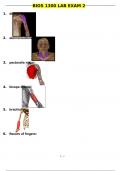
UVIC MATH 100 EXAM STUDY GUIDE
tan'x - Answers -sec^2x
cot'x - Answers --csc^2 x
sec' x - Answers -secxtanx
csc'x - Answers --cscxcot x
sin^2x+cos^2x - Answers -1
tan^2x+1 - Answers -sec^2x
1+cot^2x - Answers -csc^2x
Logₓ(M*N) - Answers -LogₓM + LogₓN
LogₓX - Answers -1
Logₓ(X^k) - Answers -K
Lim ᶜ√f(x)
x-d - Answers -ᶜ√L (where c is a positive integer)
Lim [f(x)]ᶜ
x-d - Answers -L^c (where c is a positive integer)
ln(e) - Answers -1
a^3+b^3 - Answers -(a+b)(a^2-ab+b^2)
a^3-b^3 - Answers -(a-b)(a^2+ab+b^2)
d/dx sin⁻¹(x) - Answers -1/√(1-x²)
d/dx cos⁻¹(x) - Answers --1/√(1-x²)
d/dx tan⁻¹(x) - Answers -1/(1+x²)
d/dx csc⁻¹(x) - Answers --1/(|x| √(x²-1))
d/dx sec⁻¹(x) - Answers -1/(|x| √(x²-1))
d/dx cot⁻¹(x) - Answers --1/(1+x²)
, Name the property of an even function - Answers -f is even if and only if f(x) = f (-x) for
all x values in the domainEx. f(x) = x^2 --> f(4) = 16 --> f(-4) = 16 --> f(3) = 9
Name the properties of an odd function - Answers -1. f is odd if and only if f(-x) = -f(x)
for all x values in the domain
2. symmetrical with respect to the origin
3. whenever (x, y) is on the graph so is (-x, -y) as well
What is the form for a rational function and what is its domain and range? - Answers -
f(x) = P(x)/Q(x)Domain: all x values when Q(x) does NOT equal 0
Intermediate Value Theorem - Answers -If f is continuous on [a,b] and k is a number
between f(a) and f(b), then there exists at least one number c such that f(c)=k
Alternative Definition of a Derivative - Answers -(f(x)-f(c))/(x-c)
f '(x) is the limit of the following difference quotient as x approaches c
y' of uvw - Answers -uvw'+uv'w+u'vw
(dy/du)(du/dx) - Answers -(dy/dx)
Extreme Value Theorem - Answers -If f is continuous on [a,b] then f has an local
maximum and an local minimum on [a,b]. The local extrema occur at critical points in
the interval or at endpoints of the interval.
Critical Number - Answers -If f'(c)=0 or does not exist, and c is in the domain of f, then c
is a critical number. (Derivative is 0 or undefined)
Rolle's theorem - Answers -Let f be continuous on [a,b] and differentiable on (a,b) and if
f(a)=f(b) then there is at least one number c on (a,b) such that f'(c)=0 (If the slope of the
secant is 0, the derivative must = 0 somewhere in the interval).
Mean Value Theorem - Answers -f'(c) = (f(b) - f(a))/ (b - a)
First Derivative Test - Answers -When testing critical values, if the first derivative
changes from negative to zero to positive, then that critical value is a local minimum of
the function. If the first derivative changes from positive to zero of negative, then that
critical value is a local maximum of the function
Second Derivative Test - Answers -if f'(c) = 0 and f''(c) > 0 then minimum; if f'(c) = 0 and
f''(c) < 0 then maximum
tan'x - Answers -sec^2x
cot'x - Answers --csc^2 x
sec' x - Answers -secxtanx
csc'x - Answers --cscxcot x
sin^2x+cos^2x - Answers -1
tan^2x+1 - Answers -sec^2x
1+cot^2x - Answers -csc^2x
Logₓ(M*N) - Answers -LogₓM + LogₓN
LogₓX - Answers -1
Logₓ(X^k) - Answers -K
Lim ᶜ√f(x)
x-d - Answers -ᶜ√L (where c is a positive integer)
Lim [f(x)]ᶜ
x-d - Answers -L^c (where c is a positive integer)
ln(e) - Answers -1
a^3+b^3 - Answers -(a+b)(a^2-ab+b^2)
a^3-b^3 - Answers -(a-b)(a^2+ab+b^2)
d/dx sin⁻¹(x) - Answers -1/√(1-x²)
d/dx cos⁻¹(x) - Answers --1/√(1-x²)
d/dx tan⁻¹(x) - Answers -1/(1+x²)
d/dx csc⁻¹(x) - Answers --1/(|x| √(x²-1))
d/dx sec⁻¹(x) - Answers -1/(|x| √(x²-1))
d/dx cot⁻¹(x) - Answers --1/(1+x²)
, Name the property of an even function - Answers -f is even if and only if f(x) = f (-x) for
all x values in the domainEx. f(x) = x^2 --> f(4) = 16 --> f(-4) = 16 --> f(3) = 9
Name the properties of an odd function - Answers -1. f is odd if and only if f(-x) = -f(x)
for all x values in the domain
2. symmetrical with respect to the origin
3. whenever (x, y) is on the graph so is (-x, -y) as well
What is the form for a rational function and what is its domain and range? - Answers -
f(x) = P(x)/Q(x)Domain: all x values when Q(x) does NOT equal 0
Intermediate Value Theorem - Answers -If f is continuous on [a,b] and k is a number
between f(a) and f(b), then there exists at least one number c such that f(c)=k
Alternative Definition of a Derivative - Answers -(f(x)-f(c))/(x-c)
f '(x) is the limit of the following difference quotient as x approaches c
y' of uvw - Answers -uvw'+uv'w+u'vw
(dy/du)(du/dx) - Answers -(dy/dx)
Extreme Value Theorem - Answers -If f is continuous on [a,b] then f has an local
maximum and an local minimum on [a,b]. The local extrema occur at critical points in
the interval or at endpoints of the interval.
Critical Number - Answers -If f'(c)=0 or does not exist, and c is in the domain of f, then c
is a critical number. (Derivative is 0 or undefined)
Rolle's theorem - Answers -Let f be continuous on [a,b] and differentiable on (a,b) and if
f(a)=f(b) then there is at least one number c on (a,b) such that f'(c)=0 (If the slope of the
secant is 0, the derivative must = 0 somewhere in the interval).
Mean Value Theorem - Answers -f'(c) = (f(b) - f(a))/ (b - a)
First Derivative Test - Answers -When testing critical values, if the first derivative
changes from negative to zero to positive, then that critical value is a local minimum of
the function. If the first derivative changes from positive to zero of negative, then that
critical value is a local maximum of the function
Second Derivative Test - Answers -if f'(c) = 0 and f''(c) > 0 then minimum; if f'(c) = 0 and
f''(c) < 0 then maximum