15.1 Drugs
Define a drug as any substance taken into the body that modifies or affects chemical
reactions in the body
15.2 Medicinal drugs
Describe the use of antibiotics for the treatment of bacterial infection
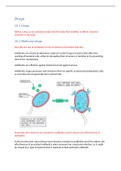
Antibiotics are chemical substances made by certain fungi or bacteria that affect the
working of bacterial cells, either by disrupting their structure or function or by preventing
them from reproducing.
Antibiotics are effective against bacteria but not against viruses.
Antibiotics target processes and structures that are specific to bacterial (prokaryotic) cells;
as such they do not generally harm animal cells.
State that some bacteria are resistant to antibiotics which reduces the effectiveness of
antibiotics
Some bacteria that cause disease have become resistant to antibiotics and this reduces the
effectiveness of prescribed antibiotics when someone has a bacterial infection, as it might
be caused by a type of bacteria that is resistant to that particular antibiotic.
, Explain how development of resistant bacteria such as MRSA can be minimised, limited to
using antibiotics only when essential and ensuring treatment is completed
Since the first antibiotic was discovered in 1928, many more have been discovered and
developed and antibiotics were and are widely overused.
Commonly prescribed antibiotics are becoming less effective due to a number of reasons:
Overuse and being prescribed when not really necessary
Patients failing to complete the fully prescribed course by a doctor
Large scale use of antibiotics in farming to prevent disease when livestock are kept in
close quarters, even when animals are not actually sick
This has led to the effectiveness of antibiotics being reduced, and the incidence of antibiotic
resistance increasing
These bacteria are commonly known as superbugs and the most common is MRSA
Ways individuals can help prevent the incidence of antibiotic resistance increasing include:
Only taking antibiotics when absolutely essential
When prescribed a course of antibiotics, ensure that the entire course is
completed even if you feel better after a few days
Plasmids with antibiotic-resistant genes can be transferred between bacterium of the same
and different species.
Explain why antibiotics kill bacteria, but do not affect viruses
Viruses cannot be treated with antibiotics.
This is because antibiotics work by disrupting cell functions such as respiration, or breaking
down the structure of the cell in some way.
However, viruses do not carry out any cell functions and do not have cell walls, cell
membranes or any cell organelles as viruses infect and utilise the machinery of animal cells
to reproduce, which are not affected by antibiotics.
Therefore, the action of antibiotics does not affect them.
15.3 Misused drugs
Describe the effects of excessive alcohol consumption and abuse of heroin, limited to:
Powerful depressant drugs
Effect on reaction times and self-control
Addiction and withdrawal symptoms
Negative social implications, e.g., crime
State that the liver is the site of breakdown of alcohol and other toxins