Learning objective 3.1
How do business activities affect the income statement
The operating cycle
= the time it takes for a company to pay cash to suppliers, sell goods and
services to customers, and collect cash from customers.
It begins when a company receives goods to sell, pays for them and sell to
customers. It ends when customers pay cash to the company.
The long-term objective for any business is to turn cash into more cash.
Until a company ceases its activities, the operating cycle is repeated
continuously. The time period assumption indicates that the
long life of a company can be reported in shorter time periods. Such as months,
quarters and years.
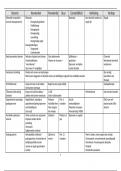
2 types of issues arise in reporting periodic income to users:
- Recognition issues : when should the effects of operating activities be
recognized?
- Measurement issues : what amounts should be recognized?
Learning Objective 3.2
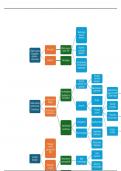
Elements of the income statement
- Operating income
- Income before income taxes.
- Net income
Operating revenues
Revenues are defined as: increases in assets or settlements of liabilities from
ongoing operations.
Result from sales of goods or services.
When revenue is earned, assets (usually cash or accounts receivable,
often increase)
Customer pays in advance a liability account (Unearned Revenue) is
created. So only cash in exchange for a promise to provide goods/services
in the future.
If the company delivers the promise the liability, revenue is recognized and
liability eliminated.
Operating expense
Expenditure = any outflow of cash for any purpose, whether to buy equipment,
pay off a bank loan or pay employees their wages.
Expenses = outflows or the using up of assets or increases in liabilities from
ongoing operations incurred to generate revenues during the period.
Therefore, not all cash expenditures are expenses, but expenses are
necessary to generate revenues.
, Restaurant operating expenses
- Food, beverage, an packaging expenses.
- Salaries and wages expenses
- Occupancy expenses renting facilities, insuring property and equipment,
using utilities.
- Other operating expenses advertising, marketing costs, repair and
maintenance of store facilities.
General and administrative expenses
- Costs of renting headquarters facilities, executive salaries, and training
managers. (not directly related to operating stores)
Depreciation expenses
- When a company uses buildings and equipment to generate revenues, a
part of the cost of these assets is reported as an expense.
Operating revenues – operating expenses = operating income. (a measure of the
profit from central ongoing operations.
Other items
Any revenues, expenses, gains, or losses that result from these other activities
are not included as part of operating income, but are instead categorized as
other items. These include the following
- Investment Income (investment revenue, interest revenue or dividend
revenue)
Using excess cash to purchase stocks or bonds in other companies.
investing activity.
- Interest expense.
- Gain(loss) on disposal of assets.
Gains increases in assets or decreases liabilities from peripheral
transactions
Losses decreases in assets or increases in liabilities from peripheral
transactions.
Income tax expense
Adding and subtracting other items to operating income gives a subtotal of
income before income taxes. Tax expense (also called provision for income taxes)
is the last expense listed on the income statement before determining net
income.
Earnings per share
Corporations are required to disclose earnings per share on the income statement
or in the notes to the financial statements. This ratio is widely used in evaluating
the operating performance and profitability of a company.
Earnings per share = Net income / Weighted average number of shares
of stock outstanding.
Learning Objective 3.3