CARBOHYDRATES
MAIN GROUPS OF CARBOHYDRATES
MONOSACCHARIDES – simple sugars
DISACCHARIDES – double sugars, made of 2 monosaccharides joined together
POLYSACCHARIDES – polymer consisting of many monosaccharides linked together
MONOSACCHARIDES
GENERAL FORMULA – (CH2O)n
GLUCOSE -Main sugar used for respiration. Starch and glycogen are polymers of glucose. Is
absorbed and transported in the bloodstream to cells.
FRUCTOSE - Sugar found naturally in fruit, honey and some vegetables.
GALACTOSE -Mainly in our diet as part of lactose disaccharide.
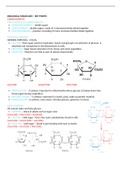
GLUCOSE GALACTOSE FRUCTOSE
TRIOSE SUGAR – 3 carbons, important in mitochondria where glucose is broken down into
triose sugars during respiration.
PENTOSE SUGARS – 5 carbons, important in nucleic acids, make up genetic material.
HEXOSE SUGAR – 6 carbons, taste sweet, includes glucose, galactose, fructose.
DISACCHARIDES
All contain alpha and beta glucose
SUCROSE – stores in plants such as sugar cane.
(GLUCOSE + FRUCTOSE = SUCROSE)
LACTOSE – milk sugar – this is the main carbohydrate found in milk.
(GLUCOSE + GALACTOSE = LACTOSE)
MALTOSE – malt sugar – found in germinating seed such as barley.
(GLUCOSE + GLUCOSE = MALTOSE)
, DISACCHARIDE EQUATION: C6H12O6 + C6H12O6 C12H22O11 + H2O
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN ALPHA AND BETA GLUCOSE
These two isomers result from different arrangements of the atoms on the side chains of the
molecule
ALPHA – same
BETA – opposite
SABO
POLYSACCHARIDES
Contain glyosidic bonds
Important in plants
GLYCOGEN – STARCH – main energy store material
Important storage carbohydrate in fungi Major carbohydrate storage molecules in
Found in animals plants
Made up of many alpha-glucose Made up of long chains of alpha glucose
Very compact Contains amylose and amylopectin.
Has more 1,6-glycosidic bonds gives many side branches Compact, useful for storage.
Can be broken down rapidly. Easily hydrolysed to glucose when energy is
needed
CELLULOSE – important structural material in plants
Cell wall
Consists of long chains of glucose joined by glycosidic bonds.
STRUCTURES
AMYLOSE SIMILARITIES AMYLOPECTIN
Made up of purely alpha Long chains of alpha glucose. Contains 1,6-glycosidic
glucose. Molecules joined by 1,4-glycosidic bonds too.
Molecules are long unbranched bonds. It’s a branched chain which
chains. changes the properties of
Compact the molecule.
Glucose molecules can be
broken off rapidly when
energy is needed.
STARCH SIMILARITIES GLYCOGEN
Made up of amylose and Long chains of glucose Held together by 1,4-glycosidic bonds
amylopectin. joined by glycosidic bonds. where one of the units has to be
Compact Contains alpha 1,4 and 1,6 inverted so bonding can take place.
glycosidic bonds Hydrogen bonds form (gives strength)
between hydroxyl group and
negatively charged O2. (cross linking)
Molecules don’t coil, straight chains.
CELLULOSE