1. What Is a Hypothesis in Statistical Research?
A hypothesis is a statement about a population parameter (such as a mean). It is based on
theory, prior research, or observation, and we use statistical tests to determine whether the
evidence from a sample supports or contradicts it.
2. Types of Hypotheses
a) Null Hypothesis (H₀)
States that there is no effect, no difference, or no relationship in the population.
Example: H₀: μ = 50 → The population mean is 50. Or H₀: μ1- μ2 = 0 → The
difference in the mean between two population is 0 (the two populations means are
the same).
b) Alternative Hypothesis (H₁ or Ha)
States that there is an effect, difference, or relationship.
Example: H₁: μ ≠ 50 → The population mean is not 50. Or H₁: μ1- μ2 ≠ 0→ → The
difference in the mean between two population is 0 (the two populations are not the
same).
Type of alternative
Hypothesis Form Description
hypothesis
Two-tailed H₁: μ ≠ μ₀ Tests for any difference (higher or lower)
One-tailed (right) H₁: μ > μ₀ Tests if the true value is greater
One-tailed (left) H₁: μ < μ₀ Tests if the true value is lower
4. When Do We Reject the Null Hypothesis?
We reject H₀ when statistical evidence shows that the sample results are unlikely to have
occurred if the null hypothesis were true.
The decision is based on:
1. p-value
o If the p-value ≤ significance level (α) (commonly 0.05), we reject H₀.
o Interpretation: There is strong enough evidence against H₀.
p-value Decision
≤ 0.05 Reject H₀ → statistically significant result
> 0.05 Fail to reject H₀ → insufficient evidence
, 2. Test statistic vs critical value
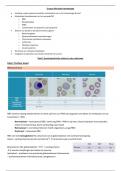
o If the test statistic falls into the rejection region, then reject H₀.
*Region in red: critical region where you reject the Null hypothesis
Term Meaning
α (alpha) Probability of making a Type I error (false positive).
β (beta) Probability of making a Type II error (false negative).
1−α Confidence level: probability of correctly not rejecting a true H₀.
1−β Power of the test: probability of correctly rejecting a false H₀.
H₀ True H₀ False
Reject H₀ Type I Error (α) Correct (Power = 1−β)
Fail to Reject H₀ Correct (1−α) Type II Error (β)
📊 Steps in Statistical Data Analysis
1. Define the Research Problem and Objectives
Clearly state the research question.
Specify what you want to measure, compare, or predict. (For example: Are you
analyzing one sample? Comparing two or more groups? Examining the
relationship/correlation between variables? Predicting one variable based on another?)
Formulate hypotheses (Null H₀ and Alternative H₁)
2. Select Variables and Plan Data Collection
Identify independent and dependent variables.
Choose measurement scales (nominal, ordinal, interval, ratio).
Decide how data will be collected: survey, experiment, observation, records, etc.
, 5. Conduct Descriptive Analysis
Purpose: To understand the basic structure and distribution of the data. Describe and
summarize your data using:
Method Examples
Central Tendency Mean, Median, Mode
Variation Standard Deviation, Range, Variance, IQR
Graphs Histogram, Bar chart, Box plot, Scatter plot
Shape of a distribution:
Skewness Type Description Typical Example
Symmetrical (normal)
Mean = Median = Mode Height, standardized test scores
(Skew = 0)
Right-skewed (positive) Tail on right, Mean > Median Income, hospital stay length
Left-skewed (negative) Tail on left, Mean < Median Retirement age, exam scores
Interpretation of Histogram:
Bell-shaped → Normal distribution
Right skewed (tail to the right) → Many small values, few large values (e.g.,
income)
Left skewed (tail to the left) → Many high values, few low values
Bimodal → Two peaks → data may come from two groups
Normality test
Test Use
Shapiro–Wilk Most common for small to medium samples
Kolmogorov–Smirnov For large samples
Interpretation:
If p > 0.05: Fail to reject normality → data is likely normal
If p ≤ 0.05: Reject normality → data is not normally distributed
6. Perform Inferential Analysis (Hypothesis Testing)
Choose and apply appropriate statistical tests and decide whether to reject or fail to reject H₀.
Report statistical results (test name, p-value, effect size). Explain findings in context of the
research question (not just numbers).
Choose the appropriate test:
DATA MAIN TEST ALTERNATIVE TESTS
One sample One sample t-test Wilcoxon if non-normal