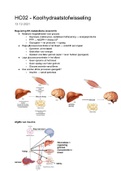
Endocrine system
Neuroendocrine hormone → produced in neuroendocrine cells
Endocrine gland hormone → produced in e.g. the GI tract
Peptide hormones and protein hormones: produced in the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, pancreas,
thyroid and parathyroid glands.
Membrane receptors (relatively quick):
• G-protein coupled receptors (adenylyl cyclase, PI metabolism)
• Tyrosine kinases
Steroid hormones, sterols, thyroxine derivatives: produced in the adrenal gland, reproductive
organs, calcitriol (vit. D derivative), thyroid gland.
• Calcium and bone metabolism
Intracellular receptors (relatively slow):
• Regulation of protein synthesis (ligand-gated transcription factors)
Hormones
• often analogues: stable agonists/antagonists; - with protein hormones (‘tropic hormones’,
parenteral):
• often more stable effector hormones that can be administered orally (synthetic steroids,
thyroxine derivatives)
Pharmaceuticals that affect hormone synthesis, hormone release or hormone metabolism.
Hypothalamus → gives signal to pituitary gland to produce hormones
,Hypothalamic-pituitary system
Specialized neurons → able to produce hormones
• Hypothalamus and pituitary gland together regulate a major part of the
endocrine system.
• Hypothalamus converts nerve impulses from the brain into a hormonal
impulse.
Pituitary gland is made up of 3 parts:
• anterior pituitary (anterior lobe) → trophic hormones
• pars intermedia (barely present in humans)
• posterior pituitary (posterior lob
Hormones from the hypothalamus regulate the release of hormones by the
anterior pituitary.
Hypothalamic-anterior pituitary system
Hormones mainly negative feedback mechanism on the upper centers.
• Hormones pre-produced and ready to go
Hypothalamic-posterior pituitary system
Vasopressin (ADH) and oxytocin.
Oxytocin
• Uterine conctraction
• Milk ejection
The synthesis of other hormones by the anterior pituitary is
• stimulated: releasing factors (RF) or hormones (RH)
• inhibited: inhibiting factors (IF) or hormones (IH)
,All hypothalamic hormones are peptides (with the exception of dopamine).
Anterior pituitary hormones
Group 1: Somatotropic hormones
• Growth hormone (somatotropin)
• Prolactin
Group 2: Glycoproteins
• Luteinizing hormone (LH)
• Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
• Thyroid-stimulationg hormone (TSH; thyrotropin)
• Chorion gonadotropin (CG)
Glycoproteins are made up of an α-subunit and a β-subunit.
Group 3: Derived from precursor protein (pro-opiomelanocortin)
• Adenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH),corticotropin
• Melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH)
• β-lipotropin (β-LPH)
Multiple hormones are produced from a large precursor molecule by enzymatic cleavage (proteases)
in various tissues.
Synthesis of peptide analogues
• Endogenous peptides are often metabolized quickly
• Knowledge of the amino acid sequence and characteristics of a peptide creates
opportunities to develop new analogues with increased stability, improved activity and
fewer side effects
• Pharmacological activity of analogues provides insight into the structure-activity relationship
(SAR).
, Possible structural changes:
1. Shortening the chain by removing an amino acid (elision)
2. Lengthening the chain by inserting an amino acid (intercalation)
3. Changing an amino acid (changing the side chain)
4. Replacing an L-amino acid by a D-amino acid
5. Blocking an end group
6. Replacing S-S bridges by ethylene bridges or by CH2 bonds
Growth hormone
GRH → GH
Effects of growth hormone
• Growth: almost all body cells, in particular chondrocytes in epiphyseal plates of long bones
(longitudinal growth), skeletal muscle.
• Metabolism: protein anabolic, glucose-sparing, lipolytic.
GHRF → stimulates release growth hormone
Somatostatin → inhibits the release growth hormone
IGF-1 (insulin-like growth factor 1) → produced in the liver
• Negative influence on release of GH in anterior pituitary
• Positive influence on release of central hypothalamus
GH itself has a negative feedback on the hypothalamus.
