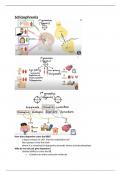
Schizophrenia
How does dopamine cross the BBB?
- L-dopa crossed via LAT1 into the endothelial cell
- then pumps it into the brain
- where it is converted to dopamine aromatic amino acid decarboxylase
Why do we not just give dopamine?
- Limited ability to cross the BB
o Contains an amine and polar molecule
, o BBB resistricts the passage of polar molecules into the brain
- So, we give dopamine precursors
- Which is converted into dopamine when it crosses the BBB
- E.g., L-Dopa
How do we diagnose a patient with Schizophrenia?-use CKS
CKS: positive symptoms: hallucinations and delusions
And negative symptoms: lack of spontaneity and lack of drive and pleasure
May have attention deficit and altered speech and language
Family history
Risk factors look for
Non CKS:
DSM-5
Diagnostic and statistical manual for mental disorders
Outlines specific symptoms to look for
2 theories on the pathology of schizophrenia
- Dopamine hypothesis
- glutamate hypothesis
MOA antipsychotics-UPDATE
Dopamine D2 receptor antagonists on the postsynaptic membrane of dopamine neurons
Increases dopamine in the associative striatum
This reduces the overactivity of dopamine in the brain regions
Associated with hallucinations
Many antipsychotics also have antagonistic effects on serotonin receptors (5HT2A),
histaminergic, cholinergic and adrenergic receptors.
Why do we get lots of side effects from antipsychotics?
- Dopamine blockade can lead to all sorts of side effects
- As there are dopamine receptors in other neural pathways
- There are 4 dopamine pathways all with differing functions
- Also, these antipsychotics may vary in affinities for different neurotransmitter
receptors
o E.g. serotonin, histamine and acetylcholine receptors
o Interactions at these receptors can lead to sedation, weigh gain and
anticholinergic effects
What are some anticholinergic side effects?
- Dry mouth
- Blurred vision
- Constipation
- Urinary retention
- Confusion
- Increased HR
- Dilated pupils
Susceptible genes to schizophrenia + why does this occur?
- KCNH2
- DTNBP2
How does dopamine cross the BBB?
- L-dopa crossed via LAT1 into the endothelial cell
- then pumps it into the brain
- where it is converted to dopamine aromatic amino acid decarboxylase
Why do we not just give dopamine?
- Limited ability to cross the BB
o Contains an amine and polar molecule
, o BBB resistricts the passage of polar molecules into the brain
- So, we give dopamine precursors
- Which is converted into dopamine when it crosses the BBB
- E.g., L-Dopa
How do we diagnose a patient with Schizophrenia?-use CKS
CKS: positive symptoms: hallucinations and delusions
And negative symptoms: lack of spontaneity and lack of drive and pleasure
May have attention deficit and altered speech and language
Family history
Risk factors look for
Non CKS:
DSM-5
Diagnostic and statistical manual for mental disorders
Outlines specific symptoms to look for
2 theories on the pathology of schizophrenia
- Dopamine hypothesis
- glutamate hypothesis
MOA antipsychotics-UPDATE
Dopamine D2 receptor antagonists on the postsynaptic membrane of dopamine neurons
Increases dopamine in the associative striatum
This reduces the overactivity of dopamine in the brain regions
Associated with hallucinations
Many antipsychotics also have antagonistic effects on serotonin receptors (5HT2A),
histaminergic, cholinergic and adrenergic receptors.
Why do we get lots of side effects from antipsychotics?
- Dopamine blockade can lead to all sorts of side effects
- As there are dopamine receptors in other neural pathways
- There are 4 dopamine pathways all with differing functions
- Also, these antipsychotics may vary in affinities for different neurotransmitter
receptors
o E.g. serotonin, histamine and acetylcholine receptors
o Interactions at these receptors can lead to sedation, weigh gain and
anticholinergic effects
What are some anticholinergic side effects?
- Dry mouth
- Blurred vision
- Constipation
- Urinary retention
- Confusion
- Increased HR
- Dilated pupils
Susceptible genes to schizophrenia + why does this occur?
- KCNH2
- DTNBP2