NR 324 Adult Health ROK 2 Answers LATEST UPDATE
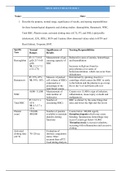
Name: _______________________________________________ Date: ___________________ 1. Describe the purpose, normal range, significance of results, and nursing responsibilities for these hematological diagnostic and clotting studies: (hemoglobin, Hematocrit, WBC, Total RBC, Platelet count, activated clotting time (ACT), PT, and INR, Lipid profile (cholesterol, LDL, HDL), BUN and Creatine (How abnormal values relate to HTN and Heart failure), Troponin, BNP. Specific Tests Normal Ranges Significance of Results Nursing Responsibilities Hemoglobin F: 11.7-16.0 g/dl (117-160 g/dl) M: 13.2-17.3 (132-173) Measurement of gas-carrying capacity of RBC Reduced in cases of anemia, hemorrhage, and hemodilution Increases in Hgb are found in polycythemia or in states of hemoconcentration, which can occur from dehydration Hematocrit F: 35%-47% M: 39%- 50% Measure of packed cell volume of RBCs expressed as a percentage of the total blood voume Determined by spinning clood in a centrifuge which causes the RBC to settle to the bottom and the plasma to go on top. Hct is the % of red blood cells in it WBC 4,000- 11,000 Measurement of total number of leukocytes Counts over 11,000 is sign of infection, inflammation, tissue injury or death and malignancies. Total RBC F: 3.8-5.1 x 10^6 M: 4.3-5.7 x 10^6 Number of circulating RBCs RBC is altered by the same things that raise and lower the Hgb and Hct levels Platelet count 150,000-400,000 Number of patelets available to maintain platelet clotting functions Counts below 100,000 signify thrombocytopenia which may cause bleeding. Spontaneous hemorrhage may occur if counts get below 10,000. Thrombocytosis is excessive platelets, occurring with inflammation and excessive clotting Activated clotting time (ACT) 70-120 sec Evaluation of intrinsic coagulation status. More accurate than aPTT. Used during dialysis, coronary artery bypass procedure, arteriograms. Prothrombin time PT 11-16 sec Assessment of extrinsic coagulation by measurement factors I, II, V, VII, X INR 2-3 Standardized system of reporting PT based on a reference calibration model and calculated by comparing the patient’s PT with a control value Cholesterol < 200 mg/dL Blood lipid. Elevated cholesterol is a risk for cardiovascular heart disease Cholesterol levels can be obtained in a nonfasting state LDL <100 mg/dL Mostly cholesterol with moderate amounts of phospholipids. Moderate risk for CAD: 130-159 High risk for CAD: >160 HDL F: >50 mg/dL M: >40 mg/dL Risk for cardiac disease is assessed by dividing total cholesterol level by the HDL level and obtaining the ratio. Low risk: ratio <3 Avg risk: ratio 3-5 Increased risk: ratio >5 BUN 7-20 mg/dL Usually determines kidney function Can help determine the effectiveness of dialysis Creatinine F: 88-128 M: 97-137 Indicator for kidney function Troponin Tropinin T: <0.1 ng/mL Tropnin I: Intermediate or suspicious for injury to myocardium: 0.5- 2.3. Positive for myocardial injury: >2.3 Contractile proteins that are released after an MI. Both troponin T and troponin I are highly specific to cardiac tissue Rapid bedside care assays are available. Explain the purpose of serial sampling in conjunction with CK-MB and serial ECGs. BNP > 100 pg/mL Peptide that causes natriuresis. Elevation helps to distinguish cardiac vs. respiratory cause of dyspnea Infusin of nesiritide (Natrecor) elevates levels temporarily

Geschreven voor
- Instelling
- Chamberlain College Of Nursing
- Vak
- NR 324 Adult Health ROK 2 Answers LATEST UPDATE (NR324ADULTHEALTHROK2ANSWERSLATESTUPDATE)
Documentinformatie
- Geüpload op
- 23 januari 2021
- Aantal pagina's
- 38
- Geschreven in
- 2020/2021
- Type
- Tentamen (uitwerkingen)
- Bevat
- Vragen en antwoorden
Onderwerpen
-
normal range
-
significance of results
-
name date 1 describe the purpose
-
and nursing responsibilities for these hematological dia
Ook beschikbaar in voordeelbundel