IB Psychology - Social Influence
written by
katerinacontreras
www.stuvia.com
Downloaded by: katerinacontreras | Want to earn
Distribution of this document is illegal $103 per month?
, Stuvia.com - The Marketplace to Buy and Sell your Study Material
Katerina Contreras
04.12.2020.
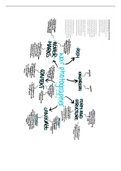
PSYCHOLOGY
___
Social Influence Part I
Key Terms Traffic Lights
Term Before we begin End of unit End of course
Acculturation
Acculturative stress
Collectivism
Conformity
Contact hypothesis
Cultural dimension
Cultural value
Discrimination
Enculturation
Individualism
In-groups and
out-groups
Jigsaw classroom
Minimal group
paradigm studies
Normative social
influence
Prejudice
Downloaded by: katerinacontreras | Want to earn
Distribution of this document is illegal $103 per month?
, Stuvia.com - The Marketplace to Buy and Sell your Study Material
Realistic group
conflict theory
Social identity
Topic 3.1: Conformity
Why do people go along with the group?
Downloaded by: katerinacontreras | Want to earn
Distribution of this document is illegal $103 per month?
, Stuvia.com - The Marketplace to Buy and Sell your Study Material
Lesson (a): Normative Social Influence
Key Questions 1. What is conformity? What is normative social influence?
2. How does Asch’s study demonstrate the effects of normative
social influence on behaviour?
3. How can Asch’s results be explained in a way that shows
group pressure might not cause conformity?
Conformity and Normative Social Influence
· Conformity = behaving in a way that is socially acceptable and expected.
- It usually refers to when someone changes their behaviour in a way that is more in-line
with a social norm.
· Normative social influence = when someone changes their behaviour to conform with social
norms, and they do so because of a fear of being left out of the group.
Memory Test: Asch’s Conformity Study
1. How many confederates did Asch use in his studies?
a. 6-8
2. What is “critical trial”?
a. The trials where the confederates gave the wrong answer.
3. What were two of the reasons why the participants went along with the group, even
when the group was wrong?
a. Social pressure
b. “They didn’t know the right answer.” (NOT TRUE)
4. What happened when one of the confederates went against the group?
a. Conformity dropped, and the naive participant said their own answer.
b. From 37% to 5%
5. What does the partner condition show about conformity?
a. Unanimity is easier than individualism.
6. What is “normative conformity”?
a. Conforming due to the fear of social rejection.
7. What happens when a participant has to write their answer?
a. Conformity drops by 2/3
Guiding Question:
How does Asch’s study demonstrate the effects of normative social influence on behaviour?
Downloaded by: katerinacontreras | Want to earn
Distribution of this document is illegal $103 per month?
written by
katerinacontreras
www.stuvia.com
Downloaded by: katerinacontreras | Want to earn
Distribution of this document is illegal $103 per month?
, Stuvia.com - The Marketplace to Buy and Sell your Study Material
Katerina Contreras
04.12.2020.
PSYCHOLOGY
___
Social Influence Part I
Key Terms Traffic Lights
Term Before we begin End of unit End of course
Acculturation
Acculturative stress
Collectivism
Conformity
Contact hypothesis
Cultural dimension
Cultural value
Discrimination
Enculturation
Individualism
In-groups and
out-groups
Jigsaw classroom
Minimal group
paradigm studies
Normative social
influence
Prejudice
Downloaded by: katerinacontreras | Want to earn
Distribution of this document is illegal $103 per month?
, Stuvia.com - The Marketplace to Buy and Sell your Study Material
Realistic group
conflict theory
Social identity
Topic 3.1: Conformity
Why do people go along with the group?
Downloaded by: katerinacontreras | Want to earn
Distribution of this document is illegal $103 per month?
, Stuvia.com - The Marketplace to Buy and Sell your Study Material
Lesson (a): Normative Social Influence
Key Questions 1. What is conformity? What is normative social influence?
2. How does Asch’s study demonstrate the effects of normative
social influence on behaviour?
3. How can Asch’s results be explained in a way that shows
group pressure might not cause conformity?
Conformity and Normative Social Influence
· Conformity = behaving in a way that is socially acceptable and expected.
- It usually refers to when someone changes their behaviour in a way that is more in-line
with a social norm.
· Normative social influence = when someone changes their behaviour to conform with social
norms, and they do so because of a fear of being left out of the group.
Memory Test: Asch’s Conformity Study
1. How many confederates did Asch use in his studies?
a. 6-8
2. What is “critical trial”?
a. The trials where the confederates gave the wrong answer.
3. What were two of the reasons why the participants went along with the group, even
when the group was wrong?
a. Social pressure
b. “They didn’t know the right answer.” (NOT TRUE)
4. What happened when one of the confederates went against the group?
a. Conformity dropped, and the naive participant said their own answer.
b. From 37% to 5%
5. What does the partner condition show about conformity?
a. Unanimity is easier than individualism.
6. What is “normative conformity”?
a. Conforming due to the fear of social rejection.
7. What happens when a participant has to write their answer?
a. Conformity drops by 2/3
Guiding Question:
How does Asch’s study demonstrate the effects of normative social influence on behaviour?
Downloaded by: katerinacontreras | Want to earn
Distribution of this document is illegal $103 per month?