Q: Exponential decay
A:
Nature has many example of physical quantities decreasing by the same factor in
equal time intervals, such as:
o The radioactivity of a sample of uranium salts
o The height of a solution in a burette as it empties through the small tap
o Or the pressure of the atmosphere with increasing height
This constant ration pattern is called exponential decay
The p.d across a capacitor discharging through a resistor decreases exponentially over
time
Q:
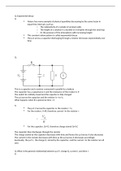
This is a capacitor and a resistor connected in parallel to a battery
The capacitor has a capacitance C and the resistance of the resistor is R
The switch S is initially closed and the capacitor is fully charged
The p.d across the capacitor and the resistor is = to V 0
What happens when S is opened at time = 0
A:
The p.d V across the capacitor or the resistor = V0
For the resistor, V=IR, therefore current I in the resistor =
o
For the capacitor, Q=VC, therefore charge stored Q=V 0C
The capacitor then discharges through the resistor
The charge stored by the capacitor decreases with time and hence the p.d across it also decreases
The current in the resistor decreases with time as the p.d across it decreases accordingly
Eventually, the p.d V , the charge Q stored by the capacitor, and the current I in the resistor are all
zero
Q: What is the general relationship between p.d V, charge Q, current I, and time t
A:
, These graphs all show exponential decay over time after the switch is opened
As such, they all have the same shape
The equations for these quantities ae as given by:
Q: Constant ratio property of exponential decay
A:
A:
Nature has many example of physical quantities decreasing by the same factor in
equal time intervals, such as:
o The radioactivity of a sample of uranium salts
o The height of a solution in a burette as it empties through the small tap
o Or the pressure of the atmosphere with increasing height
This constant ration pattern is called exponential decay
The p.d across a capacitor discharging through a resistor decreases exponentially over
time
Q:
This is a capacitor and a resistor connected in parallel to a battery
The capacitor has a capacitance C and the resistance of the resistor is R
The switch S is initially closed and the capacitor is fully charged
The p.d across the capacitor and the resistor is = to V 0
What happens when S is opened at time = 0
A:
The p.d V across the capacitor or the resistor = V0
For the resistor, V=IR, therefore current I in the resistor =
o
For the capacitor, Q=VC, therefore charge stored Q=V 0C
The capacitor then discharges through the resistor
The charge stored by the capacitor decreases with time and hence the p.d across it also decreases
The current in the resistor decreases with time as the p.d across it decreases accordingly
Eventually, the p.d V , the charge Q stored by the capacitor, and the current I in the resistor are all
zero
Q: What is the general relationship between p.d V, charge Q, current I, and time t
A:
, These graphs all show exponential decay over time after the switch is opened
As such, they all have the same shape
The equations for these quantities ae as given by:
Q: Constant ratio property of exponential decay
A: