and CO2 Lung
between the blood in the air and the Position of the
lungs. Diaphragm heart
Abdominal Cavity
Bronchioles
Tissue Function/Adaptation in the lungs
Cartilage - Holds the lumen of the trachea and bronchi open/gives support.
- Prevents collapse of the trachea/bronchi during inhalation.
Goblet Cells - Secrete mucus to trap bacteria, viruses and dust particles. Mucus contains
water and mucin proteins
Ciliated Epithelium - Move in a coordinated way to move/sweep mucus up from the lungs towards
the throat.
Squamous Epithelium - Very thin lining cells found in alveoli.
- Provides short diffusion distance for gas exchange
Elastic Tissue - Stretched during inhalation
- Recoil during exhalation to help increase air pressure/help air be expelled from
the lungs.
, Nasal Cavity:
- Has a large surface area with a good blood supply, this warms the air to body temperature.
- A hairy lining, secretes mucus to trap dust and bacteria, protecting lung tissue from irritation and
infection.
- Moist surfaces increase the humidity of the incoming air, reducing evaporation from the exchange
surfaces.
Trachea:
- The main airway carrying air from the nose to the chest.
- A wide tube supported by incomplete rings of strong, flexible cartilage to stop it from collapsing.
- The rings are incomplete so food can move through the oesophagus behind.
- Lined with ciliated epithelium and goblet cells. Goblet cells secrete mucus onto the
lining of the trachea, to trap dust and microorganisms that have escaped the nose
lining.
- Cilia move in a rhythmical wave moving mucus up from the bottom of the trachea
up to the throat it is mostly then digested.
Bronchus:
- Trachea divides into the bronchi in the chest cavity
- Cartilage present in blocks.
- Ciliated columnar epithelium with goblet cells
- Circular smooth muscles
- Similar in structure to the trachea, but smaller.
Bronchioles:
- Bronchi divide to form small bronchioles
containing no cartilage rings.
- Epithelium changes towards being cuboidal, cilia
are no longer present., circular smooth muscle still present.
- They contain smooth muscle, which can contract and relax, changing the
amount of air reaching the lungs.
- Lined with a thin layer of flattened epithelium, making some gaseous
exchange possible.
Blood from
Endothelium of Pulmonary Artery Alveoli:
Pulmonary Capillary Blood cells pushed - Tiny air sacs, the main gas exchange surfaces, unique to mammalian
against capillary wall
2Low O High CO
2
lungs.
- Consists of a layer of thin, flattened epithelial cells, collagen and elastic
fibres which allow the alveoli to stretch as air is drawn in, when they return to
To Pulmonary Vein their resting size, they help squeeze the air out, this is known as elastic recoil.
Squamous epithelium Structure Cartilage Ciliated Goblet Smooth Squamous Elastic
of alveolus
Film of moisture
Epithelium Cells Muscle Epithelium Tissue
Trachea Yes (c- Yes Yes Yes No Yes
shaped)
- Air is moved as a Bronchus Yes Yes Yes Yes No Yes
result of pressure (blocks)
changes in the thorax Bronchioles No Yes à No No Yes No Yes
brought about by Alveoli No No No No Yes Yes
breathing movements.
- The ribcage provides a case where air pressure can be lowered within it. The diaphragm is a domed
shaped muscle at the floor of the thorax. The thorax is lined by pleural membranes and the space
within them is filled with lubricating fluid, so the membranes can easily slide over each other as you
breathe.