Department of Mathematics Elementary Graph Theory Lecture 1
Elementary Graph Theory
Introduction
1. Konigsberg bridge problem
Consider this town plan of Konigsberg in East Prussia. The pregel river runs
through the middle of town and a set of 7 bridges links the banks and two
islands in the river. The problem is to find a walk through the town that begins
and ends at the same place, crossing each bridge exactly once.
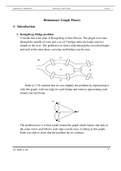
Euler in 1736 realized that we can simplify the problem by representing it
with this graph, with one edge for each bridge and vertices representing each
islands and each bank.
The problem now is to find a path around the graph which begins and ends at
the same vertex and follows each edge exactly once. Looking at this graph,
Euler was able to show that the problem has no solution.
Dr. Didar A. Ali 1
, Department of Mathematics Elementary Graph Theory Lecture 1
2. Paths on a die
To find a circuit on a die visiting each face exactly once we consider this
graph: 1
2
5
6
4 3
There is one vertex for each face and an edge connecting faces. We want
to find a closed circuit on the graph visiting each vertex exactly once. One of
the solution is 1,3,6,4,5,2,1
Fundamental Concepts
Definition: A graph (denoted as G (V, E) ) consists of a non-empty set of
vertices or nodes V and a set of edges or arcs E .
Number of vertices in a graph is called order, usually it is denoted by p or
p(G) .
Number of edges in a graph is called size it is denoted by q or q(G) .
Look at the following graph:
a b z f k
c d h
A graph G
Set of vertices V(G) {a, b,c,d,f , h, k, z} , the order of G , p(G) 8 .
Set of edges E(G) {e1 ,e 2 ,e3 ,e 4 ,e5 ,e6 ,e7 ,e8 ,e9 } , the size of G , q(G) 9
Dr. Didar A. Ali 2
Elementary Graph Theory
Introduction
1. Konigsberg bridge problem
Consider this town plan of Konigsberg in East Prussia. The pregel river runs
through the middle of town and a set of 7 bridges links the banks and two
islands in the river. The problem is to find a walk through the town that begins
and ends at the same place, crossing each bridge exactly once.
Euler in 1736 realized that we can simplify the problem by representing it
with this graph, with one edge for each bridge and vertices representing each
islands and each bank.
The problem now is to find a path around the graph which begins and ends at
the same vertex and follows each edge exactly once. Looking at this graph,
Euler was able to show that the problem has no solution.
Dr. Didar A. Ali 1
, Department of Mathematics Elementary Graph Theory Lecture 1
2. Paths on a die
To find a circuit on a die visiting each face exactly once we consider this
graph: 1
2
5
6
4 3
There is one vertex for each face and an edge connecting faces. We want
to find a closed circuit on the graph visiting each vertex exactly once. One of
the solution is 1,3,6,4,5,2,1
Fundamental Concepts
Definition: A graph (denoted as G (V, E) ) consists of a non-empty set of
vertices or nodes V and a set of edges or arcs E .
Number of vertices in a graph is called order, usually it is denoted by p or
p(G) .
Number of edges in a graph is called size it is denoted by q or q(G) .
Look at the following graph:
a b z f k
c d h
A graph G
Set of vertices V(G) {a, b,c,d,f , h, k, z} , the order of G , p(G) 8 .
Set of edges E(G) {e1 ,e 2 ,e3 ,e 4 ,e5 ,e6 ,e7 ,e8 ,e9 } , the size of G , q(G) 9
Dr. Didar A. Ali 2