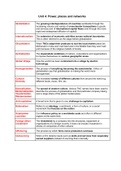
Intro
Contingency approach in organization theory:
Characteristics of management & organization depend on task environment and related contingency
factors
Contingency factors: technology, environmental turbulence, size of organization etc.
Organizational characteristics: formalization, centralization, task descriptions, use of control
mechanisms etc.
A contingency is a circumstance or condition that may or may not apply depending on a firm.
Be aware of the danger of “cultural attribution”
When looking for influence of differences in institutional/cultural environment, always control for
differences in: organization size, age; industry, technology etc.
2 strategies of dealing with contingency factors in empirical research: inclusion of control variables
and matching samples.
Study: how does culture influence risk-taking?
- Individualism, uncertainty avoidance and harmony
A whole range of contingency factors that they control(included in the analysis).
Strategy of “matched samples”
•Select narrow, but comparable subjects in the cultures to be compared
•Draw conclusions from this comparison regarding differences between the cultures in general
•Assumption: differences between the narrow samples are representative for the general
differences
Globalization (Rodrik, 2018)
A qualitative shift towards a global economic system that is no longer based on autonomous national
economies but on a consolidated global marketplace for production, distribution, and consumption
(Holm & Sørensen, 1995).
Globalization process is slowing down
Or is globalization even reversing (2007 crisis)
,Forces promoting(further) globalization:
•Decrease of transportation costs
•Decrease of communication costs
•Integration international financial markets (capital can flow easily from one country to another)
•Mass media, social media
•International migration (money flow from migrating people to the country of origin)
Forces impeding(further) globalization:
•Economic: Lower company profits outside home market; decreasing economic gains of trade
liberalization
•Social: Unbalanced distribution of benefits
•Cultural: Search for cultural authenticity
•Political Limits of democracy
Limits to globalization: economic (important engine for having higher profits)
•Lower company profits outside home market (on average)
•At the country level globalization has two effects:
– Wealth creation
– Wealth redistribution
•The redistributive effects get larger relative to the wealth creation effects as the level of trade
liberalization increases
•What if the “losers from free trade” need to be compensated?
The more free the trade, the less is the wealth created to compensate the losers from globalization
Limits to globalization: social
•Unbalanced distribution of benefits (distribution of income between capital and labour)
•Ordinary workers in the USA have not profited from globalization
,Limits to globalization: cultural
•Search for cultural authenticity (borrowing from other cultures is not always good)
•The issue of “cultural appropriation” (it is bad taking elements from other cultures and incorporate
them in your culture)
Limits to globalization: political
•The trilemma of globalization, sovereignty and democracy
Tension between democracy and globalization
Four possible scenarios:
1.Convergence
2.Specialization
3.Incremental adaptation
4.Hybridization
Scenario 1: Convergence
•The Anglo-American version of capitalism will be adopted worldwide (as in Europe after WW-II)
•But: contradicted by successes of, e.g., Japan, Korea, China
Scenario 2: Specialization
•Economies will specialize in where they have a comparative advantage, e.g., based on Porter’s
“diamond” factors
•But: a large proportion of trade is intra-industry trade
Scenario 3: Incremental adaptation
•Countries tend to evolve in the direction of the most efficient system and practices
•However, cultures and institutions constrain countries & firms in this process
Scenario 4: Hybridization
•Parts of the economy/society become part of the global system
•Other parts may remain largely unaffected, e.g.:
- Healthcare, Education, Personal services, Construction
•Globalization is a qualitative shift towards a more integrated social and economic world system
•Globalization seems to have come to a halt
•There are economic, social, cultural and political factors that play a role in this
•Further globalization in the future can follow different scenarios
, Culture
Culture is difficult to define, because it encompasses so many elements:
•Ideas and values
•Patterns of behaviour
•Artifacts
•Symbols etc
A synthetic definition:
Culture consists of patterns, explicit and implicit, of and for behaviour acquired and transmitted by
symbols, constituting the distinctive achievements of human groups, including their embodiments in
artifacts; the essential core of culture consists of traditional (i.e., historically derived and selected)
ideas and especially their attached values; culture systems may, on the one hand, be considered as
products of action, on the other as conditioning elements of further action (Kroeber & Kluckhohn,
1952: 181).
Another synthetic definition:
Culture is a property of a group. It is a group’s shared collective meaning system through which the
group’s collective values, attitudes, beliefs, customs, and thoughts are understood. It is an emergent
property of the member’s social interaction and a determinant of how group members
communicate .... Culture may be taken to be a consensus about the meanings of symbols, verbal and
nonverbal, held by members of a community (Lee, 2002: 277).
Internalized culture (values and beliefs, which reenforce each other)
Maslow’s “hierarchy of needs” is an example of the cultural relativity of values. (can be different in
different cultures)
•What are beliefs?
•Beliefs are propositions about objects or concepts or relations between objects/concepts
•Example: Causality (“working hard leads to success”)
•Example: Traditional beliefs in Chinese culture:
•All individuals have the potential to self-cultivate (Confucianism)
•The layout of the physical environment influences good and bad luck (Feng shui)
Contingency approach in organization theory:
Characteristics of management & organization depend on task environment and related contingency
factors
Contingency factors: technology, environmental turbulence, size of organization etc.
