What are the NMDA and AMPA (briefly) receptors
and how do they work?
N-methyl-D-aspartate (NDMA)
receptor is a glutamate
receptor
Glutamate is the human
brain’s primary excitatory
neurotransmitter.
Postsynaptic glutamate-gated
ion channels allow the
passage of positively charged
ions into the postsynaptic cell and may be further classified as either:
- AMPA receptors
- NMDA receptors
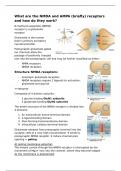
Structure NMDA receptors:
- Ionotropic glutamate receptors
- NMDA receptors require 2 ligands for activation:
glutamate and glycine
tetramer
Composed of 4 distinct subunits:
- 2 glycine binding GluN1 subunits
- 2 glutamate binding GlyN2 subunits
The entire structure of the NMDA receptor is divided into
4 domains:
1. An extracellular amino-terminal domain
2. A ligand-binding domain
3. Pore-forming transmembrane domain
4. Intracellular carboxy-terminal domain
Glutamate releases from presynaptic terminal into the
synaptic cleft at a very high concentration binds to
postsynaptic NMDA receptor induce channel pore
opening = gating
At resting membrane potential:
The inward current through the NMDA receptor is interrupted by the
movement of Mg2+ ions into the channel, where they become lodged.
As the membrane is depolarized:
, The Mg2+ block is displaced from the channel and the current is free to
pass into the cell
- The substantial current through the NMDA receptor requires the
release of glutamate by the presynaptic terminal AND depolarization
of the postsynaptic membrane
The NMDA channels conduct Ca2+ ions
- The magnitude of Ca2+ flux passing through the NMDA receptor
channel specifically signals the level of pre-and postsynaptic
coactivation
Structure AMPA receptors:
The pore forming subunit of AMPAR’s = GluA1-4, consist of 4 domains:
1. N-terminal domain (NTD)
2. Region C-terminal domain (CTD) connects the NTD to the ligand-
gated binding domain (LBD)
3. LBD: upon glutamate binding, the LBD undergoes conformational
changes that result in channel gating
4. Transmembrane domain (TMD): consist of 3 membrane spanning
segments: M1. M3 and M4 and a re-entrant helix loop (M2) forms
an ion channel in the membrane that when open, conducts cations
Function:
AMPA receptors are a key regulatory element of synaptic plasticity = the
ability of synapses to modify their responses according to the inputs they
receive
They mediate fast excitatory synaptic transmission + responsible for the
initial depolarization of the postsynaptic neuron
When glutamate binds to the AMPA receptors, they open and allow Na+ to
enter the neuron depolarizes the neuron
and how do they work?
N-methyl-D-aspartate (NDMA)
receptor is a glutamate
receptor
Glutamate is the human
brain’s primary excitatory
neurotransmitter.
Postsynaptic glutamate-gated
ion channels allow the
passage of positively charged
ions into the postsynaptic cell and may be further classified as either:
- AMPA receptors
- NMDA receptors
Structure NMDA receptors:
- Ionotropic glutamate receptors
- NMDA receptors require 2 ligands for activation:
glutamate and glycine
tetramer
Composed of 4 distinct subunits:
- 2 glycine binding GluN1 subunits
- 2 glutamate binding GlyN2 subunits
The entire structure of the NMDA receptor is divided into
4 domains:
1. An extracellular amino-terminal domain
2. A ligand-binding domain
3. Pore-forming transmembrane domain
4. Intracellular carboxy-terminal domain
Glutamate releases from presynaptic terminal into the
synaptic cleft at a very high concentration binds to
postsynaptic NMDA receptor induce channel pore
opening = gating
At resting membrane potential:
The inward current through the NMDA receptor is interrupted by the
movement of Mg2+ ions into the channel, where they become lodged.
As the membrane is depolarized:
, The Mg2+ block is displaced from the channel and the current is free to
pass into the cell
- The substantial current through the NMDA receptor requires the
release of glutamate by the presynaptic terminal AND depolarization
of the postsynaptic membrane
The NMDA channels conduct Ca2+ ions
- The magnitude of Ca2+ flux passing through the NMDA receptor
channel specifically signals the level of pre-and postsynaptic
coactivation
Structure AMPA receptors:
The pore forming subunit of AMPAR’s = GluA1-4, consist of 4 domains:
1. N-terminal domain (NTD)
2. Region C-terminal domain (CTD) connects the NTD to the ligand-
gated binding domain (LBD)
3. LBD: upon glutamate binding, the LBD undergoes conformational
changes that result in channel gating
4. Transmembrane domain (TMD): consist of 3 membrane spanning
segments: M1. M3 and M4 and a re-entrant helix loop (M2) forms
an ion channel in the membrane that when open, conducts cations
Function:
AMPA receptors are a key regulatory element of synaptic plasticity = the
ability of synapses to modify their responses according to the inputs they
receive
They mediate fast excitatory synaptic transmission + responsible for the
initial depolarization of the postsynaptic neuron
When glutamate binds to the AMPA receptors, they open and allow Na+ to
enter the neuron depolarizes the neuron