Kolb : chapter 15
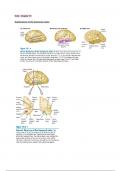
Subdivisions of the temporal cortex
, ● Human temporal regions
○ Lateral surface → auditory
○ Ventral visual stream on the lateral temporal lobe
■ Visual regions → inferotemporal cortex (TE)
● The lateral (sylvian) fissure contains tissue forming the insula
○ Includes gustatory and auditory association cortex
● The superior temporal sulcus (STS) separates the superior and middle temporal gyri and
houses a significant amount of the neocortex
● Medial temporal region = limbic cortex
○ Amygdala and uncus, hippocampus and surrounding cortex (subiculum,
entorhinal cortex, perirhinal cortex) and the fusiform gyrus
● Cortical areas TH and TF = parahippocampal cortex
● Fusiform gyrus and inferior temporal gyrus are functionally part of the lateral temporal
cortex
● Boundary of temporal and parietal lobes = temporal-parietal junction TPJ
○ Region at the end of the sylvian fissure, including ventral regions and adjacent
temporal cortex
○ The TPJ consistently shown to be active in neuroimaging studies investigating
attention, memory, language and social processing
○ TPJ = central to decision making in a social context
Connections of the temporal cortex
● Temporal lobes are rich in internal connections → afferent projections from the sensory
systems and efferent projections to the parietal and frontal association regions, limbic
system, and basal ganglia
● Neocortex of the lobes is connected by the corpus callosum
, ● Medial temporal cortex and amygdala are connected by anterior commissure
Five distinct types of cortical-cortical connections
1. A hierarchical sensory pathway subserves stimulus recognition.
1.1. The hierarchical progression of connections emanates from the primary and
secondary auditory and visual areas, ending in the temporal pole
1.1.1. Visual projections form the ventral stream of visual processing
1.1.2. Auditory projections form a parallel stream of auditory processing
2. A dorsal auditory pathway is concerned with directing movements with respect to
auditory information
2.1. Projecting from the auditory areas to the posterior parietal cortex
2.2. Analogous to part of the dorsal visual pathway (detecting spatial location)
3. A polymodal pathway probably underlies stimulus categorization
3.1. Parallel projections converge in polymodal regions of the superior temporal
sulcus
4. A medial temporal projection crucial to long term memory
4.1. auditory/visual projections go into medial temporal/limbic regions into
hippocampus/amygdala
4.1.1. Hippocampal projection forms the perforant pathway (causes
dysfunction of hippocampal activity when damaged)
5. A frontal lobe projection necessary for various aspects of movement control,
short term memory and affect
5.1. Parallel projections reach the frontal lobe
Anatomy of the ventral stream
● First pathway = a set of subcortical projections from every region of the occipitotemporal
pathway extend to the neostriatum (striatum) (compromising the caudate nucleus +
putamen of the basal ganglia) → network supports types of habit and skill learning
dependent on vision
, ● Second pathway = amygdala bound projections from inferior temporal regions allow
processing of emotionally salient stimuli
● Third pathway = from inferotemporal cortex to ventral striatum → supports the
assignment of stimulus valence (potency)
● Remaining pathways = from inferotemporal cortex to other regions
○ Involved in long term memory, object-reward associations, object working
memory
A theory of temporal lobe function
Temporal lobe houses :
● Primary auditory cortex
● Secondary auditory cortex and visual cortex
● Limbic cortex
● Amygdala and hippocampus
Amygdala = adds affective tone to sensory input and memories
Hippocampus = cortical object recognition and memory, organizing memories of objects in
space
Subdivisions of the temporal cortex
, ● Human temporal regions
○ Lateral surface → auditory
○ Ventral visual stream on the lateral temporal lobe
■ Visual regions → inferotemporal cortex (TE)
● The lateral (sylvian) fissure contains tissue forming the insula
○ Includes gustatory and auditory association cortex
● The superior temporal sulcus (STS) separates the superior and middle temporal gyri and
houses a significant amount of the neocortex
● Medial temporal region = limbic cortex
○ Amygdala and uncus, hippocampus and surrounding cortex (subiculum,
entorhinal cortex, perirhinal cortex) and the fusiform gyrus
● Cortical areas TH and TF = parahippocampal cortex
● Fusiform gyrus and inferior temporal gyrus are functionally part of the lateral temporal
cortex
● Boundary of temporal and parietal lobes = temporal-parietal junction TPJ
○ Region at the end of the sylvian fissure, including ventral regions and adjacent
temporal cortex
○ The TPJ consistently shown to be active in neuroimaging studies investigating
attention, memory, language and social processing
○ TPJ = central to decision making in a social context
Connections of the temporal cortex
● Temporal lobes are rich in internal connections → afferent projections from the sensory
systems and efferent projections to the parietal and frontal association regions, limbic
system, and basal ganglia
● Neocortex of the lobes is connected by the corpus callosum
, ● Medial temporal cortex and amygdala are connected by anterior commissure
Five distinct types of cortical-cortical connections
1. A hierarchical sensory pathway subserves stimulus recognition.
1.1. The hierarchical progression of connections emanates from the primary and
secondary auditory and visual areas, ending in the temporal pole
1.1.1. Visual projections form the ventral stream of visual processing
1.1.2. Auditory projections form a parallel stream of auditory processing
2. A dorsal auditory pathway is concerned with directing movements with respect to
auditory information
2.1. Projecting from the auditory areas to the posterior parietal cortex
2.2. Analogous to part of the dorsal visual pathway (detecting spatial location)
3. A polymodal pathway probably underlies stimulus categorization
3.1. Parallel projections converge in polymodal regions of the superior temporal
sulcus
4. A medial temporal projection crucial to long term memory
4.1. auditory/visual projections go into medial temporal/limbic regions into
hippocampus/amygdala
4.1.1. Hippocampal projection forms the perforant pathway (causes
dysfunction of hippocampal activity when damaged)
5. A frontal lobe projection necessary for various aspects of movement control,
short term memory and affect
5.1. Parallel projections reach the frontal lobe
Anatomy of the ventral stream
● First pathway = a set of subcortical projections from every region of the occipitotemporal
pathway extend to the neostriatum (striatum) (compromising the caudate nucleus +
putamen of the basal ganglia) → network supports types of habit and skill learning
dependent on vision
, ● Second pathway = amygdala bound projections from inferior temporal regions allow
processing of emotionally salient stimuli
● Third pathway = from inferotemporal cortex to ventral striatum → supports the
assignment of stimulus valence (potency)
● Remaining pathways = from inferotemporal cortex to other regions
○ Involved in long term memory, object-reward associations, object working
memory
A theory of temporal lobe function
Temporal lobe houses :
● Primary auditory cortex
● Secondary auditory cortex and visual cortex
● Limbic cortex
● Amygdala and hippocampus
Amygdala = adds affective tone to sensory input and memories
Hippocampus = cortical object recognition and memory, organizing memories of objects in
space