Tears for diagnostic testing of brain disease
(Prof. Gijs)
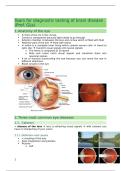
1. Anatomy of the eye
In front of the iris is the cornea
Cornea is transparent because light needs to go through
Anterior chamber is between the lens and cornea which is filled with fluid
Posterior part of the eye lined with retina
In retina is a complete inner lining which contain neuron cells travel to
optic disc transmit visual signals into neural signals
o The retina is composed of 10 layers
o Rods and cones catch visual signals and transform them into
neuronal signals
A lot of muscles surrounding the eye because you can move the eye in
different directions
Blood vessels in the eye
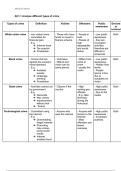
2. Three most common eye diseases
2.1. Cataract
= disease of the lens lens is refracting visual signals with cataract you
have no sharpening of your vision
2.1.1.Definition and causes
= clouding of the lens
Slow progression and painless
Pictures
o Left
1
, Healthy individual: lens is refracting the eye to the center
centering then you get a sharp vision
o Right = cataract
Not centralized in the retina = blurry vision
Causes
o Age
o Metabolic disease (eg diabetes)
o Ocular diseases (eg uveitis)
o Ocular surgery
o Trauma
o Congenital
o Medication (eg steroids)
Treatment = lens which is replacing your original lens?
2.1.2.Symptoms
Decreased vision
Halo’s = light sources very large glow around it
Monocular diplopia = double vision in one eye
2.2. Glaucoma
= disease of the papil
Progressive neuropathy
(A) Excavation optic disc, thinning of nerve fibers
o All nerves and axons come together and go to the brain
o Healthy: small entry side with a lot of nerves and blood vesels
o Glaucoma has a larger entry side
(B) Visual field loss
o They will still have a sharp image but in the periphery they will lose
vision
o Sharp central vision but not complete because loss of visual field
o They don’t see black spots because the brain is filling it in
A B
2
, Neuroretinal rim
Cup/disc ratio = diameter of cup expressed as fraction of diameter of disc
Picture
o Blue: optic cup
o Green: optic disc
o Inbetween is a rim
Rim is decreasing and cup is altered
o Upper donut is healthy example
Visual field loss
Very slowly progressive, brain fills in missing spots
o Damage is irreversible and difficult to treat tunnel vision in late
stages
2.2.1.Glaucoma main risk factor = increase intraocular pressure (IOP)
Misbalance between aqueous humor production and outflow
Not directly the cause
Normal IOP because the eye is a closed ball
o Pressure increases press against tissues of the eye especially
the retina
o Signals cannot travel to the brain
IOP is caused by misbalance between production and outflow
3
, o Production is normal but outflow is blocked
2.2.2.Treatment
Medication, topical eye drops
o Reduce aqueous humor production (eg beta blokkers)
o Increase aqueous humor outflow (eg prostaglandins)
Laser: shoot wholes to increase drainage
Surgery: fluid is given an alternative outflow
o Trabeculectomy (bleb)
o Implants (drainage)
o Shunts
2.3. Age-related macula degeneration (AMD)
= disease of the retina
= degeneration of the macula
Types of AMD
o Dry AMD (90%)
No exucative
No neovascularisation
o Wet AMD (10%)
Exucative
Neovascularization
Fast progression, fast loss of vision
Observations in the retina
o Drusen = extracellular waste products between RPE and Bruch
membrane
o Hyper- and hypopigmentation on the RPE
o Atrophy RPE (degeneration)
2.3.1.AMD symptoms (dry AMD)
Gradual vision loss over months/years
(A) Metamorphopsia = deformation of the squares
(B) (Para)central scotoma = black spot in the center of your vision
B
4
(Prof. Gijs)
1. Anatomy of the eye
In front of the iris is the cornea
Cornea is transparent because light needs to go through
Anterior chamber is between the lens and cornea which is filled with fluid
Posterior part of the eye lined with retina
In retina is a complete inner lining which contain neuron cells travel to
optic disc transmit visual signals into neural signals
o The retina is composed of 10 layers
o Rods and cones catch visual signals and transform them into
neuronal signals
A lot of muscles surrounding the eye because you can move the eye in
different directions
Blood vessels in the eye
2. Three most common eye diseases
2.1. Cataract
= disease of the lens lens is refracting visual signals with cataract you
have no sharpening of your vision
2.1.1.Definition and causes
= clouding of the lens
Slow progression and painless
Pictures
o Left
1
, Healthy individual: lens is refracting the eye to the center
centering then you get a sharp vision
o Right = cataract
Not centralized in the retina = blurry vision
Causes
o Age
o Metabolic disease (eg diabetes)
o Ocular diseases (eg uveitis)
o Ocular surgery
o Trauma
o Congenital
o Medication (eg steroids)
Treatment = lens which is replacing your original lens?
2.1.2.Symptoms
Decreased vision
Halo’s = light sources very large glow around it
Monocular diplopia = double vision in one eye
2.2. Glaucoma
= disease of the papil
Progressive neuropathy
(A) Excavation optic disc, thinning of nerve fibers
o All nerves and axons come together and go to the brain
o Healthy: small entry side with a lot of nerves and blood vesels
o Glaucoma has a larger entry side
(B) Visual field loss
o They will still have a sharp image but in the periphery they will lose
vision
o Sharp central vision but not complete because loss of visual field
o They don’t see black spots because the brain is filling it in
A B
2
, Neuroretinal rim
Cup/disc ratio = diameter of cup expressed as fraction of diameter of disc
Picture
o Blue: optic cup
o Green: optic disc
o Inbetween is a rim
Rim is decreasing and cup is altered
o Upper donut is healthy example
Visual field loss
Very slowly progressive, brain fills in missing spots
o Damage is irreversible and difficult to treat tunnel vision in late
stages
2.2.1.Glaucoma main risk factor = increase intraocular pressure (IOP)
Misbalance between aqueous humor production and outflow
Not directly the cause
Normal IOP because the eye is a closed ball
o Pressure increases press against tissues of the eye especially
the retina
o Signals cannot travel to the brain
IOP is caused by misbalance between production and outflow
3
, o Production is normal but outflow is blocked
2.2.2.Treatment
Medication, topical eye drops
o Reduce aqueous humor production (eg beta blokkers)
o Increase aqueous humor outflow (eg prostaglandins)
Laser: shoot wholes to increase drainage
Surgery: fluid is given an alternative outflow
o Trabeculectomy (bleb)
o Implants (drainage)
o Shunts
2.3. Age-related macula degeneration (AMD)
= disease of the retina
= degeneration of the macula
Types of AMD
o Dry AMD (90%)
No exucative
No neovascularisation
o Wet AMD (10%)
Exucative
Neovascularization
Fast progression, fast loss of vision
Observations in the retina
o Drusen = extracellular waste products between RPE and Bruch
membrane
o Hyper- and hypopigmentation on the RPE
o Atrophy RPE (degeneration)
2.3.1.AMD symptoms (dry AMD)
Gradual vision loss over months/years
(A) Metamorphopsia = deformation of the squares
(B) (Para)central scotoma = black spot in the center of your vision
B
4