Public International Law (Lecture Notes)
Lecture 1
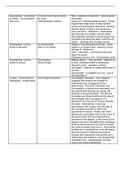
Public International Law consists of rules and principles that regulates the relations between States
and other entities, provided they have international legal personality.
Between States
Between States and other entities possessing international legal personality
Covering a range of activities
E.g. international agreements, diplomatic relations, trade, protection of human
rights, conduct of armed conflict
History
1. 1648 – Peace of Westphalia
Series of peace treaties marking the end of the religious Thirty Years War
The birth of the modern State – territorial units as equal sovereigns
2. 17th century – Hugo Grotius
‘father of international law’
Author of international law’s most important texts
The law of armed conflict and aggression
Binding force of treaties
Freedom of seas
Two theories on international law
Natural law
Law is not made, but found
Universal values existing by nature and can be found through human reasoning
Positive law
Law is not given, but man-made
Law is made by sovereigns (States) and can be found in treaties and customary law
Modern era
Peace of Westphalia marks the beginning of modern international law
Creation of modern sovereign States
Use of treaties to regulate interaction between States
Emergence of international organizations
E.g. Universal Postal Union (1874), International Committee of Red Cross (1863), Permanent Court of
Arbitration (1899)
Focus on Europe
o Colonization outside Europe
Outbreak of World War I
o After WW I
, Establishment of the League of Nations, based in Geneva
To secure international peace
Permanent Court of International Justice in The Hague
However: World War II
After WW II
The United Nations established with its main objective being protecting and restoring
international peace and security
The United Nations – six main organs (art. 7 UN Charter)
General Assembly
Security Council
Economic and Social Council
Trusteeship Council
International Court of Justice
Secretariat
The United Nations – Security Council (Chapter V UN
Charter)
15 members
o 5 permanent members with a veto (China,
France, UK, USA, Russia)
o 10 non-permanent members elected for a
two-year period
The only UN body with the power to adopt binding resolution
o ‘Chapter VII resolution’
o In cases where there is a threat to or breach of international peace and security, or an act of
aggression
The United Nations – International Court of Justice (Chapter XIV UN Charter)
Consent-based jurisdiction to settle disputes between States
o ONLY States
o Binding decision
Advisory jurisdiction to advice UN organs on a legal question
o ONLY UN organs
o Binding decision?
Some major issues…
Cold War
o The world divided into two blocks
o No armed violence, yet a failure of collective security
, o SC paralyzed, unable to adopt a resolution and to act effectively
Decolonization
o UN Special Committee on Decolonization
o Allowing a process of self-determination of peoples
o Largely completed, still few territories waiting to be decolonized
Lecture 2
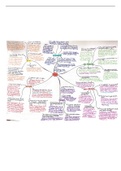
Theory of Sources
Where does international law come from?
− Code of international law?
− International parliament?
− International legislation?
International law is made on a decentralized basis by the actions of States which make up the
international community
Consensual (positivist) theory
Article 38 ICJ Statute
Hierarchy of Sources
Primary sources – law creating
Treaties, international custom and general principles of law
Based on the consent of States
Subsidiary sources – law identifying
Judicial decisions and teachings of highly qualified publicists
Courts cannot make law, they apply the law
Hierarchy between the primary sources?
Lecture 1
Public International Law consists of rules and principles that regulates the relations between States
and other entities, provided they have international legal personality.
Between States
Between States and other entities possessing international legal personality
Covering a range of activities
E.g. international agreements, diplomatic relations, trade, protection of human
rights, conduct of armed conflict
History
1. 1648 – Peace of Westphalia
Series of peace treaties marking the end of the religious Thirty Years War
The birth of the modern State – territorial units as equal sovereigns
2. 17th century – Hugo Grotius
‘father of international law’
Author of international law’s most important texts
The law of armed conflict and aggression
Binding force of treaties
Freedom of seas
Two theories on international law
Natural law
Law is not made, but found
Universal values existing by nature and can be found through human reasoning
Positive law
Law is not given, but man-made
Law is made by sovereigns (States) and can be found in treaties and customary law
Modern era
Peace of Westphalia marks the beginning of modern international law
Creation of modern sovereign States
Use of treaties to regulate interaction between States
Emergence of international organizations
E.g. Universal Postal Union (1874), International Committee of Red Cross (1863), Permanent Court of
Arbitration (1899)
Focus on Europe
o Colonization outside Europe
Outbreak of World War I
o After WW I
, Establishment of the League of Nations, based in Geneva
To secure international peace
Permanent Court of International Justice in The Hague
However: World War II
After WW II
The United Nations established with its main objective being protecting and restoring
international peace and security
The United Nations – six main organs (art. 7 UN Charter)
General Assembly
Security Council
Economic and Social Council
Trusteeship Council
International Court of Justice
Secretariat
The United Nations – Security Council (Chapter V UN
Charter)
15 members
o 5 permanent members with a veto (China,
France, UK, USA, Russia)
o 10 non-permanent members elected for a
two-year period
The only UN body with the power to adopt binding resolution
o ‘Chapter VII resolution’
o In cases where there is a threat to or breach of international peace and security, or an act of
aggression
The United Nations – International Court of Justice (Chapter XIV UN Charter)
Consent-based jurisdiction to settle disputes between States
o ONLY States
o Binding decision
Advisory jurisdiction to advice UN organs on a legal question
o ONLY UN organs
o Binding decision?
Some major issues…
Cold War
o The world divided into two blocks
o No armed violence, yet a failure of collective security
, o SC paralyzed, unable to adopt a resolution and to act effectively
Decolonization
o UN Special Committee on Decolonization
o Allowing a process of self-determination of peoples
o Largely completed, still few territories waiting to be decolonized
Lecture 2
Theory of Sources
Where does international law come from?
− Code of international law?
− International parliament?
− International legislation?
International law is made on a decentralized basis by the actions of States which make up the
international community
Consensual (positivist) theory
Article 38 ICJ Statute
Hierarchy of Sources
Primary sources – law creating
Treaties, international custom and general principles of law
Based on the consent of States
Subsidiary sources – law identifying
Judicial decisions and teachings of highly qualified publicists
Courts cannot make law, they apply the law
Hierarchy between the primary sources?