Organizational characteristics: formalization, centralization, task descriptions, use of control
mechanisms etc.
A contingency is a circumstance or condition that may or may not apply depending on a firm.
Be aware of the danger of “cultural attribution”
When looking for influence of differences in institutional/cultural environment, always control for
differences in: organization size, age; industry, technology etc.
2 strategies of dealing with contingency factors in empirical research: inclusion of control variables
and matching samples.
Study: how does culture influence risk-taking?
- Individualism, uncertainty avoidance and harmony
A whole range of contingency factors that they control(included in the analysis).
Strategy of “matched samples”
•Select narrow, but comparable subjects in the cultures to be compared
•Draw conclusions from this comparison regarding differences between the cultures in general
•Assumption: differences between the narrow samples are representative for the general
differences
Globalization (Rodrik, 2018)
A qualitative shift towards a global economic system that is no longer based on autonomous national
economies but on a consolidated global marketplace for production, distribution, and consumption
(Holm & Sørensen, 1995).
Globalization process is slowing down
Or is globalization even reversing (2007 crisis)
,Forces promoting(further) globalization:
•Decrease of transportation costs
•Decrease of communication costs
•Integration international financial markets (capital can flow easily from one country to another)
•Mass media, social media
•International migration (money flow from migrating people to the country of origin)
Forces impeding(further) globalization:
•Economic: Lower company profits outside home market; decreasing economic gains of trade
liberalization
•Social: Unbalanced distribution of benefits
•Cultural: Search for cultural authenticity
•Political Limits of democracy
Limits to globalization: economic (important engine for having higher profits)
•Lower company profits outside home market (on average)
•At the country level globalization has two effects:
– Wealth creation
– Wealth redistribution
•The redistributive effects get larger relative to the wealth creation effects as the level of trade
liberalization increases
•What if the “losers from free trade” need to be compensated?
The more free the trade, the less is the wealth created to compensate the losers from globalization
Limits to globalization: social
•Unbalanced distribution of benefits (distribution of income between capital and labour)
•Ordinary workers in the USA have not profited from globalization
,Limits to globalization: cultural
•Search for cultural authenticity (borrowing from other cultures is not always good)
•The issue of “cultural appropriation” (it is bad taking elements from other cultures and incorporate
them in your culture)
Limits to globalization: political
•The trilemma of globalization, sovereignty and democracy
Tension between democracy and globalization
Four possible scenarios:
1.Convergence
2.Specialization
3.Incremental adaptation
4.Hybridization
Scenario 1: Convergence
•The Anglo-American version of capitalism will be adopted worldwide (as in Europe after WW-II)
•But: contradicted by successes of, e.g., Japan, Korea, China
Scenario 2: Specialization
•Economies will specialize in where they have a comparative advantage, e.g., based on Porter’s
“diamond” factors
•But: a large proportion of trade is intra-industry trade
Scenario 3: Incremental adaptation
•Countries tend to evolve in the direction of the most efficient system and practices
•However, cultures and institutions constrain countries & firms in this process
Scenario 4: Hybridization
•Parts of the economy/society become part of the global system
•Other parts may remain largely unaffected, e.g.:
- Healthcare, Education, Personal services, Construction
•Globalization is a qualitative shift towards a more integrated social and economic world system
•Globalization seems to have come to a halt
•There are economic, social, cultural and political factors that play a role in this
•Further globalization in the future can follow different scenarios
, Culture
Culture is difficult to define, because it encompasses so many elements:
•Ideas and values
•Patterns of behaviour
•Artifacts
•Symbols etc
A synthetic definition:
Culture consists of patterns, explicit and implicit, of and for behaviour acquired and transmitted by
symbols, constituting the distinctive achievements of human groups, including their embodiments in
artifacts; the essential core of culture consists of traditional (i.e., historically derived and selected)
ideas and especially their attached values; culture systems may, on the one hand, be considered as
products of action, on the other as conditioning elements of further action (Kroeber & Kluckhohn,
1952: 181).
Another synthetic definition:
Culture is a property of a group. It is a group’s shared collective meaning system through which the
group’s collective values, attitudes, beliefs, customs, and thoughts are understood. It is an emergent
property of the member’s social interaction and a determinant of how group members
communicate .... Culture may be taken to be a consensus about the meanings of symbols, verbal and
nonverbal, held by members of a community (Lee, 2002: 277).
Internalized culture (values and beliefs, which reenforce each other)
Maslow’s “hierarchy of needs” is an example of the cultural relativity of values. (can be different in
different cultures)
•What are beliefs?
•Beliefs are propositions about objects or concepts or relations between objects/concepts
•Example: Causality (“working hard leads to success”)
•Example: Traditional beliefs in Chinese culture:
•All individuals have the potential to self-cultivate (Confucianism)
•The layout of the physical environment influences good and bad luck (Feng shui)