LECTURE 1 – SUPPLY AND DEMAND
Economics studies the functioning of ‘economies’, in particular market economies. A market
economy is an economy in which decisions about production and consumption are
decentralized and made by many firms and individuals. Adam Smith’s invisible hand:
individuals pursuing their own interests often promote the interest of society as a whole.
Microeconomics
Microeconomics studies how firms and individuals make decisions and how they interact
(for example, in competitive markets). Market failures can happen, the questions then are
‘When does the invisible hand not work?’ and ‘How to intervene to solve market failures?’.
This happens in market structures other than competitive markets.
Macroeconomics
Macroeconomics is concerned with the overall functioning of the economy in the aggregate
(GDP, inflation, etc.), with overall ups and downs such as recessions, economic growth etc.
The demand curve
The demand curve shows how much people are willing to buy/demand at different prices;
relationship between demand and price.
o Shift of the demand curve: change in the quantity demanded at any given price
(keeping the price constant). This just means an increase or decrease in demand. For
example; people buying more roses on Valentine’s Day.
Factors that cause the demand curve to shift:
o Changes in tastes
o Changes in the prices of related goods
~ Substitutes: rise in price of good 1 increases demand for good 2.
~ Complements: rise in price of good 1 decreases demand for good 2.
o Changes in income:
~ Normal goods: rise in income increases demand
~ Inferior goods: rise in income decreases demand
o Changes in expectations
o Changes in number of consumers
o Other: all factors affecting the willingness to pay of consumers.
o Movement along demand curve: a change in the quantity demanded arising from a
change in the price. For example; more carpooling due to rising car prices.
1
, This picture shows the difference of
shift of the demand curve vs.
movement along the demand curve.
Consumer surplus & the demand curve
How much do buyers on a market gain from the existence of the market (welfare)?
Individual consumer surplus = the net gain to an individual buyer from the purchase of a
good. It is equal to the difference between the buyer’s willingness to pay and the price paid.
Total consumer surplus = the sum of the individual consumer surpluses of all the buyers of a
good.
The total consumer surplus generated by
purchases of a good at a given price is
equal to the area below the demand curve
but above that price (as you can see here
in this picture on the right).
A decrease in price increases the
consumer surplus!! The consumer pays a
lower price and is thus better off.
The supply curve
The supply curve shows how much people are willing to sell/supply at different prices; it
shows the relationship between the supplied quantity and the price.
o Shift in the supply curve: change in the quantity supplied at any given price (the
price keeps constant). For example; strawberry farmers open roadside stands during
harvest season.
Factors that cause the supply curve to shift:
o Changes in tastes
o Changes in input prices (costlier = less supply)
~ An input is a good that is used to produce another good.
o Changes in technology
~ Turn inputs into output more efficiently
o Changes in expectations
~ Expect stock price to rise = less supplied
o Other: weather/climate; number of producers; factors that affect the willingness
to sell.
2
, o Movement along supply curve: change in the quantity supplied as a result of a
change in the price. For example; more people put their house for sale when house
prices rise.
Producer surplus & the supply curve
How much do sellers on a market gain from the existence of the market (welfare)?
Individual producer surplus is the net gain to a seller from selling a good. It is equal to the
difference between the price received and the willingness to sell / opportunity costs.
~ Opportunity costs are the costs of any activity measured in terms of the value of the
best alternative that is not chosen.
Total producer surplus in a market is the sum of the individual producer surpluses of all the
sellers of a good.
The total producer surplus from sales of a
good at a given price is the area above the
supply curve but below that price.
A rise in price increases the producer
surplus!
Market equilibrium
If the price is above its equilibrium level, this creates excess supply. Moreover, this creates a
surplus. But there is excess supply now, so there is an incentive to reduce the price.
If the price is below its equilibrium level, this creates excess demand: shortage. There is an
excess demand so there is an incentive to increase the price. The market price now moves
towards the equilibrium price.
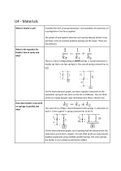
Supply and demand equations
Suppose the demand function is giving by Pd = -0.05Qd + 4 and the supply function is given
by Ps = 0.05Qs. If you want to determine the equilibrium price, you have to say demand is
equal to supply:
-0.05Q + 4 = 0.05Q So, now we know the quantity (Q) is 40. You determine
-0.01Q = -4 the equilibrium price by filing this in the formula:
Q = 40 P = 0.05 x 40 P=2
3