TOPIC 5
PLANT TISSUE
Tissue - group of similar cells with the same structure performing a similar functions/ are
specialised to perform certain functions
Organism - a complex structure which is made up of individual cells, organised into
tissues, organs and systems
There are 5 types:
1. Epidermis (protection)
2. Parenchyma (storage)
3. Collenchyma and sclerenchyma (strength+support)
4. Xylem and phloem ( transport)
5. Meristematic (ends of roots, stems, leaves)
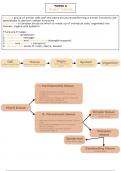
Cell Tissue Organ System
Number of similar cells Number of different tissues
Number of different
Number of systems
Organism
organs
1. Meristematic tissue
• Actively dividing cells (mitosis)
• Usually found at root and shoot tips (apical
meristems)
• Responsible for increase in girth of roots and
stems (secondary meristems)
• Eventually forms permeant tissue
Plant tissue
Simple tissue
2. Permanent tissue Parenchyma, collenchyma,
sclerenchyma
• Cells aren't actively dividing for growth, only for
repair
• Structurally specialised to form to perform
speci
• Found throughout the plant except in
meristematic regions
Complex
tissue
Epidermal
Roots, stems, leaves
Conducting tissue
Phloem, xylem
, PERMANENT TISSUES:
COMPLEX TISSUE
1. Epidermis
Location:
Find as the outermost covering of roots, stems, leaves
Appearance:
• Single of cells
• Cells are thin walled and brick shaped
Function
• Provides inner tissues with protection
1. In leaves and stem:
Structure:
• No intercellular air-spaces (tightly packed)
• Tissue is covered by a cuticle which is waxy and transparent
• Have specialised epidermal cell called the guard cell (surrounds stomata, kidney
shaped, have chloroplasts)
Function:
• Controls opening and closing of stomata
• Stomata allows for the entry and exit of gases
• Waxy cuticles:
• Reduce the loss of water vapour
• Allow sunlight to pass through for photosynthesis
• Protects against infection by viruses, bacteria and fungi
• Prevent loss of water from within
Root hair and stomata are
Stomata: modi ed epidermis
• Formed by 2 guard cells
• Open during day (absorbs CO2), closed at night (prevents water loss)
• Performs gaseous exchange and transpiration
• Regulates water
2. In roots:
Structure:
• Epidermis of root has specialised cell called a root hair (epidermal with elongated
extension)
• No cuticle present
• Unicellular
Function:
• Root hair increases surface area to increase absorption of water and mineral salts
fi
PLANT TISSUE
Tissue - group of similar cells with the same structure performing a similar functions/ are
specialised to perform certain functions
Organism - a complex structure which is made up of individual cells, organised into
tissues, organs and systems
There are 5 types:
1. Epidermis (protection)
2. Parenchyma (storage)
3. Collenchyma and sclerenchyma (strength+support)
4. Xylem and phloem ( transport)
5. Meristematic (ends of roots, stems, leaves)
Cell Tissue Organ System
Number of similar cells Number of different tissues
Number of different
Number of systems
Organism
organs
1. Meristematic tissue
• Actively dividing cells (mitosis)
• Usually found at root and shoot tips (apical
meristems)
• Responsible for increase in girth of roots and
stems (secondary meristems)
• Eventually forms permeant tissue
Plant tissue
Simple tissue
2. Permanent tissue Parenchyma, collenchyma,
sclerenchyma
• Cells aren't actively dividing for growth, only for
repair
• Structurally specialised to form to perform
speci
• Found throughout the plant except in
meristematic regions
Complex
tissue
Epidermal
Roots, stems, leaves
Conducting tissue
Phloem, xylem
, PERMANENT TISSUES:
COMPLEX TISSUE
1. Epidermis
Location:
Find as the outermost covering of roots, stems, leaves
Appearance:
• Single of cells
• Cells are thin walled and brick shaped
Function
• Provides inner tissues with protection
1. In leaves and stem:
Structure:
• No intercellular air-spaces (tightly packed)
• Tissue is covered by a cuticle which is waxy and transparent
• Have specialised epidermal cell called the guard cell (surrounds stomata, kidney
shaped, have chloroplasts)
Function:
• Controls opening and closing of stomata
• Stomata allows for the entry and exit of gases
• Waxy cuticles:
• Reduce the loss of water vapour
• Allow sunlight to pass through for photosynthesis
• Protects against infection by viruses, bacteria and fungi
• Prevent loss of water from within
Root hair and stomata are
Stomata: modi ed epidermis
• Formed by 2 guard cells
• Open during day (absorbs CO2), closed at night (prevents water loss)
• Performs gaseous exchange and transpiration
• Regulates water
2. In roots:
Structure:
• Epidermis of root has specialised cell called a root hair (epidermal with elongated
extension)
• No cuticle present
• Unicellular
Function:
• Root hair increases surface area to increase absorption of water and mineral salts
fi