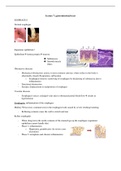
ESOPHAGUS
Normal esophagus
Squamous epithelium!
Epithelium→ lamina propria→ mucosa
➔ Submucosa
➔ Smooth muscle
fibers
Obstructive diseases
- Mechanical obstruction: atresia is most common (atresia= when orifice in the body is
abnormally closed)→aspiration, suffocation
o Esophageal stenosis: narrowing of esophagus by thickening of submucosa due to
inflammation
- Functional obstruction
- Ectopia: displacement or malposition of esophagus
Vascular diseases
- Esophageal varices: enlarged veins due to obstructed portal blood flow→ results in
hypertension
Esophagitis: inflammation of the esophagus
Mallory Weiss tears: common tears in the esophageal wall caused by severe retching/vomiting
- Refluxing contents cause the wall to stretch and tear
Reflux esophagitis
- When (long term) the acidic contents of the stomach go up the esophagus (squamous
epithelium cannot handle this)
- Phase 1: inflammation
o Hyperemia, granulocytes (in severe cases
ulceration)
- Phase 2: metaplasia and chronic inflammation
,Barrett esophagus
- Complication of chronic GERD,
characterized by intestinal
metaplasia
o Intestinal metaplasia
▪ Squamous cells of
esophagus are
replaced with
intestinal type
epithelium
• Glandular structures
Cancer
Development of esophageal carcinoma (reminder: carcinoma= malignant cancer arising in epithelial
tissue/lining of organs)
1. Esophagitis→ intestinal metaplasia→ dysplasia→adenocarcinoma (Barrett carcinoma)
2. Dysplasia→ squamous cell carcinoma
Adenocarcinoma (Barrett carcinoma): neoplasia of epithelial tissue with gland-like pattern, arises after
long term gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
Squamous cell carcinoma: associated with alcohol and tobacco use and poverty
Adenocarcinoma in esophagus is more common than the squamous cell carcinoma
- You would think that because the esophagus has squamous epithelium, the squamous cell
carcinoma would have a higher prevalence.
- However, due to intestinal metaplasia as a precursor for the adenocarcinoma, the
adenocarcinoma has a higher prevalence
Esophageal carcinoma: predisposing factors
- Squamous cell carcinoma
o Smoking
o Alcohol
o Achalasia
o Stricture
- Adenocarcinoma
o Reflux esophagitis
o Intestinal metaplasia
,Dysplasia: presence of abnormal cells within a tissue/organ
(precursor of cancer)
- If inflammation continues molecular changes can occur
- Changes in morphology
- Cytonuclear atypia
o Large nuclei
o Irregular shape of nuclei
o Coarse chromatin pattern
Dysplasia of squamous epithelium
- Right picture: large nuclei and not a lot of differentiation
- As long as it’s not invading→dysplasia (and not carcinoma)
When it starts to invade→ squamous cell carcinoma
- Areas of tumor cells (blueish) infiltrate in deeper walls of the esophagus
STOMACH
Normal stomach
, Anatomy of the stomach: 4 main regions
- Cardia
o Lined by mainly foveolar cells (mucin secreting) that form shallow
glands
- Fundus
o Parietal cells
o Cells contain chief cells (produce and secrete digestive enzymes)
- Body
o Parietal cells
o Cells contain chief cells (produce and secrete digestive enzymes)
- Antrum (part of pylorus which connects to the body of the stomach)
o Glands contain endocrine cells (G cells)
Gastric mucosa
- Foveolar layer: mucus production
- Glandular layer consists of multiple cell types
- Smooth muscle: muscularis mucosae
Histology of the body (of the stomach)
- 2 most important types of cells in corpus part of the stomach
o Parietal cells (pink in histology picture)
▪ Acid production
▪ Intrinsic factor production
• Important protein
• Binds to vitamin B12
• Without intrinsic
factor→ no intake B12
o Chief cells (blue in histology picture)
▪ Pepsinogen production
• Protein important for
digestion of food
• Breaks up into smaller molecules when in contact with acid fluid in
stomach
Histology antrum of stomach: lower part of the stomach
- Same foveolar lining as corpus
- Glandular layer differs
o Cells more pale
o No parietal and chief cells
o More mucus producing cells with
antibacterial functions
o Hormone producing cells
▪ Hard to point out in histological
slide
▪ Important one: gastrin
• Protein that stimulates production of acidic fluid by parietal cells
Gastritis: inflammation of the gastric mucosa