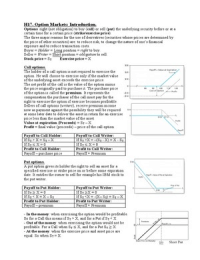
CHAPTER 13 – FISCAL POLICY, DEFICITS AND DEBT
I. FISCAL. POLICY AND THE AS-AD MODEL
Fiscal policy is discretionary (active), and does not activate automatically, independent of
governmental intervention.
Expansionary fiscal policy
Is designed AD, and therefore GDP (and remove
inefficiency/unemployment).
Used to remedy a negative GDP gap – rightward
shift of AD.
a. Government spending
Fiscal policy should move to a government budget
deficit (tax revenues < government spending).
b. Tax
Tax decrease > increase in government spending
necessary to achieve the same rightward shift of
AD.
c. Combination of both.
Contractionary fiscal policy
Is designed to AD, and therefore inflation.
Used to remedy a positive GDP gap (inflation) –
leftward shift of AD.
a. Government spending
Fiscal policy should move to a government budget
surplus (tax revenues > government spending).
b. Tax
Tax increase > decrease in government spending
necessary to achieve the same leftward shift of AD.
c. Combination of both.
II. BUILT-IN STABILITY
To a certain degree, government tax revenues change automatically and in ways that stabilize
the economy over the course of the business cycle.
“Nondiscretionary budgetary policy”Nondiscretionary budgetary policy”
Automatic or built-in stabilizers
- Anything that increases/reduces the budget deficit/
surplus without action by policymakers.
There is a direct relationship between the level of GDP
and tax revenues (see graph):
- Taxes reduce spending and AD.
- Reductions in spending are desirable when the
economy is moving towards inflation (and vice versa).
1
, Economic importance
Built-in stability reduces the severity of business fluctuations. They can only dampen, not
counteract, swings in real GDP.
However:
Fiscal policy – tax rates and government expenditures, or;
Monetary policy – central bank / interest rates;
May still be needed to correct recession or inflation.
III. EVALUATING FISCAL POLICY
Economists use the cyclically adjusted budget to find out whether a government’s
discretionary fiscal policy is:
a. Expansionary
b. Neutral
c. Contractionary
By:
Adjusting actual federal budget deficits and surpluses;
Which will account for the changes in tax revenues that happen automatically whenever
GDP changes.
Comparing actual government spending with the tax revenues that would have
occurred if the economy had achieved full-employment GDP.
IV. PROBLEMS, CRITICISMS AND COMPLICATIONS
Problems of timing
- Recognition lag – the time between the start of a recession and the awareness of people that
it is happening. It sometimes takes months to be able to confidently conclude that a
recession has begun.
- Administrative lag – lag between the time that the need for fiscal action is realized, and
when the necessary action is actually taken.
- Operational lag – lag between the time fiscal action is taken and the time that action starts
affecting the economy.
Future policy reversals
Fiscal policy may fail to achieve its intended purpose if households expect future policy
reversals.
Crowding-out effect
Expansionary fiscal policy:
- May increase the interest rate and reduce
investment spending
Weakening or canceling the stimulus of the
expansionary policy.
Crowding out interest-sensitive consumption
spending.
It is caused by the government’s increased
borrowing to finance its budget deficits/debts.
2
I. FISCAL. POLICY AND THE AS-AD MODEL
Fiscal policy is discretionary (active), and does not activate automatically, independent of
governmental intervention.
Expansionary fiscal policy
Is designed AD, and therefore GDP (and remove
inefficiency/unemployment).
Used to remedy a negative GDP gap – rightward
shift of AD.
a. Government spending
Fiscal policy should move to a government budget
deficit (tax revenues < government spending).
b. Tax
Tax decrease > increase in government spending
necessary to achieve the same rightward shift of
AD.
c. Combination of both.
Contractionary fiscal policy
Is designed to AD, and therefore inflation.
Used to remedy a positive GDP gap (inflation) –
leftward shift of AD.
a. Government spending
Fiscal policy should move to a government budget
surplus (tax revenues > government spending).
b. Tax
Tax increase > decrease in government spending
necessary to achieve the same leftward shift of AD.
c. Combination of both.
II. BUILT-IN STABILITY
To a certain degree, government tax revenues change automatically and in ways that stabilize
the economy over the course of the business cycle.
“Nondiscretionary budgetary policy”Nondiscretionary budgetary policy”
Automatic or built-in stabilizers
- Anything that increases/reduces the budget deficit/
surplus without action by policymakers.
There is a direct relationship between the level of GDP
and tax revenues (see graph):
- Taxes reduce spending and AD.
- Reductions in spending are desirable when the
economy is moving towards inflation (and vice versa).
1
, Economic importance
Built-in stability reduces the severity of business fluctuations. They can only dampen, not
counteract, swings in real GDP.
However:
Fiscal policy – tax rates and government expenditures, or;
Monetary policy – central bank / interest rates;
May still be needed to correct recession or inflation.
III. EVALUATING FISCAL POLICY
Economists use the cyclically adjusted budget to find out whether a government’s
discretionary fiscal policy is:
a. Expansionary
b. Neutral
c. Contractionary
By:
Adjusting actual federal budget deficits and surpluses;
Which will account for the changes in tax revenues that happen automatically whenever
GDP changes.
Comparing actual government spending with the tax revenues that would have
occurred if the economy had achieved full-employment GDP.
IV. PROBLEMS, CRITICISMS AND COMPLICATIONS
Problems of timing
- Recognition lag – the time between the start of a recession and the awareness of people that
it is happening. It sometimes takes months to be able to confidently conclude that a
recession has begun.
- Administrative lag – lag between the time that the need for fiscal action is realized, and
when the necessary action is actually taken.
- Operational lag – lag between the time fiscal action is taken and the time that action starts
affecting the economy.
Future policy reversals
Fiscal policy may fail to achieve its intended purpose if households expect future policy
reversals.
Crowding-out effect
Expansionary fiscal policy:
- May increase the interest rate and reduce
investment spending
Weakening or canceling the stimulus of the
expansionary policy.
Crowding out interest-sensitive consumption
spending.
It is caused by the government’s increased
borrowing to finance its budget deficits/debts.
2