Scenario:
A patient develops DVT (deep brain thrombosis) after prolonged bed rest. You need to explain
the role of venous return in preventing blood clots.
Reasearch Questions:
1. Which arteries supply the femoral head and why is blood flow crucial in fractures?
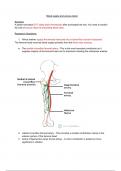
The femoral head receives blood supply primarily from the three main sources:
● The medial circumflex femoral artery - This is the most important contributor as it
supplies majority of the femoral head via it’s branches including the retinacular arteries
2. Lateral circumflex femoral artery - This provides a smaller contribution mainly to the
anterior portion of the femoral head
3. Artery of ligamentum teres (fovea artery) - A minor contributor in adults but more
significant in children
, Why is blood flow crucial in fractures?
Blood flow to the femoral head is vulnerable in fractures as:
● The medial circumflex femoral artery is easily disrupted due to its course along the
femoral neck
● The femoral head has limited collateral circulation meaning damage to the main supply
can lead to avascular necrosis where the bone dies due to lack of blood
● The interscapular location of the femoral neck which makes it more likely that the blood
supply is compromised increasing the risk of nonunion or necrosis.
This is why early diagnosis and management us crucial like joint replacement or surgical fixation
to prevent complications.
2. How does the calf muscle assist venous return?
The calf muscles pump plays a crucial role in venous return by helping blood flow back to the
heart particularly from the lower limb. This is essential as the vines have low pressure and must
work against gravity.