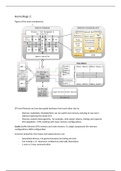
Figure of the main components:
CPU and Memory are two decoupled hardware from each other due to:
- Memory modularity (modulariteit), we can switch out memory and plug in new one’s
without replacing the whole CPU
- Memory module heterogeneity: for example, clock speed, latency, timings and capacity.
- CPU adaptivity: 1 CPU working with many memory configurations.
Cache: buffer between CPU memory and main memory. To adapt (aanpassen) the memory
configurations, BIOS configuration.
Common properties from input and output devices are:
- Specialised devices, not general-purpose but doing one task.
- Can include a J.V. Neumann architecture internally themselves
- 1-way or 2-way communication
, Hardware components acts at different speeds than your CPU, this is because of:
- Internal procession (e.g. MS Kinect)
- Signal digitisation (e.g. a mouse has an infrared and need to convert the signal)
- Data transfer mode
- Heterogeneity: number & diversity of devices.
Computer architecture components communicate via BUS. A Bus is a connection between:
- Components inside a device
- Components inside a CPU (internal bus)
- Components inside Computer (memory bus, PCIe bus, PCI bus, USB)
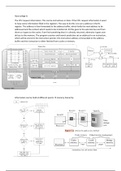
A bus consist of 3 tracks, each have a variable width:
- Control bus: Controls communication between the components
- Address bus: Address requests
- Data bus: Data is send over
Line-based communication:
- Sender puts information on bus
- Information travel through bus
- Receiver takes information from
the bus
No other information can be put on a bus until it’s empty and ready again (bus-busy).