IAP 100 Test 5: Nervous System and Special Senses
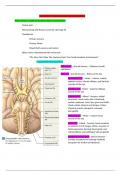
There will be a couple of questions about cranial nerves.
Twelve pairs
Named along with Roman numerals I through XII
Classified as:
Primary sensory
Primary Moter
Mixed (both sensory and motor)
Often names remembered with mnemonic
“Oh, Once One Takes The Anatomy Final, Very Good Vacations Are Heavenly”
Cranial Nerves and Functions
Olfactory (I) – Special Sensory – Olfactory (smell)
epithelium
Optic (II) – Special Sensory – Retina of the eye
Oculomotor (III) – Motor – Inferior, medial,
superior rectus, inferior oblique, and intrinsic
muscles of the eye
Trochlear (IV) – Moter – Superior oblique
muscle of the eye
Trigeminal (V) – Mixed – Sensory: orbital
structures, nasal cavity, skin of forehead,
eyelids, eyebrows, nose, lips, gums and teeth;
cheek, palate, pharynx and tongue. Moter:
Chewing muscles (temporal, masseter,
pterygoids)
Abducens (VI) – Motor – Lateral rectus
muscle of the eye
Facial (VII) – Mixed – Sensory: taste receptors
on anterior 2/3 of tongue. Moter: muscles of
facial expression, lacrimal (tear) gland, and
submandibular and sublingual salivary glands
Vestibulocochlear (VIII) – Special Sensory –
Cochlea (receptors for hearing) Vestibule
(receptors for motion and balance)
, Glossopharyngeal (IX) – Mixed – Sensory: posterior 1/3 of tongue; pharynx and palate; receptors
for blood pressure, pH, oxygen, and carbon dioxide
Vagus (X) – Mixed – Sensory: pharynx, auricle and external acoustic meatus, diaphragm, visceral
organs in thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities. Motor: Palatal and pharyngeal muscles and
visceral organs in thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities
Accessory (XI) – Motor – Voluntary muscles of palate, pharynx and larynx (with vagus nerve);
sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles
Hypoglossal (XII) – Motor – Tongue muscles
Know the concepts of continuous vs saltatory propagation
Continuous Propagation
Occurs in unmyelinated fibers and is relatively slow ( about 1 meter a second)
Each successive area of axon has to depolarize
Saltatory Propagation
Occurs in myelinated axons and is much faster ( from 18-140 meters per second)
Myelin
Composed of fat, so it insulates areas of the axon
Voltage Na+ gates underneath myelin do not open
Myelin blocks the flow of Na+ ions across the membrane
Depolarization of membrane occurs only at Nodes of Ranvier
Know the difference between general and special senses
General Senses
Receptors occur throughout the body
GENERAL SENSES include:
Temperature
Pain
Touch
Pressure
Vibration
PROPRIOCEPTION (body position)
, Special Senses
Receptors concentrated in the sense organs and located in the head
SPECIAL SENSES include:
OLFACTION (smell)
GUSTATION (taste)
VISION
EQUILIBRIUM (balance)
HEARING
Understand the differences between rods and cones.
RODS
Very light-sensitive and enable us to see in dim light
Do not discriminate among colors of light
Found on periphery of retinal surface
CONES
Detect color
Give sharper, clearer images, but require brighter light
Most are found in the MACULA, the center of which is the FOVEA CENTRALIS
Site of sharpest vision
How does sensory information travel to the brain?
Rods and cones synapse with BIPOLAR CELLS, which synapse with GANGLION CELLS
Axons of ganglion cells deliver sensory information to the brain
HORIXONTAL CELLS and AMACRINE CELLS
Regulate communication between photoreceptors and ganglion cells
Adjust sensitivity of the retina
There will be a couple of questions about cranial nerves.
Twelve pairs
Named along with Roman numerals I through XII
Classified as:
Primary sensory
Primary Moter
Mixed (both sensory and motor)
Often names remembered with mnemonic
“Oh, Once One Takes The Anatomy Final, Very Good Vacations Are Heavenly”
Cranial Nerves and Functions
Olfactory (I) – Special Sensory – Olfactory (smell)
epithelium
Optic (II) – Special Sensory – Retina of the eye
Oculomotor (III) – Motor – Inferior, medial,
superior rectus, inferior oblique, and intrinsic
muscles of the eye
Trochlear (IV) – Moter – Superior oblique
muscle of the eye
Trigeminal (V) – Mixed – Sensory: orbital
structures, nasal cavity, skin of forehead,
eyelids, eyebrows, nose, lips, gums and teeth;
cheek, palate, pharynx and tongue. Moter:
Chewing muscles (temporal, masseter,
pterygoids)
Abducens (VI) – Motor – Lateral rectus
muscle of the eye
Facial (VII) – Mixed – Sensory: taste receptors
on anterior 2/3 of tongue. Moter: muscles of
facial expression, lacrimal (tear) gland, and
submandibular and sublingual salivary glands
Vestibulocochlear (VIII) – Special Sensory –
Cochlea (receptors for hearing) Vestibule
(receptors for motion and balance)
, Glossopharyngeal (IX) – Mixed – Sensory: posterior 1/3 of tongue; pharynx and palate; receptors
for blood pressure, pH, oxygen, and carbon dioxide
Vagus (X) – Mixed – Sensory: pharynx, auricle and external acoustic meatus, diaphragm, visceral
organs in thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities. Motor: Palatal and pharyngeal muscles and
visceral organs in thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities
Accessory (XI) – Motor – Voluntary muscles of palate, pharynx and larynx (with vagus nerve);
sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles
Hypoglossal (XII) – Motor – Tongue muscles
Know the concepts of continuous vs saltatory propagation
Continuous Propagation
Occurs in unmyelinated fibers and is relatively slow ( about 1 meter a second)
Each successive area of axon has to depolarize
Saltatory Propagation
Occurs in myelinated axons and is much faster ( from 18-140 meters per second)
Myelin
Composed of fat, so it insulates areas of the axon
Voltage Na+ gates underneath myelin do not open
Myelin blocks the flow of Na+ ions across the membrane
Depolarization of membrane occurs only at Nodes of Ranvier
Know the difference between general and special senses
General Senses
Receptors occur throughout the body
GENERAL SENSES include:
Temperature
Pain
Touch
Pressure
Vibration
PROPRIOCEPTION (body position)
, Special Senses
Receptors concentrated in the sense organs and located in the head
SPECIAL SENSES include:
OLFACTION (smell)
GUSTATION (taste)
VISION
EQUILIBRIUM (balance)
HEARING
Understand the differences between rods and cones.
RODS
Very light-sensitive and enable us to see in dim light
Do not discriminate among colors of light
Found on periphery of retinal surface
CONES
Detect color
Give sharper, clearer images, but require brighter light
Most are found in the MACULA, the center of which is the FOVEA CENTRALIS
Site of sharpest vision
How does sensory information travel to the brain?
Rods and cones synapse with BIPOLAR CELLS, which synapse with GANGLION CELLS
Axons of ganglion cells deliver sensory information to the brain
HORIXONTAL CELLS and AMACRINE CELLS
Regulate communication between photoreceptors and ganglion cells
Adjust sensitivity of the retina