Summary Translational Radiopharmaceutical Sciences
Lecture 1 : Introduction
Molecular the visualisation characterisation and measurement of biological processes the morecular
imaging at
:
,
and cellular level humans and other
in .
living systems
->
application of radionuclides to medicine
modalities
Imaging
Radiography
First medical
imaging technology
·
Transmission of
X-rays from source to detector
Attenuation by absorption and scattering
Image is a picture of X-ray distribution
computed Tomography
X-ray transmission at a large number of angles
·
Tomography spatially : resolved display of
anatomy
.
Advantages
·
-High spatial resolution
Bone and tumor
imaging
-
-Anatomic
imaging
Disadvantages
·
-
Radiation exposure
-Limited 'Molecular' applications
-
Limited soft tissue resolution
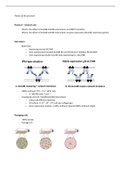
MRI
·
Tomographic imaging
·
How does it Work
-
All protons have a spir
introduced and the protons aligh with that field
A
strong Magnetic field is
-
-
radiofrequency puise disrupts
A the proton and forces it into another direction (go' or 100
-The proton is pushed so the protons realligh with the field
against its nature ,
magnetic
-
This releases
electromagnetic energy ,
is detected by MRE
Tissues differentiated by how the proton releases the
are
quickly energy
-
-> difference in local
magnetic properties
·
Radio Waves
Advantages
·
-High Spatial resolution
combines morphologic and functional
imaging
-
·
Disadvantages
-Low
sensitivity
-Long scan and postprocessing time
-restricted in Vivo delivery
,
,
,
Lecture 1 : Introduction
Molecular the visualisation characterisation and measurement of biological processes the morecular
imaging at
:
,
and cellular level humans and other
in .
living systems
->
application of radionuclides to medicine
modalities
Imaging
Radiography
First medical
imaging technology
·
Transmission of
X-rays from source to detector
Attenuation by absorption and scattering
Image is a picture of X-ray distribution
computed Tomography
X-ray transmission at a large number of angles
·
Tomography spatially : resolved display of
anatomy
.
Advantages
·
-High spatial resolution
Bone and tumor
imaging
-
-Anatomic
imaging
Disadvantages
·
-
Radiation exposure
-Limited 'Molecular' applications
-
Limited soft tissue resolution
MRI
·
Tomographic imaging
·
How does it Work
-
All protons have a spir
introduced and the protons aligh with that field
A
strong Magnetic field is
-
-
radiofrequency puise disrupts
A the proton and forces it into another direction (go' or 100
-The proton is pushed so the protons realligh with the field
against its nature ,
magnetic
-
This releases
electromagnetic energy ,
is detected by MRE
Tissues differentiated by how the proton releases the
are
quickly energy
-
-> difference in local
magnetic properties
·
Radio Waves
Advantages
·
-High Spatial resolution
combines morphologic and functional
imaging
-
·
Disadvantages
-Low
sensitivity
-Long scan and postprocessing time
-restricted in Vivo delivery
,
,
,