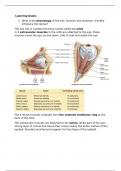
Learning Goals:
1. What is the physiology of the eye, function and anatomy (+briefly
introduce the retina)?
The eye sits in a protective bony socket called the orbit
6 extraocular muscles in the orbit are attached to the eye: these
muscles move the eye up and down, side to side and rotate the eye.
The 4 rectus muscles originate from the common tendinous ring at the
back of the orbit
The extraocular muscles are attached to the sclera: white part of the eye,
strong layer of connective tissue that covers nearly the entire surface of the
eyeball. Provides architectural support for the shape of the eyeball.
,The wall of the eyeball is composed of 3 layers:
1. Fibrous:
The outermost layer, composed of dense avascular connective
tissue. 2 different regions:
1) Sclera: white and opaque, though tendon like protects and
shapes the eyeball and provides a sturdy anchoring site for the
extrinsic eye muscles
2) Cornea
2. Vascular
- Choroid
- Ciliary body
- Iris
- Pupil
3. Inner layers
- Retina
Choroid= layer containing blood vessels that lines the back of the eye and is
located between the retina and the sclera. Separated by these two structures
by Bruch’s membrane
Ciliary body= structure containing muscle
and is located behind the iris. It suspends the
lens in place via suspensory
ligaments/zonules and functions primarily to
control the shape of the lens and produce
aqueous humor.
For distance vision: the muscles relax, which
increases tension on the suspensory
ligaments. This stretches and flattens the lens,
decreasing its focal power
For near vision: the ciliary muscles contract.
This decreases tension of the suspensory
ligaments, causing the lens to relax and become
thicker and more spherical increasing focal
power
, Cornea= the clear front window of the eye, which transmits and focuses
(sharpness or clarity) light into the eye
Composed of 5 histologically layers (superficialdeep)
4. Epithelium: highly innervated by pain fibers
5. Bowman’s membrane
6. Stroma: makes up 90% of the cornea. Composed of bundles of
collagen fibers
7. Descemet’s membrane
8. Endothelium: lines the posterior surface of the cornea
Fovea= the center of the macula which provides the sharp vision. The retina
is thinner in the fovea.
Iris= the colored part of the eye which helps regulate the amount of light
entering the eye. When there is bright light, the iris closes the pupil to let in
less light. And when there is low light, the iris opens up the pupil to let in
more light
The iris contains 2 muscles that can vary the size of the pupil: one makes it
smaller when it contracts, the other makes it larger
Lens= focuses light rays onto the retina. The lens is transparent. Small
fibers: zonules, are attached to the capsule holding the lens, suspending it
from the eye wall. The lens is surrounded by the lens capsule
Macula= the area in the retina that contains special light-sensitive cells. In
the macula these light sensitive cells allow us to see fine details clearly in the
center of our visual field. Distinguished by the relative absence of large blood
vessels improves quality vision
Optic nerve= a bundle of more than a million nerve fibers carrying visual
messages from the retina to the brain.
Pupil= dark center opening in the middle of the iris. Allows light to enter the
eye and reach the retina. It appears dark because of the light-absorbing
pigments in the retina. The pupil changes size to adjust for light available.
Retina= the nerve layer lining the back of the eye. The retina senses light
and creates electrical impulses that are sent through the optic nerve to the
brain
Peripheral retina= provides us with our peripheral (side) vision
1. What is the physiology of the eye, function and anatomy (+briefly
introduce the retina)?
The eye sits in a protective bony socket called the orbit
6 extraocular muscles in the orbit are attached to the eye: these
muscles move the eye up and down, side to side and rotate the eye.
The 4 rectus muscles originate from the common tendinous ring at the
back of the orbit
The extraocular muscles are attached to the sclera: white part of the eye,
strong layer of connective tissue that covers nearly the entire surface of the
eyeball. Provides architectural support for the shape of the eyeball.
,The wall of the eyeball is composed of 3 layers:
1. Fibrous:
The outermost layer, composed of dense avascular connective
tissue. 2 different regions:
1) Sclera: white and opaque, though tendon like protects and
shapes the eyeball and provides a sturdy anchoring site for the
extrinsic eye muscles
2) Cornea
2. Vascular
- Choroid
- Ciliary body
- Iris
- Pupil
3. Inner layers
- Retina
Choroid= layer containing blood vessels that lines the back of the eye and is
located between the retina and the sclera. Separated by these two structures
by Bruch’s membrane
Ciliary body= structure containing muscle
and is located behind the iris. It suspends the
lens in place via suspensory
ligaments/zonules and functions primarily to
control the shape of the lens and produce
aqueous humor.
For distance vision: the muscles relax, which
increases tension on the suspensory
ligaments. This stretches and flattens the lens,
decreasing its focal power
For near vision: the ciliary muscles contract.
This decreases tension of the suspensory
ligaments, causing the lens to relax and become
thicker and more spherical increasing focal
power
, Cornea= the clear front window of the eye, which transmits and focuses
(sharpness or clarity) light into the eye
Composed of 5 histologically layers (superficialdeep)
4. Epithelium: highly innervated by pain fibers
5. Bowman’s membrane
6. Stroma: makes up 90% of the cornea. Composed of bundles of
collagen fibers
7. Descemet’s membrane
8. Endothelium: lines the posterior surface of the cornea
Fovea= the center of the macula which provides the sharp vision. The retina
is thinner in the fovea.
Iris= the colored part of the eye which helps regulate the amount of light
entering the eye. When there is bright light, the iris closes the pupil to let in
less light. And when there is low light, the iris opens up the pupil to let in
more light
The iris contains 2 muscles that can vary the size of the pupil: one makes it
smaller when it contracts, the other makes it larger
Lens= focuses light rays onto the retina. The lens is transparent. Small
fibers: zonules, are attached to the capsule holding the lens, suspending it
from the eye wall. The lens is surrounded by the lens capsule
Macula= the area in the retina that contains special light-sensitive cells. In
the macula these light sensitive cells allow us to see fine details clearly in the
center of our visual field. Distinguished by the relative absence of large blood
vessels improves quality vision
Optic nerve= a bundle of more than a million nerve fibers carrying visual
messages from the retina to the brain.
Pupil= dark center opening in the middle of the iris. Allows light to enter the
eye and reach the retina. It appears dark because of the light-absorbing
pigments in the retina. The pupil changes size to adjust for light available.
Retina= the nerve layer lining the back of the eye. The retina senses light
and creates electrical impulses that are sent through the optic nerve to the
brain
Peripheral retina= provides us with our peripheral (side) vision