Management Accounting (1CV10)
summary of Q2 2021/2022
By Isabel Rutten
Financial Accounting (AM - Atrill and McLaney)
(Externe verslaggeving)
Chapter 1
Accounting is about collecting, analyzing and communicating financial information. This
information is used to base decisions on by managers, investors, suppliers, etc.
Chapter 2
Statement of cash flows: a cash flow statement and shows change in cash over period
Income statement: a profit and loss account and shows change in wealth over period.
Statement of financial position: a balance sheet which shows wealth & cash position.
Start/end of a period: statement of financial position. Throughout a period: other two.
Each statement provides a part of the picture of financial performance and position of the
business. Cash is a vital resource that is necessary for any business to function effectively
(statement of cash flows) but changes in cash do not give insights into the profit generated
(income statement). Thus use statement of financial position also for insights in total wealth.
Balance sheet can be both of vertical layout as horizontal layout.
An asset a) is a resource which provides a right for the potential to receive economic
benefits, b) of which this right is exclusive for the business, c) where the business already
exercises control over the resource, and d) the resource is capable of measurement in
monetary terms. assets = non-current assets + currents assets.
Tangible assets: property, inventories, cash. Intangible: trade receivable, patents.
Non-current assets: long-term investments for which full value will not be realized within the
accounting year, e.g. real estate. Three approaches to decide asset value:
- historic value: asset value = net book value = historic costs – depreciation
- fair value: asset value = fair value = current market value
- impairment of non-curr assets: if net book value > fair value then asset value = fair value
Current assets: short-term investments e.g. cash, stock. Same asset value approaches but
no depreciation.
Claims: the obligations of the business to provide cash, or some other form of benefit, to an
outside parties. Claims = Equity + Liabilities.
Liabilities: The claims of other parties. Current liabilities: related to settlement in short
term e.g. trade payables. Non-current liabilities: related to settlement in the long term.
Liabilities = current liabilities + non-current liabilities.
Equity: the claims of the owners against the business e.g. share capital. Equity = assets –
liabilities. Equity at end of period = Equity at start of period + profit/loss for the period.
1
Fundamentals of Financial and Management Accounting (1CV10) summary of Q2
2021/2022 by Isabel Rutten
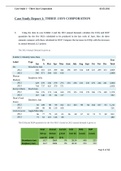
,Example statement of cash flows, income statement,
statement of financial position >
Chapter 3
Accounting equation: assets = claims i.e. resources of business = obligations of business
Effects of transactions on balance sheet: - negative effect on both: payment to supplier
- positive effect on both assets and claims: purchase goods on credit, payment to supplier
- positive and negative effect on assets: cash purchase goods
- positive and negative effect on assets and positive effect on claims: cash sale of goods
Profit = revenues – expenses. Revenues: goods and services delivered to clients, sales.
Expenses: value of all production resources used/consumed to deliver the goods&services
New equity = old equity + profit. The income statement is the profit and loss account which
is a specification of the change in equity during the period. This and the old balance sheet is
used to make the new balance sheet including its changed equity.
Layout income statement is as follows: Gross profit = sales revenue – cost of sales.
Operating profit = gross profit – operating expenses.
Profit for the period = operating profit – interest payable + interest receivable
If tax applies: profit for the period = profit before taxation – taxation
Revenues should be recognized when the goods/services are delivered. Criteria:
amount of revenue can be measured reliably, it is probable that economic revenue will be
received, ownership and control should pass to the buyer.
Matching convention: expenses should be matched to the revenue they helped to
generate. Ways:
- Timing (accrued/prepaid expenses): e.g. you pay electricity expenses beforehand
- Depreciation (depreciation expenses): two methods:
1. Straight line: all years have the same amounts
2. Reducing balance: all years have same percentage of net book value (carrying amount)
For Example: machine, 5 years, costs 15000, residual value 5000.
Straight line: Yearly depreciation: (15000 - 5000) / 5 = 2000
Reducing balance: yearly depreciation %: [1 – ()^(1/5)*100 = 19.725...%
depr year 1: 19.725…% of 15000 ≈ 2958.88.
depr year 2: 19.725…% of (15000 - 2958.88) ≈ 2375.21
For both: net book value after 5 years is 5000.
- Costing inventories (cost of inventories): three standard methods:
a) First-In-First-Out (FIFO): the earliest acquired inventories held are the first to be used
b) Last-In-First-Out (LIFO): the latest acquired inventories held are the first to be used
c) Weighted Average Costs (AVCO): the acquired inventories go into a pool where cost
is calculated by weighted average.
note: cost of sales is impacted by method as well!
2
Fundamentals of Financial and Management Accounting (1CV10) summary of Q2
2021/2022 by Isabel Rutten
, Appendix A
Double entry bookkeeping – Ledger account: Every transaction influences (at least) two
accounts. Transactions are recorded in a set of ledger accounts (grootboekrekeningen). A
ledger account looks like “T”, or called T-account. Equity changes because of 1) operational
events (e.g. sales, cost of sales) and 2) capital-related events (e.g. new capital, dividend
payments). To determine result we open accounts that track revenues and expenses.
Debit: increase asset (and expense), decrease in liability (and revenue) i.e. assets,expenses
Credit: incr in liability (and revenue), decr in asset (and expense) i.e.equity,liabilities,revenue
Start period: StartAssets = StartEquity + StartLiabilities
End period: EndingAssets = EndEquity + EndLiabilities
EndAssets = StartEquity + Revenues – Expenses + EndLiabilities
EndAssets + Expenses = Start Equity + Revenues + Endliabilities.
Steps: 0. Information you have is starting balance sheet and transactions during the year.
1. Open ledger accounts for the balance sheet headers.
2. Analyze i.e. for each transactions note influence on the corresponding ledger accounts.
3. Record on ledger accounts.
4. Prepare trial balance sheet (for all ledger accounts), trial balance is (of course) balanced.
Also fill in the P&L account (profits and liabilities, not balanced yet) and the balance sheet
(which is trial balance without the parts of the P&L account). Then, determine the profit/loss
in the P&L account and add that to the equity of the balance sheet. Write the P&L account
and the new balance sheet in the horizontal or vertical layout.
5. Open P&L ledger account with its corresponding data. Add this to the retained earnings
ledger account. Close ledger accounts to balance sheet.
6. Ending balance sheet: transfer the balance in individual accounts to balance sheet.
Chapter 4
Equity of a limited company:
Two types of shares: ordinary shares and preference shares.
Changes of the nominal value of shares: share splits (more), share consolidating (less).
Capital reserves arise for two main reasons:
(1) issuing shares at above the nominal value; (2) upwards revaluing non-current assets.
Revenue reserves arise by
(1) retained trading profits; (2) gains on the disposal of non-current assets.
Chapter 5
Financial statements required under IAS 1 (sets out overall requirements for financial
statements): statement of financial position, statement of cash flows, statement of changes
of equity, notes on accounting policies and other explanatory notes, statement of
comprehensive income.
3
Fundamentals of Financial and Management Accounting (1CV10) summary of Q2
2021/2022 by Isabel Rutten