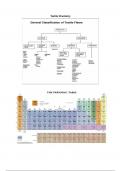
Textile Chemistry
,cotton fabric → yarns → fibres → micro fibres →polymers (cellulose) → glucose molecules → atoms
Three
atomic nucleus:
protons and neutrons, surrounded by electrons
Protons → positively charged +
Neutrons → no charge / neutral
Electrons → negatively charged -
Atoms are electrically neutral !!
The mass of protons, electrons and neutrons:
u = atomic mass unit
Protons → 1 u
Neutrons → 1 u
Electrons → 0 u
Atomic number = number of protons (can be found in periodic table)
Atomic weight = Mass number = total number of protons AND neutrons in an atom (also
called atomic mass number)
If you want to calculate the amount of neutrons → atomic mass - atomic number = neutrons
in atom
1
, Ions
Ions have the same number of protons, but a different number of electrons.
Number of protons can be found in the table.
For instance, CI → 17 protons. In the image above, the white balls around the one red (the
protons) are the electrons. So count these,
If you have more electrons than protons → negative charge → Anion
If you have less electrons than protons → positive charge → Cation
Isotopes have the same number of protons but
a different number of neutrons.
Same atomic number, different atomic mass
because the neutrons differ.
Eg. Carbon-12, Carbon-14 etc
The number at the bottom is the
number of protons. (8 in this case)
The top number (above the O) is the
mass.
2
,cotton fabric → yarns → fibres → micro fibres →polymers (cellulose) → glucose molecules → atoms
Three
atomic nucleus:
protons and neutrons, surrounded by electrons
Protons → positively charged +
Neutrons → no charge / neutral
Electrons → negatively charged -
Atoms are electrically neutral !!
The mass of protons, electrons and neutrons:
u = atomic mass unit
Protons → 1 u
Neutrons → 1 u
Electrons → 0 u
Atomic number = number of protons (can be found in periodic table)
Atomic weight = Mass number = total number of protons AND neutrons in an atom (also
called atomic mass number)
If you want to calculate the amount of neutrons → atomic mass - atomic number = neutrons
in atom
1
, Ions
Ions have the same number of protons, but a different number of electrons.
Number of protons can be found in the table.
For instance, CI → 17 protons. In the image above, the white balls around the one red (the
protons) are the electrons. So count these,
If you have more electrons than protons → negative charge → Anion
If you have less electrons than protons → positive charge → Cation
Isotopes have the same number of protons but
a different number of neutrons.
Same atomic number, different atomic mass
because the neutrons differ.
Eg. Carbon-12, Carbon-14 etc
The number at the bottom is the
number of protons. (8 in this case)
The top number (above the O) is the
mass.
2