The lymphatic system is made up of a network of tissues, organs
and vessels that all work together to move lymph, which is a
colourless fluid, back into your circulatory system. The main
function of the lymphatic system is to work as our immune
system, to filter out harmful pathogens in the blood, to discard
waste material from cells and transport beneficial nutrients.
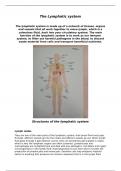
Structures of the lymphatic system
Lymph nodes
They are one of the main parts of the lymphatic system; that lymph fluid must pass
through. Afferent vessels go into the nodes and efferent vessels go out. When lymph
fluid goes through it gets filtered, cancer cells can sometimes get trapped in nodes
which is why the lymphatic organs are often screened. Lymphocytes and
macrophages are multiplied here and deal with any pathogens, cell debris and ingest
microorganisms in the lymph fluid. Haematopoiesis occurs here which includes the
production of lymphocytes and monocytes. Dendrite cells trap antigenic material
(which is anything that produces an immune response) that is in the lymph fluid.
, Nodes can swell when you have a low immune system as cell debris can build up.
- Axillary nodes are located in the upper axillary region (also known as the
armpit). There are 20-40 separate nodes whose functions are to drain the
abdomen, chest wall and vessels in the region.
- Supratrochlear are a small group of nodes located superficially on the
forearm. They can swell when there is infection in the hand or forearm.
- Abdominal nodes are in a membrane attached to the abdominal wall. They
trap pathogens and eliminate them.
- Inguinal nodes are both superficial and deep within the groin area. These
nodes are the major drainage system and immune system for the legs,
genitals and pelvic region.
- Popliteal nodes are in the leg behind the knee and are a drainage system for
the legs and feet.
Lymph vessels
Lymph vessels have thinner walls than veins and arteries and transport the lymph
fluid. They are found in all parts of the body except for the CNS, teeth/bones and
cartilage. Lymph capillaries are spread out through the bodies tissues and have blind
ends. They do not have a ‘heart’ so rely on muscles contracting nearby and
lymphangion to increase pressure and move the lymph along towards the subclavian
veins; and have valves to keep the flow one-way.
Lymph ducts
There are two main ducts, the left lymphatic duct/ thoracic and right lymphatic duct
which Lymphatic vessels empty into. These two ducts then connect to the subclavian
vein before draining into blood vessels in the neck region, emptying lymph fluid into
the bloodstream. The subclavian vein runs below your collarbone. Returning lymph