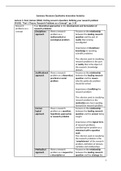
Case 5 Set point
Learning goals:
75% of energy gets lost via heat. So if you ride on a bike at 100 watt for 45 minutes. You actually
produce 100 x 4 watt energy. Times 60*45s = 1440000 joules = 1440 kjoules.
1080 kjoules
Divide joules by 4.184 to get calories
What are the components of energy expenditure?
o what influences energy expenditure and how is it regulated? (BMR +SMR)
Energy expenditure is measured to asses metabolic needs, fuel utilisation and the thermic
effect of food, drinks, drugs and emotional components
Total daily energy expenditure, TEE: Whole body consumption of O2 and CO2. Is
measured from oxidation of fuels (average daily…
o Sleeping metabolic rate
o Energy cost of arousal
o Thermic effect of food
o Activity-induced energy expenditure
Basal metabolic rate, BMR: The energy expended when an individual is lying at
complete rest. Approx. 60% of the total daily energy expenditure. (indirect
calorimetry, respiratory chamber)
o BMR is higher in females in the luteal phase compared to the follicular phase
o FFM is the most important determinant of BMR, therefore it is higher in men
o Sleeping metabolic rate: Energy expended when an individual is sleeping.
Measure during 3-6 am, lowest activity hours. Difference BMR and SMR is 5%
o Arousal: Being awake
Resting energy expenditure: The energy in subjects at rest post-absorptive state.
Around 10% of BMR
Activity thermogenesis/diet-induced energy expenditure: The increase in energy
expenditure associated with digestion, absorption and storage of food. Around 10%
of total daily expenditure.
o Non-exercise activity thermogenesis, NEAT: The combined energy costs of
the physical activities of daily living
o Activity induced energy expenditure: Movement produced by skeletal
muscles, resulting in energy expenditure
o Formula to measure total
o ADMR * 0.9 = MR…
There are 5 important factors that impact the total daily energy expenditure (TDEE). TDEE is
the number of calories burned in a given day.
- Physical activity:
o Extra energy burned by being physically active
o Accounts for 15 to 30% of TDEE
- Diet-related thermogenesis: Refers to the additional calories burned when eating a
meal or snack. Accounts for 10-30% of TDEE. Eating more protein requires more
energy to digest
- Climate and temperature: Can increase or decrease TDEE. Both higher and lower
temperatures boost resting metabolic rate and increase calorie burn
Learning goals:
75% of energy gets lost via heat. So if you ride on a bike at 100 watt for 45 minutes. You actually
produce 100 x 4 watt energy. Times 60*45s = 1440000 joules = 1440 kjoules.
1080 kjoules
Divide joules by 4.184 to get calories
What are the components of energy expenditure?
o what influences energy expenditure and how is it regulated? (BMR +SMR)
Energy expenditure is measured to asses metabolic needs, fuel utilisation and the thermic
effect of food, drinks, drugs and emotional components
Total daily energy expenditure, TEE: Whole body consumption of O2 and CO2. Is
measured from oxidation of fuels (average daily…
o Sleeping metabolic rate
o Energy cost of arousal
o Thermic effect of food
o Activity-induced energy expenditure
Basal metabolic rate, BMR: The energy expended when an individual is lying at
complete rest. Approx. 60% of the total daily energy expenditure. (indirect
calorimetry, respiratory chamber)
o BMR is higher in females in the luteal phase compared to the follicular phase
o FFM is the most important determinant of BMR, therefore it is higher in men
o Sleeping metabolic rate: Energy expended when an individual is sleeping.
Measure during 3-6 am, lowest activity hours. Difference BMR and SMR is 5%
o Arousal: Being awake
Resting energy expenditure: The energy in subjects at rest post-absorptive state.
Around 10% of BMR
Activity thermogenesis/diet-induced energy expenditure: The increase in energy
expenditure associated with digestion, absorption and storage of food. Around 10%
of total daily expenditure.
o Non-exercise activity thermogenesis, NEAT: The combined energy costs of
the physical activities of daily living
o Activity induced energy expenditure: Movement produced by skeletal
muscles, resulting in energy expenditure
o Formula to measure total
o ADMR * 0.9 = MR…
There are 5 important factors that impact the total daily energy expenditure (TDEE). TDEE is
the number of calories burned in a given day.
- Physical activity:
o Extra energy burned by being physically active
o Accounts for 15 to 30% of TDEE
- Diet-related thermogenesis: Refers to the additional calories burned when eating a
meal or snack. Accounts for 10-30% of TDEE. Eating more protein requires more
energy to digest
- Climate and temperature: Can increase or decrease TDEE. Both higher and lower
temperatures boost resting metabolic rate and increase calorie burn