Vectors in the Plane and Three-Space
A vector is a quantity that has magnitude and direction, for example, velocity or
force. It is often represented by an arrow.
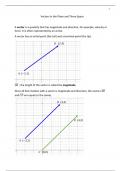
A vector has an initial point (the tail) and a terminal point (the tip).
𝐵 (2,4)
𝐴 (−2,1)
⃗⃗⃗⃗⃗ ; the length of the vector is called the magnitude.
𝐴𝐵
Since all that matters with a vector is magnitude and direction, the vectors ⃗⃗⃗⃗⃗
𝐴𝐵
and ⃗⃗⃗⃗⃗
𝐶𝐷 are equal (or the same).
𝐵 (2,4)
𝐷 (4,3)
𝐴 (−2,1)
𝐶 (0,0)
, 2
⃗⃗⃗⃗⃗ = 𝐶𝐷
𝐴𝐵 ⃗⃗⃗⃗⃗ , so we can “move’ vectors around as long as we don’t change the
magnitude (length) or direction (can move parallel).
Given 2 points in either ℝ2 or ℝ3 , say 𝐴(−2,1) and 𝐵(2,4), we can create a
vector by subtracting the coordinates:
⃗⃗⃗⃗⃗
𝐴𝐵 = (2 − (−2), 4 − 1) = < 4,3 >.
To add vectors we put the tail of one to the tip of the other:
⃗⃗⃗⃗⃗
𝐴𝐵 + ⃗⃗⃗⃗⃗
𝐶𝐷 ⃗⃗⃗⃗⃗
𝐶𝐷
⃗⃗⃗⃗⃗
𝐶𝐷
⃗⃗⃗⃗⃗
𝐴𝐵
We can multiply vectors by a (real) number, called a scalar:
⃗⃗⃗⃗⃗ ⃗⃗⃗⃗⃗
3𝐴𝐵
𝐴𝐵
, 3
If we multiply a vector by a negative number it creates a vector in the opposite
direction:
⃗⃗⃗⃗⃗
𝐴𝐵
⃗⃗⃗⃗⃗
−2𝐴𝐵
Ex. Find ⃗⃗⃗⃗⃗ ⃗⃗⃗⃗⃗ and ⃗⃗⃗⃗⃗
𝐴𝐵 + 2𝐴𝐶 ⃗⃗⃗⃗⃗ :
𝐴𝐵 − 2𝐴𝐶
⃗⃗⃗⃗⃗
2𝐴𝐶
⃗⃗⃗⃗⃗ ⃗⃗⃗⃗⃗
𝐴𝐵 + 2𝐴𝐶
⃗⃗⃗⃗⃗
−2𝐴𝐶
⃗⃗⃗⃗⃗
𝐴𝐵
⃗⃗⃗⃗⃗ − 2𝐴𝐶
𝐴𝐵 ⃗⃗⃗⃗⃗ ⃗⃗⃗⃗⃗
𝐴𝐶