With Complete Solutions
,
, Endogenous - VERIFIED ANSWERSwithin the genes
How much of hearing losses are genetic? - VERIFIED ANSWERS50%
Nonsyndromic - VERIFIED ANSWERSno other associated abnormalities
Syndromic - VERIFIED ANSWERShearing loss many may accompany other structures and
systems such as craniofacial structures, kidneys, skin, eyes, etc.
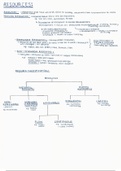
Autosomal Dominant (ASD) Inhearitance - VERIFIED ANSWERSDeaf parent Dd& Hearing
parent dd
Deaf parent passes the D to two kids and the d to the other two kids
The hearing parent passes a d to each kid
The two kids with Dd are deaf and the two kids with dd are hearing
Autosomal Recessive (ASR) Inheritance - VERIFIED ANSWERSCarrier father Rr and carrier
mother Rr
The hearing kid receives RR
2 Hearing carrier receives Rr
One deaf kid receives rr
X-linked inheritance - VERIFIED ANSWERSHearing father XY
Hearing carrier mother Xx
Hearing boy XY
Hearing girl XX
Deaf boy xY
Hearing carrier girl Xx
Affected males. female carriers
Mitochondrial Inheritance - VERIFIED ANSWERSOnly inherited from the mother's egg
Only females can transmit the the trait to offspring
They pass it to all of their offspring
Prenatal - VERIFIED ANSWERSprior to birth in utero
Perinatal - VERIFIED ANSWERSshortly before or after birth (~8 weeks to +4 weeks)
Postnatal - VERIFIED ANSWERSafter birth
Congenital - VERIFIED ANSWERSbefore birth (they are born with it)
Ear Pain is known by what term? - VERIFIED ANSWERSotalgia
Discharge is known by what term? - VERIFIED ANSWERSotorrhea