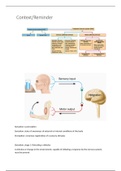
Sensation vs perception
Sensation: state of awareness of external or internal conditions of the body
Perception: conscious registration of a sensory stimulus
Sensation, stage 1: Detecting a stimulus
A stimulus or change in the environment, capable of initiating a response by the nervous system,
must be present
,Sensation, stage 2: Transduction
A receptor or sense organ must pick up stimulus and transduce it to a nerve impulse
Stimulus is capable of causing membrane of the recptor to dpolarise, causing a generator/receptor
potential
When generator potential reaches threshold level, an AP is initated
Sensation, stage 3: Into the brain
Impulse is conducted along a nueral pathway from receptor/sense organ to the brain
Carried along afferent pathway & terminates at the spinal cord or brain
Most impulses pass thro’thalamus- directs info to relevant sensory area of cortex
Sensation, stage 4: Registration in the sensory cortex
Region of the brain must translate impulse into a sensation
Generally in sensory areas of the cerebral cortex
Each area of sensory cortex corresponds to a specific area of sensation
Some sensory impulses terminate in spinal cord or brain stem & can initiate motor activies (reflex)
,
Sensation: state of awareness of external or internal conditions of the body
Perception: conscious registration of a sensory stimulus
Sensation, stage 1: Detecting a stimulus
A stimulus or change in the environment, capable of initiating a response by the nervous system,
must be present
,Sensation, stage 2: Transduction
A receptor or sense organ must pick up stimulus and transduce it to a nerve impulse
Stimulus is capable of causing membrane of the recptor to dpolarise, causing a generator/receptor
potential
When generator potential reaches threshold level, an AP is initated
Sensation, stage 3: Into the brain
Impulse is conducted along a nueral pathway from receptor/sense organ to the brain
Carried along afferent pathway & terminates at the spinal cord or brain
Most impulses pass thro’thalamus- directs info to relevant sensory area of cortex
Sensation, stage 4: Registration in the sensory cortex
Region of the brain must translate impulse into a sensation
Generally in sensory areas of the cerebral cortex
Each area of sensory cortex corresponds to a specific area of sensation
Some sensory impulses terminate in spinal cord or brain stem & can initiate motor activies (reflex)
,