UCI Bio 93 Final Examination / 2025-2026
Version with Correct and Verified
Answers from Reliable Study Resources
/ Already Graded A+
What are the four most common elements in living matter?
Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, and Carbon --make up 96% of all living
matter.
Properties of Acids
Donate H+ to a solution, accept electrons, and have a pH of <7
What happens in the S phase of the cell cycle?
DNA Synthesis
What happens in the G1 phase of the cell cycle?
Growth -- cell contents are duplicated.
What happens in the G2 phase of the cell cycle?
More growth and preparation for division.
What happens in the M phase of the cell cycle?
Mitosis (and cytokinesis -- division of the cell).
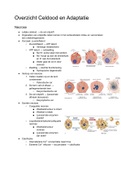
What are the subphases of mitosis?
Prophase, Pre-metaphase, Metaphase, Anaphase, and Telophase.
How many checkpoints are there in the cell cycle?
3 -- G1 checkpoint, G2 checkpoint, and the M checkpoint.
What is a Karyotype?
A layout of Metaphase chromosomes matched with their homologous
pairs.
,What is a diploid cell?
A cell with 46 chromosomes -- somatic cells.
What is a haploid cell?
A cell with 23 chromosomes -- sex cells.
What does the mesoderm give rise to?
the notochord (similar to a spinal chord).
What does the endoderm give rise to?
the digestive tract.
What does the ectoderm give rise to?
the nervous system (brain)/neural plate.
If 2n = 18, how many chromosomes come from the mother?
9 -- half from mom and half from dad
Meiosis
Meiosis is a specialized type of cell division that reduces the
chromosome number by half, creating four haploid cells, each
genetically distinct from the parent cell that gave rise to them.
What two structures does the chiasma connect?
Non-sister chromatids.
What are the steps of meiosis?
Prophase I, Metaphase I, Anaphase I, Telophase I & cytokinesis (then
a second set of phases)
What does meiosis 1 deal with?
homologous chromosomes.
What happens in prophase 1?
The chromosomes condense, the nuclear envelope breaks down,
chromosomes cross over, and meiotic spindle forms.
What happens in metaphase 1?
the pairs of homologous chromosomes are now tightly condensed
and coiled and become arranged on the metaphase plate.
What happens in anaphase 1?
, the pairs of chromosomes are pulled apart by the spindle fibers
(microtubules).
What happens in Telophase 1 and cytokinesis?
The homologous chromosome pairs complete their migration to the
two poles as a result of the action of the spindle. Now a haploid set of
chromosomes is at each pole, with each chromosome still having two
chromatids. A nuclear envelope reforms around each chromosome
set, the spindle disappears, and cytokinesis follows.
What happens during meiosis 2?
sister chromatids separate.
What happens in prophase 2 of meiosis?
A new spindle forms around the chromosomes.
What happens in metaphase 2 of meiosis?
Metaphase 2 chromosomes line up at the equator.
What happens in anaphase 2 of meiosis?
Centromeres divide chromatids move to opposite poles of the cells.
What happens during telophase 2 of meiosis?
A nuclear envelope forms around each set of chromosomes and the
cytoplasm divides.
What makes meiosis a unique form of cell division
Synapsis and crossing over -- occurs in prophase 1, pairing up of
homologous chromosomes, homologous chromosomes cross over
and exchange corresponding genetic information (the DNA
exchanged contain the same genes, but may have different alleles).
How does meiosis increase genetic variability?
Independent assortment (meiosis 1 -- homologous chromosomes
separate independently), crossing over (genetic recombination,
prophase 1), and random fertilization (any egg can join with any
sperm -- most effective way to obtain genetic variability).
What is the law of segregation?
Alleles coding for the same trait separate independently during
gamete formation.
What is non-disjunction?
Version with Correct and Verified
Answers from Reliable Study Resources
/ Already Graded A+
What are the four most common elements in living matter?
Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, and Carbon --make up 96% of all living
matter.
Properties of Acids
Donate H+ to a solution, accept electrons, and have a pH of <7
What happens in the S phase of the cell cycle?
DNA Synthesis
What happens in the G1 phase of the cell cycle?
Growth -- cell contents are duplicated.
What happens in the G2 phase of the cell cycle?
More growth and preparation for division.
What happens in the M phase of the cell cycle?
Mitosis (and cytokinesis -- division of the cell).
What are the subphases of mitosis?
Prophase, Pre-metaphase, Metaphase, Anaphase, and Telophase.
How many checkpoints are there in the cell cycle?
3 -- G1 checkpoint, G2 checkpoint, and the M checkpoint.
What is a Karyotype?
A layout of Metaphase chromosomes matched with their homologous
pairs.
,What is a diploid cell?
A cell with 46 chromosomes -- somatic cells.
What is a haploid cell?
A cell with 23 chromosomes -- sex cells.
What does the mesoderm give rise to?
the notochord (similar to a spinal chord).
What does the endoderm give rise to?
the digestive tract.
What does the ectoderm give rise to?
the nervous system (brain)/neural plate.
If 2n = 18, how many chromosomes come from the mother?
9 -- half from mom and half from dad
Meiosis
Meiosis is a specialized type of cell division that reduces the
chromosome number by half, creating four haploid cells, each
genetically distinct from the parent cell that gave rise to them.
What two structures does the chiasma connect?
Non-sister chromatids.
What are the steps of meiosis?
Prophase I, Metaphase I, Anaphase I, Telophase I & cytokinesis (then
a second set of phases)
What does meiosis 1 deal with?
homologous chromosomes.
What happens in prophase 1?
The chromosomes condense, the nuclear envelope breaks down,
chromosomes cross over, and meiotic spindle forms.
What happens in metaphase 1?
the pairs of homologous chromosomes are now tightly condensed
and coiled and become arranged on the metaphase plate.
What happens in anaphase 1?
, the pairs of chromosomes are pulled apart by the spindle fibers
(microtubules).
What happens in Telophase 1 and cytokinesis?
The homologous chromosome pairs complete their migration to the
two poles as a result of the action of the spindle. Now a haploid set of
chromosomes is at each pole, with each chromosome still having two
chromatids. A nuclear envelope reforms around each chromosome
set, the spindle disappears, and cytokinesis follows.
What happens during meiosis 2?
sister chromatids separate.
What happens in prophase 2 of meiosis?
A new spindle forms around the chromosomes.
What happens in metaphase 2 of meiosis?
Metaphase 2 chromosomes line up at the equator.
What happens in anaphase 2 of meiosis?
Centromeres divide chromatids move to opposite poles of the cells.
What happens during telophase 2 of meiosis?
A nuclear envelope forms around each set of chromosomes and the
cytoplasm divides.
What makes meiosis a unique form of cell division
Synapsis and crossing over -- occurs in prophase 1, pairing up of
homologous chromosomes, homologous chromosomes cross over
and exchange corresponding genetic information (the DNA
exchanged contain the same genes, but may have different alleles).
How does meiosis increase genetic variability?
Independent assortment (meiosis 1 -- homologous chromosomes
separate independently), crossing over (genetic recombination,
prophase 1), and random fertilization (any egg can join with any
sperm -- most effective way to obtain genetic variability).
What is the law of segregation?
Alleles coding for the same trait separate independently during
gamete formation.
What is non-disjunction?