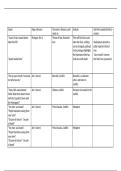
NSG222 - Exam 2 Study Guide Questions and Answers
Terms in this set (108)
- Inspect for size, shape, and symmetry
- The newborn's chest should be round, symmetric, and 2 to 3 cm smaller than the
head circumference
- Nipples may be engorged and may secrete a white discharge
- extra nipples, called supernumerary nipples
- usually barrel shaped
Chest
- Fine crackles normal, diminished breath sounds not
- S1 and S2 heart sounds are accentuated
- A displaced point of maximal impulse may indicate tension pneumothorax or
cardiomegaly.
- Murmurs are common during the first few hours as the foramen ovale is closing,
should be evaluated if they persist
Normal newborn blood values
• Respirations: 30 to 60 breaths per minute; irregular, shallow, unlabored; short
Respiratory System Adaptations
periods of apnea (<15 seconds); symmetrical chest movements
The newborn's primary method of heat production. Brown fat (adipose tissue) is
nonshivering thermogenesis oxidized in response to cold exposure, is able to convert chemical energy directly
into heat when activated by the sympathetic nervous system.
conduction, convection, evaporation, radiation
Mechanisms of heat exchange
transfer of heat from object to object when the two objects are in direct contact with
Conduction
each other
flow of heat from body surface to cooler surrounding air or to air circulating over a
Convection
body surface
Evaporation loss of heat when a liquid is converted to a vapor
, Radiation loss of body heat to cooler, solid surfaces in close proximity but not in direct contact
- balance between heat loss and heat production
Thermoregulation
- need for a neutral thermal environment (NTE)
• Large body surface area
Overheating due to...? • Limited insulation
• Limited sweating ability
- starts when placenta is detached and liver takes over
Hepatic System Function
- iron storage, carb metabolism, bilirubin conjugation
• Three groups of jaundice based on mechanism of accumulation of bilirubin
• Overproduction
Bilirubin conjugation
• Decreased conjugation
• Impaired excretion
• Development of a mucosal barrier to prevent the
penetration of harmful substances
• Physiologic capacity of the newborn stomach is
less than anatomic capacity
Gastrointestinal System Adaptations • Cardiac sphincter and nervous control of stomach
are immature leading to regurgitation and
uncoordinated peristaltic activity
• To gain weight the newborn requires an intake of
108 kcal/kg/day from birth to 6 months of age
• Meconium, then transitional stool, then milk stool
• Breast-fed newborns: yellow-gold, loose, stringy to pasty, sour-smelling
Stools
• Formula-fed newborns: yellow, yellow-green, loose, pasty, or formed, unpleasant
odor
Palmar & plantar grasp reflex
Grasp reflexes
- place a finger or stroke inside newborn's hands, will grasp
- Startle reflex
Moro reflex - when hear a loud noise
- throw out arms
Rooting reflex Cheek is stroked and the infant's mouth will move towards it
- Helps baby feed
Sucking reflex - When something touches the hard palate of the mouth, they will start sucking
- Disappears after 4 months
- Newborn's toes fan out when the sole of the foot is touched
Babinski reflex
- disappears about 1 year of age
Crawling reflex - disappears in weeks/months
Step reflex -disappears about 3-4 months
- fencing reflex
Tonic neck reflex
- head is turned to one side, leg and arm on that will extend but other arm will flex
• Birth to 30 minutes to 2 hours after birth
First period of reactivity
• Newborn is alert, moving, may appear hungry
• 30 to 120 minutes old
Period of decreased responsiveness
• Period of sleep or decreased activity
• 2 to 8 hours
Second period of reactivity
• Newborn awakens and shows an interest in stimuli
Newborn Behavioral Response: Orientation Response to stimuli
Terms in this set (108)
- Inspect for size, shape, and symmetry
- The newborn's chest should be round, symmetric, and 2 to 3 cm smaller than the
head circumference
- Nipples may be engorged and may secrete a white discharge
- extra nipples, called supernumerary nipples
- usually barrel shaped
Chest
- Fine crackles normal, diminished breath sounds not
- S1 and S2 heart sounds are accentuated
- A displaced point of maximal impulse may indicate tension pneumothorax or
cardiomegaly.
- Murmurs are common during the first few hours as the foramen ovale is closing,
should be evaluated if they persist
Normal newborn blood values
• Respirations: 30 to 60 breaths per minute; irregular, shallow, unlabored; short
Respiratory System Adaptations
periods of apnea (<15 seconds); symmetrical chest movements
The newborn's primary method of heat production. Brown fat (adipose tissue) is
nonshivering thermogenesis oxidized in response to cold exposure, is able to convert chemical energy directly
into heat when activated by the sympathetic nervous system.
conduction, convection, evaporation, radiation
Mechanisms of heat exchange
transfer of heat from object to object when the two objects are in direct contact with
Conduction
each other
flow of heat from body surface to cooler surrounding air or to air circulating over a
Convection
body surface
Evaporation loss of heat when a liquid is converted to a vapor
, Radiation loss of body heat to cooler, solid surfaces in close proximity but not in direct contact
- balance between heat loss and heat production
Thermoregulation
- need for a neutral thermal environment (NTE)
• Large body surface area
Overheating due to...? • Limited insulation
• Limited sweating ability
- starts when placenta is detached and liver takes over
Hepatic System Function
- iron storage, carb metabolism, bilirubin conjugation
• Three groups of jaundice based on mechanism of accumulation of bilirubin
• Overproduction
Bilirubin conjugation
• Decreased conjugation
• Impaired excretion
• Development of a mucosal barrier to prevent the
penetration of harmful substances
• Physiologic capacity of the newborn stomach is
less than anatomic capacity
Gastrointestinal System Adaptations • Cardiac sphincter and nervous control of stomach
are immature leading to regurgitation and
uncoordinated peristaltic activity
• To gain weight the newborn requires an intake of
108 kcal/kg/day from birth to 6 months of age
• Meconium, then transitional stool, then milk stool
• Breast-fed newborns: yellow-gold, loose, stringy to pasty, sour-smelling
Stools
• Formula-fed newborns: yellow, yellow-green, loose, pasty, or formed, unpleasant
odor
Palmar & plantar grasp reflex
Grasp reflexes
- place a finger or stroke inside newborn's hands, will grasp
- Startle reflex
Moro reflex - when hear a loud noise
- throw out arms
Rooting reflex Cheek is stroked and the infant's mouth will move towards it
- Helps baby feed
Sucking reflex - When something touches the hard palate of the mouth, they will start sucking
- Disappears after 4 months
- Newborn's toes fan out when the sole of the foot is touched
Babinski reflex
- disappears about 1 year of age
Crawling reflex - disappears in weeks/months
Step reflex -disappears about 3-4 months
- fencing reflex
Tonic neck reflex
- head is turned to one side, leg and arm on that will extend but other arm will flex
• Birth to 30 minutes to 2 hours after birth
First period of reactivity
• Newborn is alert, moving, may appear hungry
• 30 to 120 minutes old
Period of decreased responsiveness
• Period of sleep or decreased activity
• 2 to 8 hours
Second period of reactivity
• Newborn awakens and shows an interest in stimuli
Newborn Behavioral Response: Orientation Response to stimuli