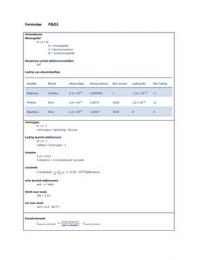
Summary Patterns of Entrepreneurship Management
Chapter 1 – The Entrepreneurial Process
More than 60 percent of ideas for start-ups come when working for someone else
Entrepreneurship: creation of a business including the generation and implementation of an idea
while understanding the team concept using effective communication.
Entrepreneurial characteristics:
- Ability to deal with ambiguity (make decisions on conflicting and/or incomplete information)
- Self-starters, optimists, perseverant, energetic, action-oriented
- Persuasive leader, people-oriented, natural networker, communicator
- Creative & highly imaginative
- Seeking for the chance to profit from change and disruption
- Tolerate risk, but temper with reality
- Work with urgency, but focus on long-term goals too
- Focus on (adaptive) execution
- Open to change
Types of entrepreneurs:
- Aspiring: dream of starting a business
- Lifestyle: enterprise that fits individual circumstances and style of life
- Growth: desire & ability to grow as fast and as large as possible
- Social: innovative solutions to society’s most social problems
- Technology: ideas triggered by developments in science and engineering
The need to control:
- Partners: decrease chance of failure of start-up, but value created is split too
- Hired managers: useful but painful, not everyone has managerial skills so bringing in an
experienced manager could be necessary
- Financing options: when control is more important than wealth sharingbootstrapping (own
money, reinvest profit) or bank loans
- Opportunity selection: if control is important start with smaller opportunity, else involve
partners, outside investors and advisers
Spiderweb model: in the start-up phase of a company it is very fragile, like a spider’s web
Finding early mentors: best found through networkingidentify highly connected people, and build
trust with them.
An entrepreneurial life is inevitably stressful, manage the different sources of stress
effectivelywww.score.org
Five-stage entrepreneurial process:
1. Conducting opportunity analysis
2. Developing the plan and setting up the company
3. Acquiring financial partners/sources of funding
, 4. Determining the resources required and implementing the plan
5. Scaling and harvesting the venture
“Don’t give up. Don’t ever give up. And when things look worst, just don’t give up.”- Richard Foreman
The entrepreneurial life is unpredictable, challenging, and often stressful. Practice how to handle
uncertainty effectively.
Chapter 2 – The art of innovation
Due to growth of internet and access to knowledge and ideas opportunities are larger, but
competitors are stronger too. Barriers to trade are rapidly being dismantled, access to capital has
become easier. Carefully listen to customers to see where service can be increased. Adaption is key.
“Successful innovation is the use of new technological knowledge, and/or new market knowledge
employed within a business model that can deliver a new product and/or service to customers who
will purchase at a price that will provide profits.”
Incremental vs. radical innovation
Disruptive innovations: disrupt status quo, harder to handle for large enterprises which are slow to
change & adapt new ideas.
Frameworks for learning innovation skills:
- Analogs: analyse existing successful businesses and get behind immediate product or service
to examine the underpinning principles”Where else can these be applied?”
- Intersection of technology trends: combine different technology trends and integrate them
in one design
- Solving points of pain: get rid of inefficiencies, inconveniences and other points of pain
Finding and assessing ideas:
- Idea assessment: is the idea a potential dead end, a niche on an existing opportunity or an
entirely unexplored chance to create a business?
- Converting an idea into an opportunity: seek and use motivation, passion and
encouragement
- Opportunity: five phases to success
o Seize the opportunity: how much value can it add to a business?, time horizon and
evaluation of opportunity costs
o Investigate the need through market research
o Develop the plan
o Determine the resources needed: personal contacts & networking, financing
requirements, sources of technical skills
o Manage the business: deliver a total solution, cultivate advanced resources
Know how to protect the idea or productchapter 8
Article: Effectual entrepreneurship
Entrepreneurs use a pattern of decision-making behaviour which is called effectuation four
principles:
- Start with your means: Who I am, What I know, Whom I know
, - Set affordable loss: decide on what you are willing to lose rather than on what you expect to
make.
- Leverage contingencies: “If you come across lemons, make lemonade!” ability to turn the
unexpected into the profitable.
- Form partnerships
Article: What makes entrepreneurs entrepreneurial?
Effectual reasoning does not begin with a specific goal, but it begins with a given set of means and
allows goals to emerge contingently over time.
Managerial thinking - causal reasoning: selecting between given means to achieve a pre-determined
goal
Strategic thinking – creative causal reasoning: generating new means to achieve pre-determined
goals
Entrepreneurial thinking – effectual reasoning: imagining possible new ends using a given set of
means
Logic behind effectual reasoning: to the extent that we can control the future, we do not need to
predict it.
Chapter 3 – Business models
Powerful business model requires blending all the aspects of the business into an integrated
operating system where every aspect becomes one.
A business model is a description of how your company intends to create value in the marketplace. It
includes that unique combination of products, services, image and distribution that your company
carries forward. It also includes the underlying organization of people, and the operational
infrastructure that they use to accomplish their work.
Frameworks for constructing business models:
- The five component model
o Articulate value proposition: value created for user of the product/service
o Identify market segment: users to whom the product/service is useful
o Define structure of value chain
o Estimate cost structure and profit potential
o Formulate competitive strategy
- Business model canvas: based on nine key topics, recommended to use in team-sessions
o Who are our key partners? Why do we need them and vice versa
o What are our key activities? What is unique about what we can do better than
others?
o What value is each subgroup of customers seeking?
o What key resources do we need to perform our activities?
o Who are our customers, and how do we contribute to the value proposition?
o How do we relate to these selected customers? (customer relationships)
o How do we segment these customers, which are most valuable? (customer
segments)
o Where are the major costs? (cost structure)
Chapter 1 – The Entrepreneurial Process
More than 60 percent of ideas for start-ups come when working for someone else
Entrepreneurship: creation of a business including the generation and implementation of an idea
while understanding the team concept using effective communication.