T3 (active hormone thyroid) → positive effect on GH
• T3 and GH both stimulate growth (anabolic)
Neuroendocrine hormone → produced in neuroendocrine cells
Endocrine gland hormone → produced in e.g. the GI tract
Peptide hormones and protein hormones: produced in the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, pancreas,
thyroid and parathyroid glands.
Membrane receptors (relatively quick):
• G-protein coupled receptors (adenylyl cyclase, PI metabolism)
• Tyrosine kinases
Steroid hormones, sterols, thyroxine derivatives: produced in the adrenal gland, reproductive
organs, calcitriol (vit. D derivative), thyroid gland.
• Calcium and bone metabolism
Intracellular receptors (relatively slow):
• Regulation of protein synthesis (ligand-gated transcription factors)
Hormones
• often analogues: stable agonists/antagonists; - with protein hormones (‘tropic hormones’,
parenteral):
• often more stable effector hormones that can be administered orally (synthetic steroids,
thyroxine derivatives)
Pharmaceuticals that affect hormone synthesis, hormone release or hormone metabolism.
Hypothalamus → gives signal to pituitary gland to produce hormones
,Hypothalamic-pituitary system
Specialized neurons → able to produce hormones
• Hypothalamus and pituitary gland together regulate a major part of the
endocrine system.
• Hypothalamus converts nerve impulses from the brain into a hormonal
impulse.
Pituitary gland is made up of 3 parts:
• anterior pituitary (anterior lobe) → trophic hormones
• pars intermedia (barely present in humans)
• posterior pituitary (posterior lob
Hormones from the hypothalamus regulate the release of hormones by the
anterior pituitary.
Hypothalamic-anterior pituitary system
Hormones mainly negative feedback mechanism on the upper centers.
• Hormones pre-produced and ready to go
Hypothalamic-posterior pituitary system
Vasopressin (ADH) and oxytocin.
Oxytocin
• Uterine conctraction
• Milk ejection
The synthesis of other hormones by the anterior pituitary is
• stimulated: releasing factors (RF) or hormones (RH)
• inhibited: inhibiting factors (IF) or hormones (IH)
,All hypothalamic hormones are peptides (with the exception of dopamine).
Anterior pituitary hormones
Group 1: Somatotropic hormones
• Growth hormone (somatotropin)
• Prolactin
Group 2: Glycoproteins
• Luteinizing hormone (LH)
• Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
• Thyroid-stimulationg hormone (TSH; thyrotropin)
• Chorion gonadotropin (CG)
Glycoproteins are made up of an α-subunit and a β-subunit.
Group 3: Derived from precursor protein (pro-opiomelanocortin)
• Adenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH),corticotropin
• Melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH)
• β-lipotropin (β-LPH)
Multiple hormones are produced from a large precursor molecule by enzymatic cleavage (proteases)
in various tissues.
Synthesis of peptide analogues
• Endogenous peptides are often metabolized quickly
• Knowledge of the amino acid sequence and characteristics of a peptide creates
opportunities to develop new analogues with increased stability, improved activity and
fewer side effects
• Pharmacological activity of analogues provides insight into the structure-activity relationship
(SAR).
, Possible structural changes:
1. Shortening the chain by removing an amino acid (elision)
2. Lengthening the chain by inserting an amino acid (intercalation)
3. Changing an amino acid (changing the side chain)
4. Replacing an L-amino acid by a D-amino acid
5. Blocking an end group
6. Replacing S-S bridges by ethylene bridges or by CH2 bonds
Growth hormone
GRH → GH
Effects of growth hormone
• Growth: almost all body cells, in particular chondrocytes in epiphyseal plates of long bones
(longitudinal growth), skeletal muscle.
• Metabolism: protein anabolic, glucose-sparing, lipolytic.
GHRF → stimulates release growth hormone
Somatostatin → inhibits the release growth hormone
IGF-1 (insulin-like growth factor 1) → produced in the liver
• Negative influence on release of GH in anterior pituitary
• Positive influence on release of central hypothalamus
GH itself has a negative feedback on the hypothalamus.
T3 (active hormone thyroid) → positive effect on GH
• T3 and GH both stimulate growth (anabolic)