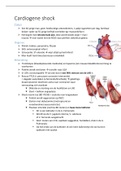
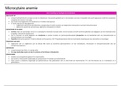
Definition:
An elementary reaction is a single-step chemical reaction that occurs in a single event or collision.
Unlike complex reactions, which involve multiple steps, an elementary reaction directly shows how
reactant
molecules interact to form products.
Characteristics of Elementary Reactions:
1. Single Step: The reaction happens in one step without intermediates.
2. Molecularity: The number of reactant molecules involved determines the reaction type.
3. Rate Law Derived from Stoichiometry: The rate of an elementary reaction can be directly
determined from its
balanced chemical equation.
Types of Elementary Reactions:
1. Unimolecular Reaction (Molecularity = 1):
- A single molecule undergoes transformation.
- Example: O3 -> O2 + O
- Rate Law: Rate = k[O3]
2. Bimolecular Reaction (Molecularity = 2):
- Two reactant molecules collide to form products.
- Example: H2 + I2 -> 2HI
- Rate Law: Rate = k[H2][I2]
3. Termolecular Reaction (Molecularity = 3):
- Three reactant molecules must collide simultaneously.
- Example: 2NO + O2 -> 2NO2
- Rate Law: Rate = k[NO][NO][O2]
- Rare because three-body collisions are unlikely.