Entrepreneurial characteristics:
- Ability to deal with ambiguity (make decisions on conflicting and/or incomplete information)
- Self-starters, optimists, perseverant, energetic, action-oriented
- Persuasive leader, people-oriented, natural networker, communicator
- Creative & highly imaginative
- Seeking for the chance to profit from change and disruption
- Tolerate risk, but temper with reality
- Work with urgency, but focus on long-term goals too
- Focus on (adaptive) execution
- Open to change
Types of entrepreneurs:
- Aspiring: dream of starting a business
- Lifestyle: enterprise that fits individual circumstances and style of life
- Growth: desire & ability to grow as fast and as large as possible
- Social: innovative solutions to society’s most social problems
- Technology: ideas triggered by developments in science and engineering
The need to control:
- Partners: decrease chance of failure of start-up, but value created is split too
- Hired managers: useful but painful, not everyone has managerial skills so bringing in an
experienced manager could be necessary
- Financing options: when control is more important than wealth sharingbootstrapping (own
money, reinvest profit) or bank loans
- Opportunity selection: if control is important start with smaller opportunity, else involve
partners, outside investors and advisers
Spiderweb model: in the start-up phase of a company it is very fragile, like a spider’s web
Finding early mentors: best found through networkingidentify highly connected people, and build
trust with them.
An entrepreneurial life is inevitably stressful, manage the different sources of stress
effectivelywww.score.org
Five-stage entrepreneurial process:
1. Conducting opportunity analysis
2. Developing the plan and setting up the company
3. Acquiring financial partners/sources of funding
, 4. Determining the resources required and implementing the plan
5. Scaling and harvesting the venture
“Don’t give up. Don’t ever give up. And when things look worst, just don’t give up.”- Richard Foreman
The entrepreneurial life is unpredictable, challenging, and often stressful. Practice how to handle
uncertainty effectively.
Chapter 2 – The art of innovation
Due to growth of internet and access to knowledge and ideas opportunities are larger, but
competitors are stronger too. Barriers to trade are rapidly being dismantled, access to capital has
become easier. Carefully listen to customers to see where service can be increased. Adaption is key.
“Successful innovation is the use of new technological knowledge, and/or new market knowledge
employed within a business model that can deliver a new product and/or service to customers who
will purchase at a price that will provide profits.”
Incremental vs. radical innovation
Disruptive innovations: disrupt status quo, harder to handle for large enterprises which are slow to
change & adapt new ideas.
Frameworks for learning innovation skills:
- Analogs: analyse existing successful businesses and get behind immediate product or service
to examine the underpinning principles”Where else can these be applied?”
- Intersection of technology trends: combine different technology trends and integrate them
in one design
- Solving points of pain: get rid of inefficiencies, inconveniences and other points of pain
Finding and assessing ideas:
- Idea assessment: is the idea a potential dead end, a niche on an existing opportunity or an
entirely unexplored chance to create a business?
- Converting an idea into an opportunity: seek and use motivation, passion and
encouragement
- Opportunity: five phases to success
o Seize the opportunity: how much value can it add to a business?, time horizon and
evaluation of opportunity costs
o Investigate the need through market research
o Develop the plan
o Determine the resources needed: personal contacts & networking, financing
requirements, sources of technical skills
o Manage the business: deliver a total solution, cultivate advanced resources
Know how to protect the idea or productchapter 8
Article: Effectual entrepreneurship
Entrepreneurs use a pattern of decision-making behaviour which is called effectuation four
principles:
- Start with your means: Who I am, What I know, Whom I know
, - Set affordable loss: decide on what you are willing to lose rather than on what you expect to
make.
- Leverage contingencies: “If you come across lemons, make lemonade!” ability to turn the
unexpected into the profitable.
- Form partnerships
Article: What makes entrepreneurs entrepreneurial?
Effectual reasoning does not begin with a specific goal, but it begins with a given set of means and
allows goals to emerge contingently over time.
Managerial thinking - causal reasoning: selecting between given means to achieve a pre-determined
goal
Strategic thinking – creative causal reasoning: generating new means to achieve pre-determined
goals
Entrepreneurial thinking – effectual reasoning: imagining possible new ends using a given set of
means
Logic behind effectual reasoning: to the extent that we can control the future, we do not need to
predict it.
Chapter 3 – Business models
Powerful business model requires blending all the aspects of the business into an integrated
operating system where every aspect becomes one.
A business model is a description of how your company intends to create value in the marketplace. It
includes that unique combination of products, services, image and distribution that your company
carries forward. It also includes the underlying organization of people, and the operational
infrastructure that they use to accomplish their work.
Frameworks for constructing business models:
- The five component model
o Articulate value proposition: value created for user of the product/service
o Identify market segment: users to whom the product/service is useful
o Define structure of value chain
o Estimate cost structure and profit potential
o Formulate competitive strategy
- Business model canvas: based on nine key topics, recommended to use in team-sessions
o Who are our key partners? Why do we need them and vice versa
o What are our key activities? What is unique about what we can do better than
others?
o What value is each subgroup of customers seeking?
o What key resources do we need to perform our activities?
o Who are our customers, and how do we contribute to the value proposition?
o How do we relate to these selected customers? (customer relationships)
o How do we segment these customers, which are most valuable? (customer
segments)
o Where are the major costs? (cost structure)