Unit 5
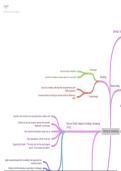
Cell cycle
All cells are formed by division of existing cells. Eukaryotic cells always divide in one of two
ways:
● Mitosis: division into two daughter cells that are genetically identical to each other and to
the parent cell
● Meiosis: division into four unique daughter cells with half the chromosomes of the parent
cell
All cells follow the same sequence of events between mitotic divisions, and this is known
as the cell cycle.
There are three main stages in the cell cycle:
1. Interphase
2. Nuclear division
3. Cell division (cytokinesis)
Interphase
Interphase consists of all the processes that occur when a cell isn’t dividing. During this
phase, the cell increases in mass and size and carries out its normal cellular functions
(synthesising proteins and replicating its DNA ready for mitosis)
Interphase consists of three phases:
1. G1 phase (Gap 1)
2. S phase (DNA replication)
3. G2 phase (Gap 2)
● G1: during G1, the new cell grows and carries out its normal life functions, such as protein
synthesis and respiration. During this stage, the largest amount of mRNA is produced, as it
is the stage at where protein synthesis occurs.
● S: during the S phase, the cell’s DNA is replicated so that each chromosome is
double-stranded. Energy is also saved up in the form of ATP, ready for the process of cell
division
● G2: this G2 phase is another gap, or growth phase. It is followed by a control checkpoint, ,
when the cell checks the DNA synthesised and repairs any errors before mitosis. Other
preparations for cell division are made, like producing tubulin, to make microtubules for
the mitotic spindle.
● Interphase: G1 + S + G2
Mitosis
This is the process of nuclear division, which places one strand of each chromosome in
each daughter nucleus. Each is now identical to the parent nucleus (as it was before DNA
replication)
Cytokinesis
Finally, the cytoplasm is divided between the two daughter cells to finish the cell cycle.
Each new cell enters G1 and resumes its normal functions.
, Mitosis
Mitosis specifically refers to the process of nuclear division that occurs before a cell
physically divides in two. During mitosis, the cell’s DNA is copied into each of the two
daughter cells. In multicellular organisms, mitosis provides new cells for growth and tissue
repair. In eukaryotes, it can also be a form of asexual reproduction, such as in yeast.
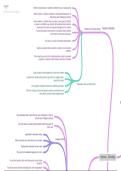
How the cell cycle fits together
The cell cycle consists of a long period of interphase,
followed by mitosis and finished with cytokinesis. Each of
these can be broken into several phases.
1. Interphase: a cell in interphase is a cell that isn’t currently dividing. During interphase, a
cell carries out its normal functions, and prepares for the next division in three phases: G1,
S and G2
● G1: a period of rapid growth and processes, immediately following cytokinesis
● S: the period during which DNA replication occurs
● G2: a second growth phase, in preparation for mitosis
2. Mitosis: the division of the nucleus into two identical copies of the original, and contains
four phases; prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
● Prophase: the cell’s chromatin condenses into discrete bodies and the mitotic spindle
starts to form
● Metaphase: the mitotic spindle aligns the chromosomes along the equator of the cell
● Anaphase: the chromatids on each chromosome separate into daughter chromosomes
● Telophase: nuclear membranes and nucleoli reform around the daughter chromosomes
3. Cytokinesis: occurs during or directly after telophase. The cytoplasm divides to complete
the process of cell division
What happens in mitosis?
Mitosis (nuclear division) makes up 5-10% of the cell cycle. Before the process of nuclear
division begins, the cell is carrying out its normal functions. DNA synthesis and checking
are complete.
● Prophase (early): Mitosis begins. The chromatin condenses and becomes inactive.
Centrioles migrate in pairs to opposite poles and the nuclear envelope and nucleolus
break up
● Prophase (late): The chromosomes are now tightly coiled and visible as separate bodies
under the microscope. The mitotic spindle begins to form at the centrioles
● Metaphase: The mitotic spindle grows further and attaches to the centromere of each
chromosome. The fibres then arrange the chromosomes to line up along the cell equator.
● Anaphase: The centromere of each chromosome breaks. Sister chromatids separate into
daughter chromosomes.
