Binary relations
When consider relations from We show this directed graph
discussing relations have - as
as we seen sometimes , we a set can a as
follows
.
S to itself.
V
Instead of R
saying R from S usually say that binary
is a relation 5 to wo is a
1
relation on S
.
L
>
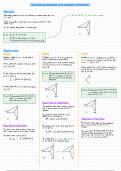
We can represent binary relations as a directed graph. 2 wh
-v
Y
-
X
Example : Let S = Ev ,
w
,
x
, Y, 2)
Let R be a
binary relation on S where
R ((v =
, w) , (v, x) , (2 , 2), (W , v) , (W , 2) (W x) ( -, ) (2
, , , , , 2)]
Properties of relations
Reflexivity Symmetry Transitivity
Informally a relation is
reflexive if every element
is A relation is symmetric if we can
go from one A relation is transitive if
for all s
,
sin S if there is
related to itself. element to another , then we can also go back
.
a path between two elements s and S' , then there
to s
A
binary relation R On a set S is symmetric if and only
is an
edge from s
A binary relation R is reflexive if and
only if for all
if we have for all s, s'ES if (5 5) ER ,
,
then
SES , (5 3) EIR (s' 5) R A relation R S transitive if
E
binary set is and only if
,
,
On a we
have for all s'ES if (5 5) ER s, ,
and (sis") ER
,
then 15 S") ER
,
.
We have
already seen that the identify relation for a Example : The binary relation Ron S =
Ev ,
w
,
x
, y, 2)
set S defined shown is not symmetric (v , X) ER ,
s
is as as
but (X , v) R There are other pairs
((5 5) SxSses]
.
Ig = ,
missing also
V
1
A binary relation R on S is reflexive if and
only if
"
Is &R wh Ev 2)
2 [
Example : The binary relation R on S =
,
W
,
X
, y, shown
is not transitive as (V , W) and (W , v) are in the
relation ,
but (v , v) is not.
Example : The binary relation R on S =
Ev ,
w
,
x
, y, 2) Y
shown is not reflexive as (v , v) &R
,
V
(W w),
R, and (y Y) # R
,
. 1
Symmetric Closure of a
Binary Relation
L
>
V 2 wh
The
symmetric
[
closure allows us to take a relation and
1
add a minimum number of pairs to make it
symmetric .
·
L
>
2 wh Y
Recall that the opposite relation for a
binary
relation R on a set S is defined as
Y · Rop =
((5; 3) =Sx 5/(s s) ,
ER] Transitive Closure of a
Binary Relation
The transitive closure allows us to take a relation and
add number of to make it
Reflexive
a minimum pairs
Closure of a
Binary Relation The symmetric closure of the binary relation R on the
transitive.
Set S is
given by
The reflexive closure allows us to take a relation and
add it The transitive closure of the binary relation R on the set
a minimum number of pairs to make reflexive .
RuRO = Rud(sis)eSxS((s 5) , E
R] S is
given by adding the set of pairs (Si , Sul to R
where S1 , S2 Sn ins with n = 2 such that for
The reflexive closure of R by , ...
is
given
all 1 i < n-1 we have (Si , Sin1) ER
seS]
.
Rulg =
Ru((s s) ,
If a relation R is both reflexive and symmetric ,
We can represent it as an Undirected Graph
A
i V
Z
·
su 3 2 W
y? · Y X