The Nervous System
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
ANATOMICAL TERMS OF LOCATION
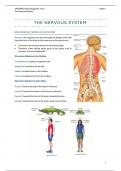
Neuraxis: An imaginary line drawn through the length of the CNS
from the front of the brain to the lower end of the spinal cord
• In humans, the neuraxis bends as we stand upright
• Therefore, when talking about parts of the spinal cord in
humans, terms are flipped 90º
Structures Relative to the Midline
Contralateral: Located on opposite side
Ipsilateral: Located on same side
Medial: Located closer to the midline
Lateral: Located further from the midline
Structures Relative to Each Other
Dorsal: Towards the top of the head or the back
Ventral: Towards the bottom of the skull or stomach
Rostral: Towards the front of the brain, towards the face
Caudal: Towards the back of the brain, away from the face
1
,4PAHPBIO Psychology BSc Year 1 Week 1
The Nervous System
Planes
Transverse plane (cross section): A slice taken of the nervous system at right angles to the neuraxis
Coronal Plane (frontal section): A slice through the brain parallel to the forehead (parallel to the ground
in the spinal cord)
Horizontal plane: A slice through the brain parallel to the ground
Sagittal plane: A slice through the brain parallel to the neuraxis and perpendicular to the ground
1.1 THE STRUCTURAL DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
2
, 4PAHPBIO Psychology BSc Year 1 Week 1
The Nervous System
1.2 THE FUNCTIONS ASSOCIATED WITH DIFFERENT PARTS OF THE
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
DIVISIONS OF THE BRAIN
Major Divisions Subdivisions Principle structure
Forebrain Telencephalon Cerebral Cortex
Basal Ganglia
Limbic System
Diencephalon Thalamus
Hypothalamus
Midbrain Mesencephalon Tectum
Tegmentum
Hindbrain Metencephalon Cerebellum
Pons FOREBRAIN (BLUE), MIDBRAIN (RED),
Myelencephalon Medulla Oblongata HINDBRAIN (YELLOW)
LOBES OF THE BRAIN
Major Divisions Subdivisions
Frontal Motor functions
Executive functions
Parietal Bodily sensations
Spatial relationships
Temporal Hearing
Occipital Vision
OVERVIEW OF THE FUNCTIONS
Structure Function
Basal Ganglia Movement
Limbic System Motivation and emotion
Thalamus Relay and integration of sensory
information
Hypothalamus Controls ANS and endocrine
system
Tectum Visual and auditory processing
Tegmentum Sleep, arousal, movement
Cerebellum Motor coordination, muscle
tone, and balance
Pons and Sleep and arousal
Medulla
Medulla Control of vital functions
Oblongata
3