Chemie Carbohydrates Klasse 12
Glucose
1. Physical Properties:
➢ Strong intermolecular forces (H-bridges)
a. State of matter: • Solid
b. Melting point • 146°C
• highly soluble in water, not soluble in heptane
2. Solubility: ➢ Contains polar groups
• None
➢ No ions
3. Conductivity:
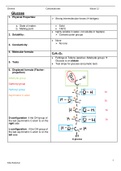
4. Molecular formula
C6H12O6
• Fehlings & Tollens (positive: Aldehyde group) →
Glucose is an aldose
5. Tests
• Test stripe for glucose (enzymatic test)
6. Displayed formula (Fischer-
projection)
Aldehyde group
Carbonyl group
Hydroxyl group
ta
Asymmetric C-atom
tü
ta
D-configuration: if the OH-group of
the last asymmetric C-atom is on the
ta
right side
L-configuration: if the OH-group of
the last asymmetric C-atom is on the
left side
D-glucose
1
Silke Redecker
, Chemie Carbohydrates Klasse 12
7. Formation of the ring
• In glucose the carbonyl group
is linked to the 5th C-atom
• New asymmetric C-atom (C1)
→ anomeric C-atom
• 2 stereoisomers
o Differ in position of OH-
group of C1
α-D-glucose Open form β-D-glucose
8. Haworth projection
• OH-group right → OH-group
below plane of ring
• OH-group left → OH-group
above plane of ring
• Beta = oben
α-D-glucose β-D-glucose
α-D-glucopyranose β -D-glucopyranose
• There is an equilibrium between the different forms
of glucose in an aqueous solution
• Mutarotation describes the phenomenon that the
9. Mutarotation
rotation angle of a freshly made solution might
change over time until it reaches a constant value
2
Silke Redecker
Glucose
1. Physical Properties:
➢ Strong intermolecular forces (H-bridges)
a. State of matter: • Solid
b. Melting point • 146°C
• highly soluble in water, not soluble in heptane
2. Solubility: ➢ Contains polar groups
• None
➢ No ions
3. Conductivity:
4. Molecular formula
C6H12O6
• Fehlings & Tollens (positive: Aldehyde group) →
Glucose is an aldose
5. Tests
• Test stripe for glucose (enzymatic test)
6. Displayed formula (Fischer-
projection)
Aldehyde group
Carbonyl group
Hydroxyl group
ta
Asymmetric C-atom
tü
ta
D-configuration: if the OH-group of
the last asymmetric C-atom is on the
ta
right side
L-configuration: if the OH-group of
the last asymmetric C-atom is on the
left side
D-glucose
1
Silke Redecker
, Chemie Carbohydrates Klasse 12
7. Formation of the ring
• In glucose the carbonyl group
is linked to the 5th C-atom
• New asymmetric C-atom (C1)
→ anomeric C-atom
• 2 stereoisomers
o Differ in position of OH-
group of C1
α-D-glucose Open form β-D-glucose
8. Haworth projection
• OH-group right → OH-group
below plane of ring
• OH-group left → OH-group
above plane of ring
• Beta = oben
α-D-glucose β-D-glucose
α-D-glucopyranose β -D-glucopyranose
• There is an equilibrium between the different forms
of glucose in an aqueous solution
• Mutarotation describes the phenomenon that the
9. Mutarotation
rotation angle of a freshly made solution might
change over time until it reaches a constant value
2
Silke Redecker