● Telophase: New nuclear membranes and nuclei form. The chromosomes start to unwind
back into chromatin and are no longer visible under the microscope
● Cytokinesis: Finally, the cytoplasm is divided between the two daughter cells to finish the
cycle. Each new cell enters interphase and resumes its normal functions
Cell cycle
All cells are formed by division of existing cells. Eukaryotic cells always divide in one of two
ways:
● Mitosis: division into two daughter cells that are genetically identical to each other and to
the parent cell
● Meiosis: division into four unique daughter cells with half the chromosomes of the parent
cell
All cells follow the same sequence of events between mitotic divisions, and this is known
as the cell cycle.
There are three main stages in the cell cycle:
1. Interphase
2. Nuclear division
3. Cell division (cytokinesis)
Interphase
Interphase consists of all the processes that occur when a cell isn’t dividing. During this
phase, the cell increases in mass and size and carries out its normal cellular functions
(synthesising proteins and replicating its DNA ready for mitosis)
Interphase consists of three phases:
1. G1 phase (Gap 1)
2. S phase (DNA replication)
3. G2 phase (Gap 2)
● G1: during G1, the new cell grows and carries out its normal life functions, such as protein
synthesis and respiration. During this stage, the largest amount of mRNA is produced, as it
is the stage at where protein synthesis occurs.
● S: during the S phase, the cell’s DNA is replicated so that each chromosome is
double-stranded. Energy is also saved up in the form of ATP, ready for the process of cell
division
● G2: this G2 phase is another gap, or growth phase. It is followed by a control checkpoint, ,
when the cell checks the DNA synthesised and repairs any errors before mitosis. Other
preparations for cell division are made, like producing tubulin, to make microtubules for
the mitotic spindle.
● Interphase: G1 + S + G2
Mitosis
This is the process of nuclear division, which places one strand of each chromosome in
each daughter nucleus. Each is now identical to the parent nucleus (as it was before DNA
replication)
Cytokinesis
Finally, the cytoplasm is divided between the two daughter cells to finish the cell cycle.
Each new cell enters G1 and resumes its normal functions.
, Mitosis
Mitosis specifically refers to the process of nuclear division that occurs before a cell
physically divides in two. During mitosis, the cell’s DNA is copied into each of the two
daughter cells. In multicellular organisms, mitosis provides new cells for growth and tissue
repair. In eukaryotes, it can also be a form of asexual reproduction, such as in yeast.
How the cell cycle fits together
The cell cycle consists of a long period of interphase,
followed by mitosis and finished with cytokinesis. Each of
these can be broken into several phases.
1. Interphase: a cell in interphase is a cell that isn’t currently dividing. During interphase, a
cell carries out its normal functions, and prepares for the next division in three phases: G1,
S and G2
● G1: a period of rapid growth and processes, immediately following cytokinesis
● S: the period during which DNA replication occurs
● G2: a second growth phase, in preparation for mitosis
2. Mitosis: the division of the nucleus into two identical copies of the original, and contains
four phases; prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
● Prophase: the cell’s chromatin condenses into discrete bodies and the mitotic spindle
starts to form
● Metaphase: the mitotic spindle aligns the chromosomes along the equator of the cell
● Anaphase: the chromatids on each chromosome separate into daughter chromosomes
● Telophase: nuclear membranes and nucleoli reform around the daughter chromosomes
3. Cytokinesis: occurs during or directly after telophase. The cytoplasm divides to complete
the process of cell division
What happens in mitosis?
Mitosis (nuclear division) makes up 5-10% of the cell cycle. Before the process of nuclear
division begins, the cell is carrying out its normal functions. DNA synthesis and checking
are complete.
● Prophase (early): Mitosis begins. The chromatin condenses and becomes inactive.
Centrioles migrate in pairs to opposite poles and the nuclear envelope and nucleolus
break up
● Prophase (late): The chromosomes are now tightly coiled and visible as separate bodies
under the microscope. The mitotic spindle begins to form at the centrioles
● Metaphase: The mitotic spindle grows further and attaches to the centromere of each
chromosome. The fibres then arrange the chromosomes to line up along the cell equator.
● Anaphase: The centromere of each chromosome breaks. Sister chromatids separate into
daughter chromosomes.
● Telophase: New nuclear membranes and nuclei form. The chromosomes start to unwind
back into chromatin and are no longer visible under the microscope
● Cytokinesis: Finally, the cytoplasm is divided between the two daughter cells to finish the
cycle. Each new cell enters interphase and resumes its normal functions