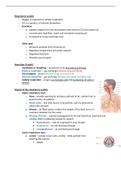
Respiratory system
- Oxygen is required for cellular respiration
- CO2 is a product of nutrient breakdown
- Functions:
o Obtains oxygen from the atmosphere and removes CO2 from body cell
o Consists tube that filter, warm and moisturize incoming air
o Transport air to gas exchange area
- Other jobs:
o Removes particles from incoming air
o Regulates temperature and water content
o Regulates blood pH
o Provides vocal sounds
How does it work?
- Ventilation or breathing – movement of air into and out of lungs
- External respiration – gas exchange between lung and blood
- Gas transport – occurs between lungs and body cells
- Internal respiration – gas exchange between the blood and body cells
- Cellular respiration – oxygen use by body cells and production of carbon
dioxide
Organs of the respiratory system
- Upper respiratory tract
o Nose – provide opening for entrance and exit of air; contain hair to
prevent entry of particles
o Nasal cavity – line with mucus, trap particle, carry to pharynx by
cilia to the stomach
o Sinuses – air filled spaces; reduce the weight of the skull, serve as
resonant chambers for the voice
o Pharynx (Throat) – common passageway for air and food from nasal and oral
cavities; Aids in producing sounds for speech
Nasopharynx – only air supposed to pass though
Oropharynx – air and food pass though
Laryngopharynx – air and food pass though
- Lower respiratory tract
o Larynx – contain vocal cords, sorting – keep particle from
entering the trachea
Glottis
, True vocal cords and opening between them
There are 2 vocal cords
False vocal cords – No sound production
True vocal cords – Sound production
Larger cartilages of the larynx:
Thyroid cartilage (Adam’s apple)
Cricoid cartilage
Epiglottic cartilage
o Trachea
Splits into right and left primary bronchi
Inner wall is lined with ciliated mucous membrane with
many goblet cells
Support by 20 incomplete (C-shaped) cartilaginous rings that
keep the airway open
o Bronchial tree
Main bronchi – first branches directly off the trachea
Lobar bronchi – branches of the main bronchi
Segmental bronchi
Bronchioles – absent cartilage
Terminal bronchioles – smallest bronchioles that conduct air
Respiratory bronchioles
Alveolar ducts – branch off respiratory bronchioles
Alveolar sacs – consist of air sacs called alveoli
Alveoli – sites of gas exchange between air and blood
o Lungs
Soft, spongy, cone shaped organs of the respiratory system
Separated medially by the mediastinum and enclosed by the diaphragm
and thoracic cage
Occupy most thoracic cavity
Right lungs have 3 lobes and left has 2 lobes
Each lung containers air passages, alveoli, nerves, blood vessels,
lymphatic vessels, and connective tissues
The pleura:
A double layered serous membrane
Visceral pleura: inner layer; attached to the surface of each lung,
touching the organ
- Oxygen is required for cellular respiration
- CO2 is a product of nutrient breakdown
- Functions:
o Obtains oxygen from the atmosphere and removes CO2 from body cell
o Consists tube that filter, warm and moisturize incoming air
o Transport air to gas exchange area
- Other jobs:
o Removes particles from incoming air
o Regulates temperature and water content
o Regulates blood pH
o Provides vocal sounds
How does it work?
- Ventilation or breathing – movement of air into and out of lungs
- External respiration – gas exchange between lung and blood
- Gas transport – occurs between lungs and body cells
- Internal respiration – gas exchange between the blood and body cells
- Cellular respiration – oxygen use by body cells and production of carbon
dioxide
Organs of the respiratory system
- Upper respiratory tract
o Nose – provide opening for entrance and exit of air; contain hair to
prevent entry of particles
o Nasal cavity – line with mucus, trap particle, carry to pharynx by
cilia to the stomach
o Sinuses – air filled spaces; reduce the weight of the skull, serve as
resonant chambers for the voice
o Pharynx (Throat) – common passageway for air and food from nasal and oral
cavities; Aids in producing sounds for speech
Nasopharynx – only air supposed to pass though
Oropharynx – air and food pass though
Laryngopharynx – air and food pass though
- Lower respiratory tract
o Larynx – contain vocal cords, sorting – keep particle from
entering the trachea
Glottis
, True vocal cords and opening between them
There are 2 vocal cords
False vocal cords – No sound production
True vocal cords – Sound production
Larger cartilages of the larynx:
Thyroid cartilage (Adam’s apple)
Cricoid cartilage
Epiglottic cartilage
o Trachea
Splits into right and left primary bronchi
Inner wall is lined with ciliated mucous membrane with
many goblet cells
Support by 20 incomplete (C-shaped) cartilaginous rings that
keep the airway open
o Bronchial tree
Main bronchi – first branches directly off the trachea
Lobar bronchi – branches of the main bronchi
Segmental bronchi
Bronchioles – absent cartilage
Terminal bronchioles – smallest bronchioles that conduct air
Respiratory bronchioles
Alveolar ducts – branch off respiratory bronchioles
Alveolar sacs – consist of air sacs called alveoli
Alveoli – sites of gas exchange between air and blood
o Lungs
Soft, spongy, cone shaped organs of the respiratory system
Separated medially by the mediastinum and enclosed by the diaphragm
and thoracic cage
Occupy most thoracic cavity
Right lungs have 3 lobes and left has 2 lobes
Each lung containers air passages, alveoli, nerves, blood vessels,
lymphatic vessels, and connective tissues
The pleura:
A double layered serous membrane
Visceral pleura: inner layer; attached to the surface of each lung,
touching the organ