IGCSE Biology – 2h: Transportation
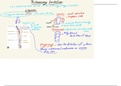
The Effect of Cube Size on Time Taken to Decolourise Practical
Method
o Collect 3 beakers and put 10cm³ of 0.5M hydrochloric acid in each backer using a
measuring cylinder.
o From the agar, cut 3 different sized cubes (1.5cm, 1cm 0.5cm).
o Place the largest agar cube into one of the beakers containing hydrochloric acid.
o Record the time taken for the acid to diffuse completely through the cube until it all
turns colourless.
o Repeat for the smaller cubes.
o Record the results.
Results
o The larger the cube, the smaller the surface area to volume ratio.
o The larger the surface area to volume ratio, the faster diffusion will occur.
o As the cubes increase in size, the surface area to volume ratio decreases.
o One celled organisms have a low demand (volume) but a high supply (surface area)
but for multicellular organisms, it is the other way round.
o Multicellular organisms require transport systems because simple diffusion would be
too slow to transport nutrients and remove waste and so they would die.
Transport in Plants
Xylem
o The xylem transports water and minerals up the plant.
o It is composed of dead cells.
Phloem
o The phloem transports products of photosynthesis from the leaves either up or
down to the rest of the plant.
o It is composed of living cells.
, The Effect of Osmosis on Plant Cells
o Cells placed in a dilute solution or water, absorbs water by osmosis and becomes
turgid.
o Cells placed in a concentrated solution loses water by osmosis and becomes flaccid.
Components of Blood
o The blood is an organ that contains many different tissues.
o It is part of the transport system.
o Blood’s main roles are to transport oxygen, glucose, carbon dioxide, urea, water,
products of digestion and heat energy around the body.
Plasma
o The plasma is the liquid part of the blood, composed of mainly water.
o It carries the blood cells around the body and carries dissolved nutrients, hormones,
carbon dioxide and urea.
o The plasma also distributes heat around the body.
Platelets
o Platelets are the smallest cells – they are really fragments of other cells.
o They release chemicals to make blood clot when we cut ourselves.
Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes)
o Red blood cells or erythrocytes are specialised cells in the blood, made in the bone
marrow.
o Their function is to transport oxygen around the body.
The Effect of Cube Size on Time Taken to Decolourise Practical
Method
o Collect 3 beakers and put 10cm³ of 0.5M hydrochloric acid in each backer using a
measuring cylinder.
o From the agar, cut 3 different sized cubes (1.5cm, 1cm 0.5cm).
o Place the largest agar cube into one of the beakers containing hydrochloric acid.
o Record the time taken for the acid to diffuse completely through the cube until it all
turns colourless.
o Repeat for the smaller cubes.
o Record the results.
Results
o The larger the cube, the smaller the surface area to volume ratio.
o The larger the surface area to volume ratio, the faster diffusion will occur.
o As the cubes increase in size, the surface area to volume ratio decreases.
o One celled organisms have a low demand (volume) but a high supply (surface area)
but for multicellular organisms, it is the other way round.
o Multicellular organisms require transport systems because simple diffusion would be
too slow to transport nutrients and remove waste and so they would die.
Transport in Plants
Xylem
o The xylem transports water and minerals up the plant.
o It is composed of dead cells.
Phloem
o The phloem transports products of photosynthesis from the leaves either up or
down to the rest of the plant.
o It is composed of living cells.
, The Effect of Osmosis on Plant Cells
o Cells placed in a dilute solution or water, absorbs water by osmosis and becomes
turgid.
o Cells placed in a concentrated solution loses water by osmosis and becomes flaccid.
Components of Blood
o The blood is an organ that contains many different tissues.
o It is part of the transport system.
o Blood’s main roles are to transport oxygen, glucose, carbon dioxide, urea, water,
products of digestion and heat energy around the body.
Plasma
o The plasma is the liquid part of the blood, composed of mainly water.
o It carries the blood cells around the body and carries dissolved nutrients, hormones,
carbon dioxide and urea.
o The plasma also distributes heat around the body.
Platelets
o Platelets are the smallest cells – they are really fragments of other cells.
o They release chemicals to make blood clot when we cut ourselves.
Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes)
o Red blood cells or erythrocytes are specialised cells in the blood, made in the bone
marrow.
o Their function is to transport oxygen around the body.